Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):91-93
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):91-98
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200006
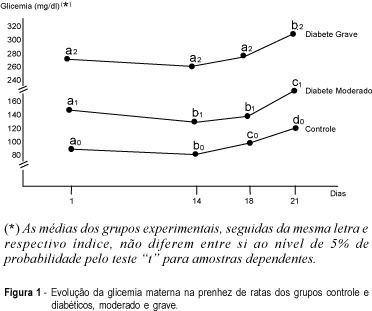
Purpose: placental alterations were evaluated in macrosomatia and fetal growth retardation in pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Three groups of rats, used as experimental models, were studied: control, moderate and severe diabetes. Material and Method: cesarian sections were carried out on the 18th or 21st day of pregnancy. Maternal and fetal glycemia, newborn weight, placental weight, relationship between placental and fetal weight, DNA, RNA and protein contents and the glycogen deposited on placental membranes were analyzed. Results: there was a higher number of macrosomic newborns in the moderate diabetes group, whose placentas were rich in DNA with progressive decrease of glycogen in their membranes towards the end of pregnancy. There was a predominance of small for date newborns in the severe diabetes group. Their placentas showed a small DNA proportion, an increase in RNA synthesis and a tendency to higher protein production, with no change in the glycogen deposit. Conclusions: we conclude that fetal growth deviation in moderate and severe maternal diabetes between the 18th and 21st days of pregnancy is related to several placental alterations. In the moderate form there were only cellular hyperplasia and disappearance of placental glycogen at the end of pregnancy. In the severe diabetes group there was thickening of maternal-fetal membranes during this period. There was cellular hyperplasia and hypertrophy associated with the maintenance of glycogen reserves in the placental membranes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(2):91-91
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):91-95
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200006
PURPOSE: compare the outcomes verified during urodynamic investigation realized in two different positions related to urinary leak point pressure under stress and to discuss its clinical relevance. METHODS: sixty-four patients with stress urinary incontinency (SUI) aged 25-80 years old, attended, during June 2003 to September 2005 were included in this study. Patients were initially submitted to urodynamic investigation in accordance with International Continence Society (ICS) techniques in orthostatic position and just after were evaluated in seating position. RESULTS: statistical significance was obtained after evaluation of Vasalva leak point pressure (VLPP) obtained in two positions (99,8 ± 33,3 versus 102,9 ± 32,4; respectivamente, posição sentada e em pé, p<0,05). Linear regression test based on frequency analyses was applied with the purpose to verify the patient percentage allocated in confidence interval in terms of Valsalva leak point pressure in seating or orthostatic positions. A rate of 90.6% of compatibility was gotten in these results. When three unities were added to VLPP values after urodynamic investigation in seating position, it was noted that 92.2% of patients was included in this interval. CONCLUSIONS: these findings suggest that the urodynamic investigation can be realized in seating position without diagnostic a therapeutic impairment allowing higher comfort to the patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):91-100
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200004
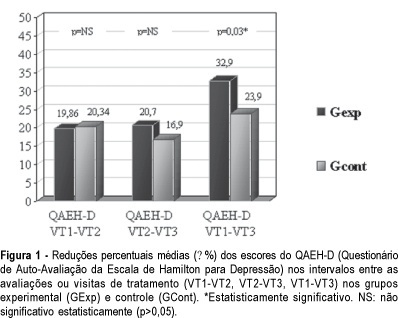
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficacy of the use of isoflavones in the treatment of depressive symptoms in climacteric women. METHODS: placebo-controlled, randomized double-blind experimental study with 84 climacteric women who were assisted at the Lauro Wanderley University Hospital Ambulatory, in João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. In the evaluation of the depressive symptoms the Self-evaluation questionnare of Hamilton's rating scale for depresion (QAEH-D) was used in the pretreatment visit (VT1), and in the 8th (VT2) and 16th (VT3) week after treatment. The experimental group (GExp) received soy extract with isoflavones, 120 mg per day, and the control group (GCont), placebo. The comparison of the scores of the QAEH-D between the VT1, VT2 and VT3 groups constituted the primary measure of efficacy (t test, p<0.05). Secondary analysis included the estimate of the "domino hypothesis" and the clinical and laboratory evaluation of side effects. RESULTS: there was a significant reduction of the QAEH-D scores in the GExp (VT2
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(2):91-95
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000200006
Predicting pregnancy outcome from one or more maternal serum factors has been the subject of numerous investigations with controversial results. The aim of this study was to evaluate the serum levels of CA-125, CA-19.9, CA-15.3, beta-hCG, estradiol, progesterone, alpha-fetoprotein and CEA in women with abortion (n=18) and with pregnancy complicated by bleeding (n=6), in comparison to the serum levels of the control group (n=7). The results showed that the serum levels of CA-125 were significantly increased in the abortion group (153.9 ± 43.3 IU/ml), but no difference was detected in pregnancy complicated by bleeding (17.4 ± 2.6 IU/ml), as compared to control (24.7 ± 13.4 IU/ml). However, high serum levels of CA-19.9 were found in the group with pregnancy complicated by bleeding in comparison with the abortion group (20.2 ± 11.4 IU/ml versus 6.6 ± 1.4 IU/ml, respectively). In relation to hormone serum levels, both, the abortion (17.38 ± 9.4 ng/ml) and bleeding (18.3 ± 8.9 ng/ml) groups showed lower serum levels of progesterone, as compared to control (60.4 ± 26.8 ng/ml). Besides, women with abortion had additional low estradiol serum levels, when compared to controls (1,327 ± 1,015 ng/ml versus 10,774 ± 9,244 ng/ml). It was concluded that the serum levels of progesterone, CA-19.9 and beta-hCG seem to add valuable information to the evaluation of a pregnancy complicated by bleeding.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):911-918
Currently, there are up to three different classifications for diagnosing septate uterus. The interobserver agreement among them has been poorly assessed.
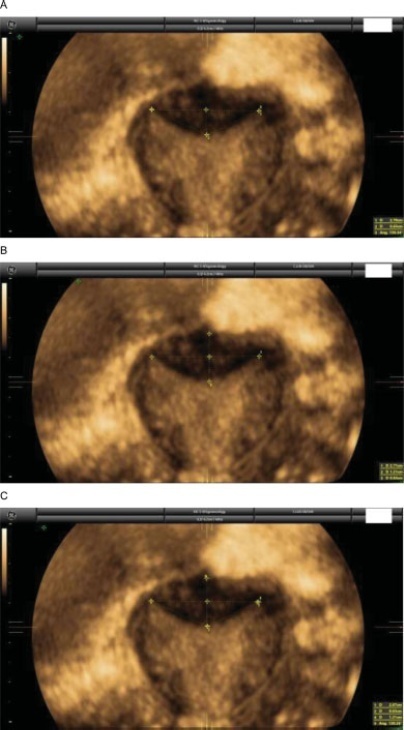
A total of 50 three-dimensional (3D) volumes of a nonconsecutive series of women with suspected uterine malformation were used. Two nonexpert examiners evaluated a single 3D volume of the uterus of each woman, blinded to each other. The following measurements were performed: indentation depth, indentation angle, uterine fundal wall thickness, external fundal indentation, and indentation-to-wall-thickness (I:WT) ratio. Each observer had to assign a diagnosis in each case, according to the three classification systems (ESHRE/ESGE, ASRM, and CUME). The interobserver agreement regarding the ESHRE/ESGE, ASRM, and CUME classifications was assessed using the Cohen weighted kappa index (k). Agreement regarding the three classifications (ASRM versus ESHRE/ESGE, ASRM versus CUME, ESHRE/ESGE versus CUME) was also assessed.
The interobserver agreement between the 2 nonexpert examiners was good for the ESHRE/ESGE (k = 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.55–0.92) and very good for the ASRM and CUME classification systems (k = 0.95; 95%CI: 0.86–1.00; and k = 0.91; 95%CI: 0.79–1.00, respectively). Agreement between the ESHRE/ESGE and ASRM classifications was moderate for both examiners. Agreement between the ESHRE/ESGE and CUME classifications was moderate for examiner 1 and good for examiner 2. Agreement between the ASRM and CUME classifications was good for both examiners.
The three classifications have good (ESHRE/ESGE) or very good (ASRM and CUME) interobserver agreement. Agreement between the ASRM and CUME classifications was higher than that for the ESHRE/ESGE and ASRM and ESHRE/ESGE and CUME classifications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):915-924
To assess obstetric/puerperal/neonatal outcomes in an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) population and to analyze disease characteristics that may be associated to adverse outcomes.
Retrospective descriptive analysis including 47 pregnant womn with IBD (28 with Crohn's disease – CD and 19 with ulcerative colitis – UC) who delivered between March 2012 and July 2018 in a tertiary hospital. We reviewed clinical records to extract demographic information, previous medical history, disease subtype, activity, severity, treatment, and obstetric, puerperal, and neonatal outcome measures.
Obstetric and neonatal complications (composite outcomes) occurred in 55.3% and 14.6% of the IBD population, respectively, and were more frequent in UC patients. Preterm birth (PTB), preeclampsia, anemia, low birth weight (LBW), and neonatal death were also more frequent in UC patients. The rate of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) was 14.9%, and it was higher in CD patients. Women with active IBD had more obstetric/neonatal adverse outcomes (fetal growth restriction and LBW in particular) and cesarean sections. Patients with medicated IBD had less obstetric/neonatal complications (PTB and LBW in specific) and cesarean sections but more PPH.
Women with IBD may have an increased risk of obstetric/puerperal/neonatal adverse outcomes. Ulcerative colitis patients had more obstetric and neonatal complications, whereas PPH was more frequent if CD patients. Other disease characteristics were considered, which allowed a better understanding of their possible influence. Although more research is needed, this work reinforces the importance of adequate surveillance to allow prompt recognition and treatment of complications.