You searched for:"Edward Araujo Júnior"
We found (59) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):216-219
To evaluate the seroprevalence of positive markers for syphilis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) I and II, human T cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) I and II, and hepatitis B and C among women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF).
We conducted a retrospective analysis among patients who underwent IVF, between January 2013 and February 2016, and who had complete screening records.
We analyzed 1,008 patients who underwent IVF, amounting to 2,445 cycles. Two patients (0.2%) tested positive for HIV I and II and none for HTLV I and II. Three patients (0.3%) had positive screening for syphilis, and two (0.2%) had positive hepatitis C antibody test (anti-HCV). A positive hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HbsAg) test was observed in 4 patients (0.4%), while 47 (4.7%) patients were positive for IgG antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbC IgG), and only 1 (0.1%) was positive for IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbC IgM). The anti-HbS test was negative in 659 patients (65.3%). Only 34.7% of the patients had immunity against the Hepatitis B virus. Patients with an anti-HbS negative result were older than those with a hepatitis B test (anti-HbS) positive result (36.3 versus 34.9; p<0.001).
The present study showed lower infection rates than the Brazilian ones for the diseases studied in patients undergoing IVF. Only a few patients were immunized against hepatitis B.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(4):217-221
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000400004
Purpose: to evaluate the influence of pregnancy, habit of smoking, and the contraceptive method in HPV infection and the frequency of cytologic findings in adolescent women with HPV infection. Methods: a total of 54,985 cytologic examinations of patients seen between July, 1993 and December, 1998 were retrospectively analyzed. Of this total, 6,498 (11.8%) examinations were from patients under 20 years old. Of the total of 6,498 cytologic examinations, 326 (5.9%) presented signs of HPV infection, with or without grade I cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Patients with diagnosis of grade II and III CIN were excluded. The control group consisted of 333 patients paired by age, without cytological signs of HPV infection. Results: in adolescents, HPV infection was more frequent in oral contraceptive users (16.9% versus 13.8%, p<0.01) and in those who presented with clue cells in cytologic smears (22.4% versus 14.7%, p<0.001). The frequency of HPV infection in couples who used condom was 0% versus 2.1% in the control group (p<0.01). The difference in the number of pregnant women (41.1% versus 44.1%) and smokers (21.8% versus 16.5%) was not statistically significant. Conclusions: HPV infection is more frequent in adolescent women in use of oral contraceptive and with clue cells as cytologic finding. HPV infection did not occur in couples who used condom. Gestation and the habit of smoking did not influence the incidence of HPV infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):222-227
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050007
To identify risk factors for weight retention in women after childbirth.
This was a prospective observational study that followed for six months adult women who delivered at a tertiary center. Were applied a structured questionnaire before hospital discharge and at six weeks and six months after childbirth, through home visits. The outcome was weight retention after childbirth (if risk >7.5 kg). The variables analyzed were: age, skin color, working during pregnancy, income, education, marital status, age at menarche, maternal age at first birth, parity, mode of delivery, birth interval, pre-pregnancy weight, gestational weight gain, percent body fat, and nutritional status. Data were first analyzed by bivariate analysis between prevalence of weight retention at six months and several covariates (p<0.2). We then calculated the Odds Ratio (OR) and their respective gross confidence intervals of 95% (95%CI) and finally performed multivariate logistic regression to control for confounding factors and to estimate the OR and 95%CI.
The frequency of weight retention >7.5 kg by 6 months after delivery was 15%. In bivariate analysis, weight retention was associated with the following variables: age at menarche <12 years (OR=3.7; 95%CI1.1-13.2), gestational weight gain ≥16 kg (OR=5.8; 95%CI 1.8-18.6), percent body fat at baseline >30% (OR=5.0; 95%CI 1.1-23.6), and nutritional status by 6 weeks postpartum >25 kg/m2 (OR=7.7; 95%CI1.6-36.1). In multivariate analysis, only excessive gestational weight gain (OR=74.1; 95%CI 9.0-609.6) remained as a risk factor.
Excessive weight gain during pregnancy should receive special attention in prenatal care in view of its association with weight retention and excess weight in women after childbirth.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):228-232
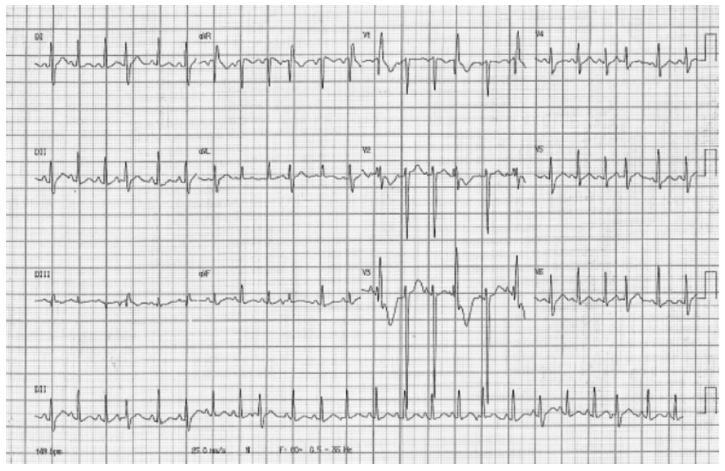
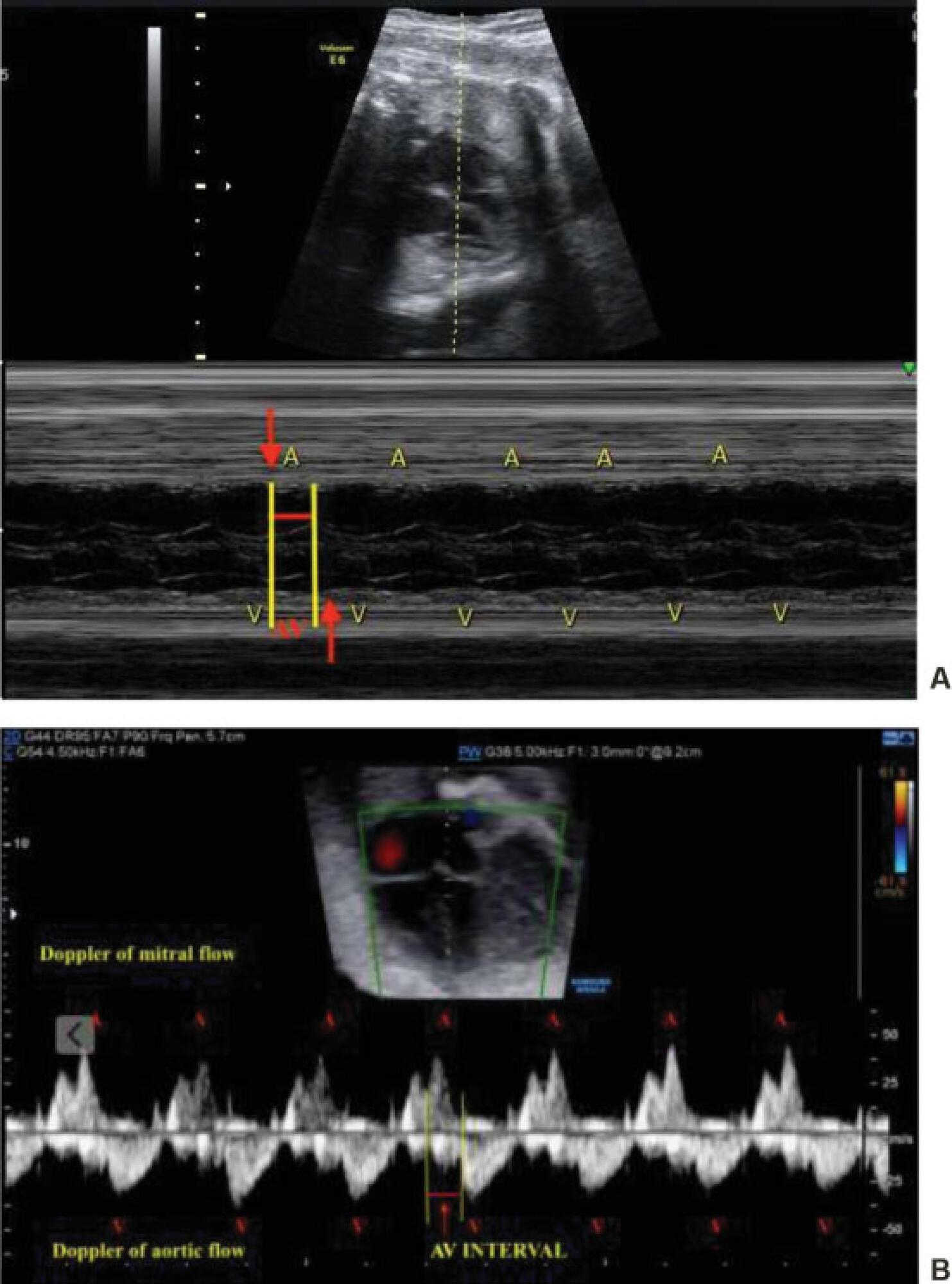
The present report describes a case of complete atrioventricular block (CAVB) diagnosed at 25 weeks of gestation in a pregnant woman with Sjögren's syndrome and positive anti-Ro/SSA antibodies. Fluorinated steroids (dexamethasone and betamethasone) and terbuline were used to increase the fetal heart rate, but the fetal heart block was not reversible, and the administration of drugs was discontinued due to maternal collateral effects. Follow-up fetal echocardiograms were performed, and the fetus evolved with pericardial effusion, presence of fibroelastosis in the right ventricle, and ventricular dysfunction. Interruption of pregnancy by cesarean section was indicated at 34 weeks of gestation, and a cardiac pacemaker was implanted in the male newborn immediately after birth. Therapy for fetuses with CAVB is controversial mainly regarding the use or not of corticosteroids; however, monitoring of the atrioventricular interval by fetal echocardiography should be performed in fetuses from pregnant women with positive autoantibodies anti-Ro/SSA and/or anti-La/SSB to prevent the progression to CAVB.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):249-251
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005308
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):29-34
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100007
To evaluate the maternal risk factors that require newborn assistance in neonatal Intensive Care Units (ICU).
A prospective observational case-control study was conducted on 222 pregnant women (1:1 case-control ratio) attended at a public maternity. The following variables were analyzed in the puerperae: age at menarche, age at first sexual intercourse, history of chronic diseases, habits, prenatal care, obstetric history, clinical complications during pregnancy and childbirth, and sociodemographic variables. The variables of the newborns were: Apgar scores, gestational age, birth weight, presence or absence of malformation, need for resuscitation, and complications during the first 24 hours. Proportions were compared using the Fisher exact test or the Person γ2 test. Multivariable models were developed by logistic regression analysis using adjusted Odds Ratio with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
Regarding reproductive history, ≥3 pregnancies and 2 or 3 previous cesareans were sytatistically significant (p=0.0 and 0.0, respectively). Among the complications that required assistance in the neonatal ICU, prematurity was responsible for 61 cases (55.5%), followed by risk of intrapartum infection in 46 cases (41.8%). Regarding the maternal history, the presence of hypertensive disease showed statistical significance (p=0.0). Premature rupture of membranes was strongly associated with the need for the neonatal ICU (Odds Ratio - OR=6.1, 95%CI 2.6-14.4).
Premature rupture of membranes and hypertensive disease should receive special attention in prenatal care due to their strong association with newborns requiring assistance in the neonatal ICU.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):294-299
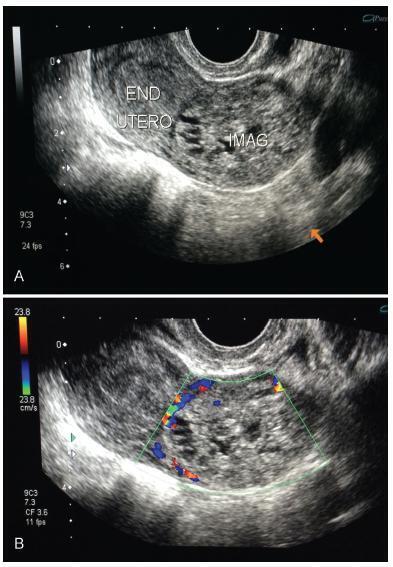
This report presents the case of a patient with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia after a partial hydatidiform mole formed in the Fallopian tube. Ectopic molar pregnancy is a rare condition, with an estimated incidence of 1 in every 20,000 to 100,000 pregnancies; less than 300 cases of it have been reported in the Western literature. The present report is important because it presents current diagnostic criteria for this rare condition, which has been incorrectly diagnosed in the past, not only morphologically but also immunohistochemically. It also draws the attention of obstetricians to the occurrence of ectopic molar pregnancy, which tends to progress to Fallopian tube rupture more often than in cases of ectopic non-molar pregnancy. Progression to gestational trophoblastic neoplasia ensures that patients with ectopic molar pregnancy must undergo postmolar monitoring, which must be just as thorough as that of patients with intrauterine hydatidiform moles, even if chemotherapy results in high cure rates.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):308-313
Pathophysiological mechanisms of peripartum cardiomyopathy are not yet completely defined, although there is a strong association with various factors that are already known, including pre-eclampsia. Peripartum cardiomyopathy treatment follows the same recommendations as heart failure with systolic dysfunction. Clinical and experimental studies suggest that products of prolactin degradation can induce this cardiomyopathy. The pharmacological suppression of prolactin production by D2 dopamine receptor agonists bromocriptine and cabergoline has demonstrated satisfactory results in the therapeutic response to the treatment. Here we present a case of an adolescent patient in her first gestation with peripartum cardiomyopathy that evolved to the normalized left ventricular function after cabergoline administration, which was used as an adjuvant in cardiac dysfunction treatment. Subsequently, despite a short interval between pregnancies, the patient exhibited satisfactory progress throughout the entire gestation or puerperium in a new pregnancy without any cardiac alterations. Dopamine agonists that are orally used and are affordable in most tertiary centers, particularly in developing countries, should be considered when treating peripartum cardiomyopathy cases.