Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):671-671
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):671-679
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100007
PURPOSE: to investigate the influence of the maternal mobility during the active phase of labor. METHODS: a prospective clinical trial was conducted through comparative analysis among a treatment group (n=50) and a control group (n=50), in the Obstetric Center of the Hospital Universitário da Universidade de São Paulo (USP). The inclusion criteria were: primigravidae with a single fetus on cephalic presentation, with 37 to 42 weeks of pregnancy, with two uterine contractions every ten minutes and with cervical dilatation until 4 cm, besides the agreement to sign the free and informed consent term. The evolution of labor for cesarean section was the exclusion criteria. The patients were assisted during the active phase of labor by the physiotherapist and encouraged for staying in vertical position and movement, according to each dilatation stage and fetus head progression. The control group had obstetric support without the presence of the physiotherapist; it was selected retrospectively, according to the same inclusion and exclusion criteria. RESULTS: 58 primigravidae between 15 and 37 years old were accompanied; 50 of them (86.2%) evolved to vaginal birth and eight (13.7%) evolved to cesarean section and were excluded. Among the patients who were accompanied, the mean of active phase was five hours and 16 minutes, while in the control group it was eight hours and 28 minutes (p<0.001). This difference was maintained in relation to the amniotic sac either whole or ragged. As for the cervix uterine evanescence, the treatment group showed a smaller period of active phase in association to a thin uterine cervix (p<0.001). In the treatment group, none of the patients used analgesics during the active phase, against 62% of the control group (p<0.001). In this group, all the patients used some kind of anesthesia for delivery; in the treatment group, among those who used anesthesia, 76% did it while the dilatation was 9 or 10 cm and 12% did not use any kind of anesthesia (p<0.05). The average weight of the newborns and the apgar did not show significant difference rates between the two groups. CONCLUSIONS: the good performance of maternal mobility has positive influences on the labor process: it increases the tolerance to pain, avoids the use of drugs during labor, improves the evolution of dilatation and reduces the duration of the active phase.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):672-675
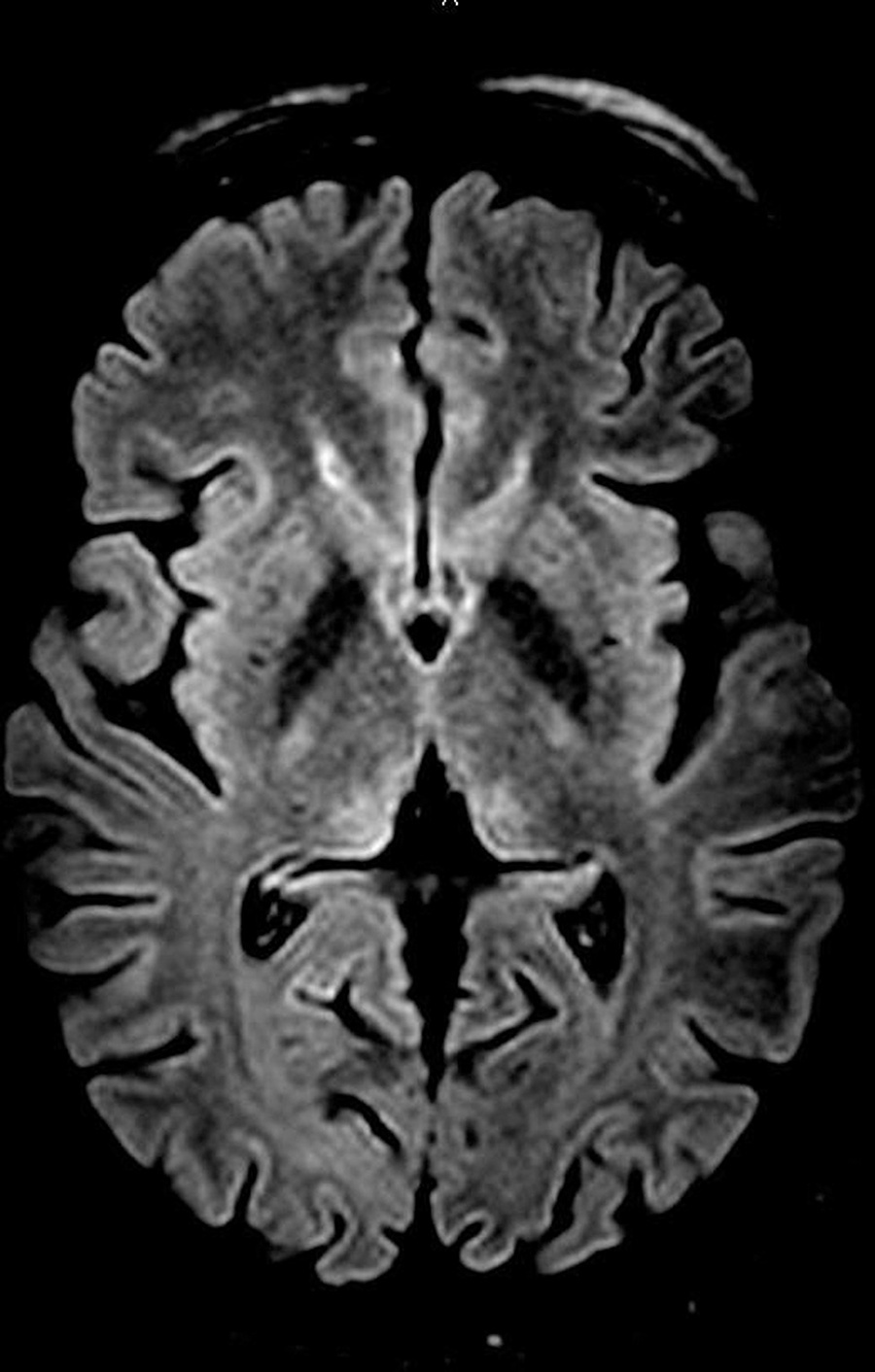
Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) is an acute neurological disorder resulting from vitamin B1 deficiency, which is common in chronic alcoholism. We report a rare case of WE due to hyperemesis gravidarum in a 25-year-old pregnant patient at 13 weeks and 5 days of gestation. Initially, the disease manifested as weakness, mental confusion, anterograde amnesia, and visual and auditory hallucinations. The diagnosis was established after the detection of suggestive findings of WE in the thalamus by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and a rapid improvement in the patient's clinical status subsequent to treatment with thiamine. Hyperemesis is a rare cause of WE, which makes the reported case important in the literature and reinforces the need for attention in clinical practice to rare but important complications of this common condition (hyperemesis gravidarum).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):672-676
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of vaginal environment of pregnant women on group B streptococcus (GBS) survival after 8, 24 e 48 h in Amies and Stuart transport media. METHODS: Three vaginal samples were collected from 30 pregnant women attending the Prenatal Care Outpatient Clinic of the Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher (CAISM), Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP). The first sample was placed directly onto Todd-Hewitt selective medium; the second was used to perform a gram-stained microscopy, and the third swab was placed in 2 mL physiological saline to which 200 µL of a suspension with 1-2 x 10(8) colony-forming units of GBS was added. After homogenization, six swabs were collected from this suspension (3 from Amie medium and 3 from Stuart medium). These six swabs were kept at room temperature for 8, 24 and 48 h and then incubated on blood agar. Bacterial growth at 37ºC was observed after a 24-h incubation period and it was semiquantitatively graded (0-3+) according to the number of colonies. Statistical analysis was performed by the exact Fisher test and the level of significance was set at 0.05. RESULTS: the recovery of GBS after 48-h storage in Amie and Stuart media was 97 e 87%, respectively. In one of the four cases where no GBS recovery was possible after 48 h of storage, vaginal pH was higher than 4.5, and in two of those cases cytolytic vaginosis was found. CONCLUSIONS: both transport media showed to be appropriate for GBS recovery up to 48 h after sampling. Characteristics of the vaginal enviroment did not influence GBS recovery as observed in this study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):672-672
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):672-673
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):673-673
Summary
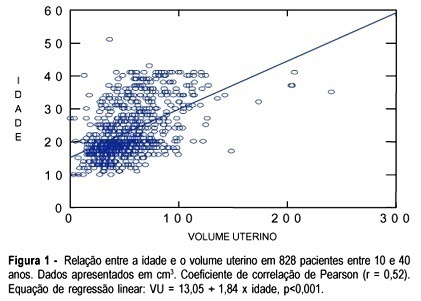
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(9):673-678
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900009
PURPOSE: to evaluate the uterine volume in women between 10 and 40 years in order to observe if the uterine volume in adolescents is smaller than the uterine volume in women between 20 and 40 years. We intend to emphasize the differences between the uterine volume of adolescents and that of adult women and to correlate with the immaturity of the genital tract of adolescents regarding gestation and delivery. METHOD: a cross-sectional study, which included 828 patients between 10 and 40 years old divided into two groups and examined using abdominal ultrasound to obtain the uterine volume measure. The first group consisted of 477 (57.7%) adolescents, and the second group of 351 (42.3%) adult women between 20 and 40 years old. In the adolescent group, ultrasound examination was performed by a single observer and in the group of adult women ultrasound examination was performed by a group of observers who used the same methodology as that of group 1. Image Point HX (Hewlett Packard) and Hitachi 525 ultrasound equipment were used with a multiple frequency probe. For the calculation of the uterine volume we used the longitudinal diameter (LD), anteroposterior diameter (APD) and transverse diameter (TD) with the (LD x APD x TD) x 0.45 formula. RESULTS: adolescents aged 10 to 17 years had a smaller uterine volume than women aged 20 to 40 years (p<0.05). Adolescents who delivered twice had a uterine volume similar to that of the patients between 20 and 40 years old with respective mean values of 62.6 ± 20.6 and 69.0±22.9 (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: adolescents less than 18 years old or primiparous have a smaller uterine volume than women between 20 to 40 years old. However, adolescents aged 18 years or older, or secundipara, have a uterine volume similar to that of women aged 20 to 40 years.