You searched for:"Mary Ângela Parpinelli"
We found (27) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):639-646
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900004
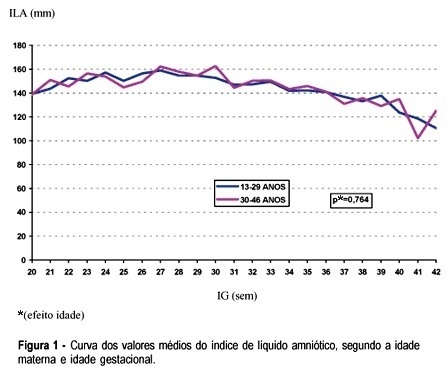
PURPOSE: to evaluate the association between the variability of amniotic fluid index (AFI) values with gestational age and some sociodemographic and obstetric variables among low-risk pregnant women. METHOD: a comparative study was carried out including 2868 low-risk pregnant women who had routine obstetric ultrasound examination, including fetal biometry and the measurement of AFI, from 20 to 42 weeks of gestation. The data were analyzed using Student's t test, analysis of variance of mean AFI values along gestational ages, according to other control variables, and also by multiple linear regression analysis. RESULTS: there was no significant variation of mean AFI values during the time of pregnancy neither when separately evaluating its association with maternal age, color, education, smoking habit, parity, and the presence of previous cesarean section scars, nor when the evaluation was performed through multivariate analysis. In this situation only the increase in gestational age showed to be associated with the decrease of AFI. Generally speaking, the mean AFI values fluctuated between 140 and 180 mm between the 20th and the 36th week, then showing values below 140 mm in a progressive decrease after this limit of gestational age. CONCLUSIONS: AFI values do not show a significant variation during pregnancy regarding the studied sociodemographic and obstetric variables.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(10):745-748
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003001000008
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a connective tissue disease that is rarely associated with pregnancy, but with potentially fatal complications during pregnancy and puerperium, such as vascular and intestinal ruptures. It can also be associated with joint laxity and pain in women; during pregnancy there is a greater risk of prematurity, because of premature rupture of membranes and/or cervical insufficiency. Uterine rupture and inversion can also be associated with this syndrome. In the present study, we describe the case of a pregnant woman with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, with a favorable evolution, without fetal complications and a good perinatal outcome.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(1):9-13
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100002
PURPOSE: to compare maternal and neonatal outcomes between spontaneous vaginal and Simpson-Braun forceps deliveries in nulliparous women. METHOD: a retrospective study including two groups of nulliparous women, who had vaginal delivery under peridural anesthesia in the obstetric unit of the CAISM-UNICAMP: the forceps group included 119 women who had Simpson-Braun forceps delivery, and the normal group included 114 women who delivered spontaneously. Neonatal outcomes, such as Apgar score and the evolution in the first days of life, were studied. Data were compared in both groups and, for statistical analysis, c² test, Fisher exact, and Student t tests were used. The differences were considered significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: the indications for Simpson-Braun forceps delivery were maternal-fetal relief (90 cases) and abbreviation of the expulsive period (29 cases). In the forceps group there were 8 cases (6.7%) of vaginal injuries; a similar result was observed in the normal group. The number of hospitalization days for the parturient and the newborns was identical, 2.4 days. The newborns in the two groups had similar Apgar scores inferior to 7 at the first minute (7.5 vs 4.3%) and at the fifth minute (1.6 vs1.7%). The weight in the two groups had similar results (3,146 and 3,016 g). The first days of life did not differ between the groups. CONCLUSIONS: the use of Simpson-Braun forceps was safe, when compared to spontaneous vaginal delivery.