Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):113-120
To evaluate the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the care of patients with miscarriage and legal termination of pregnancy in a university hospital in Brazil.
A cross-sectional study of women admitted for abortion due to any cause at Hospital da Mulher Prof. Dr. J. A. Pinotti of Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP), Brazil, between July 2017 and September 2021. Dependent variables were abortion-related complications and legal interruption of pregnancy. Independent variables were prepandemic period (until February 2020) and pandemic period (from March 2020). The Cochran-Armitage test, Chi-squared test, Mann-Whitney test, and multiple logistic regression were used for statistical analysis.
Five-hundred sixty-one women were included, 376 during the prepandemic period and 185 in the pandemic period. Most patients during pandemic were single, without comorbidities, had unplanned pregnancy, and chose to initiate contraceptive method after hospital discharge. There was no significant tendency toward changes in the number of legal interruptions or complications. Complications were associated to failure of the contraceptive method (odds ratio [OR] 2.44; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.23–4.84), gestational age (OR 1.126; 95% CI 1.039–1.219), and preparation of the uterine cervix with misoprostol (OR 1.99; 95% CI 1.01–3.96).
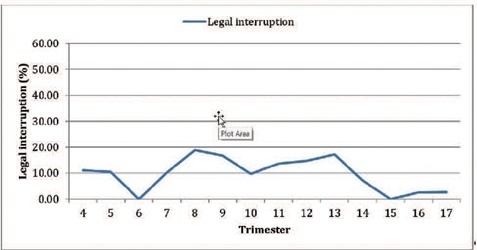
There were no significant differences in duration of symptoms, transportation to the hospital, or tendency of reducing the number of legal abortions and increasing complications. The patients’ profile probably reflects the impact of the pandemic on family planning.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):113-113
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):113-118
To identify risk factors related to postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) and severe PPH with blood loss quantified objectively.
This is a complementary analysis of a prospective cohort study that included pregnant women delivering vaginally. The total blood loss was obtained through the sum of the volume collected from the drape with the weight of gauzes, compresses and pads used by women within 2 hours. Exploratory data analysis was performed to assess mean, standard deviation (SD), frequency, percentage and percentiles. The risk factors for postpartum bleeding were evaluated using linear and logistic regression.
We included 270 women. Themean blood loss at 120 minutes was 427.49 mL (±335.57 mL). Thirty-one percent (84 women) bled > 500mL and 8.2% (22 women) bled > 1,000 mL within 2 hours. Episiotomy, longer second stage of labor and forceps delivery were related to blood loss > 500mL within 2 hours, in the univariate analysis. In the multivariate analysis, only forceps remained associated with bleeding > 500 mL within 2 hours (odds ratio [OR] = 9.5 [2.85-31.53]). Previous anemia and episiotomy were also related to blood loss > 1,000mL.
Prolonged second stage of labor, forceps and episiotomy are related to increased incidence of PPH, and should be used as an alert for the delivery assistants for early recognition and prompt treatment for PPH.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):113-116
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200009
Takayasu's arteritis is an idiopathic occlusive inflammation of the aorta and its major branches. The disease shows a striking predilection for young women and thus is occasionally associated with pregnancy. The authors describe a case of a pregnant patient with Takayasu's arteritis. The pregnancy was accompanied by a multidisciplinary group in a satisfactory way. There was only one hospitalization due to an exacerbation of the symptoms during the 32nd week of gestation, controlled by medical treatment. A vaginal delivery occurred at 37 weeks. A live infant weighing 2,750 g was delivered and the patient had an uncomplicated course.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(2):113-120
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000200007
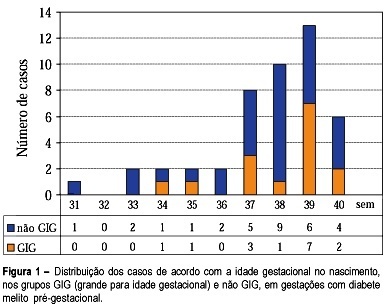
Purpose: to study fetal surveillance examinations in pregnancies complicated by pregestational diabetes mellitus, and to correlate them with large for gestational age (LGA) newborns. Methods: Between March 1999 and June 2001, 46 singleton pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus without fetal anomalies were followed prospectively. From the 28th gestational week on, the following examinations were performed weekly: fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index (AFI), and dopplervelocimetry of umbilical and middle cerebral arteries. The newborns with birthweight above the 90th percentile according to local standard values were characterized as LGA infants. Fisher's exact test and Student's t test were used for statistical analysis. Results: The mean gestational age at delivery was 37.6 weeks and 15 (32.6%) newborns were LGA. LGA fetuses showed significant increase in the AFI mean performed in the 32nd (16.5 cm, p=0.02), 33rd (16.7 cm, p=0.03), 34th (17.0 cm, p=0.02), 35th (17.9 cm, p=0.000), 36th (15.8 cm, p=0.03) and 37th (17.5 cm, p=0.003) weeks. Non-LGA fetuses presented the following mean AFI values: 13.5cm (32nd week), 13.1cm (33th week), 13.4 (34th week), 12.8 (35th week), 12.5 (36th week) and 12.8cm (37th week). AFI values equal to or above 18.0 cm were associated with the occurrence of LGA infants, when detected at the following gestational ages: 34th (60%, p=0.03), 35th (71.4%, p=0.01), 36th (80%, p=0.02) and 37th (66.7%, p=0.04) week. Non-LGA infants presented the following proportion of AFI values equal to or above 18.0 cm: 40.0% (34th week), 28.6% (35th week), 20.0% (36th week), and 33.3% (37th week). Conclusions: abnormal increase in AFI, mainly with values equal to or above 18.0 cm, is related to LGA infants at delivery. The maternal treatment should be adjusted to achieve the best result for maternal-fetal control, according to the AFI values during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(2):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200009
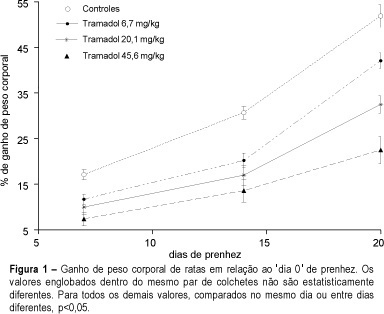
Purpose: to examine the effects of tramadol hydrochloride on rat pregnancy. Methods: five groups of 10 pregnant albino rats each were treated from the 1st up to the 20th day of pregnancy as follows: GI = intact controls; GII = controls which received 0.5 ml of distilled water (drug vehicle) once a day by gavage; GIII, GIV and GV = groups treated respectively with 6.7, 20.1 or 45.6 mg/kg of tramadol hydrochloride once a day by gavage in a final volume of 0.5 mL. Body weight gain was monitored by weighing at the beginning and on the 7th, 14th and 20th day of pregnancy. At term the animals were killed under deep ether anesthesia and the following parameters were evaluated: number of implantations, of resorptions, of viable fetuses and of placentae; presence of major malformations; maternal and fetal mortality and weights of fetuses and placentae. Results: tramadol significantly affected maternal body weight gain, this effect being more apparent in groups IV and V (mean reductions of weight gain of 41 and 56%, respectively). In group III the weight gain was affected more at days 7 and 14 (33% mean gain reductions) than at day 20 (19%). Drug treatment affected significantly and in a dose-dependent fashion the following parameters: individual weight of fetuses (GV = -39.2%), offspring weight (GIV = -51.7%; GV = -44.2%), number of placentae (GIV = -28.4%; GV = -11.6%), individual weight of placentae (GV = -10%) and the total weight of placentae (GIV = -28.4%; GV = -16.8%). Though among the treated animals there was an increase in resorptions and deaths at birth, these events were not significantly different from those found in controls. Conclusions: Tramadol showed definite deleterious effects on albino rat pregnancy, and these effects were exerted not only on the maternal but also the on fetal organisms. Overall, the effects were more pronounced at the 14th than at the 20th day of pregnancy, thus suggesting that the organogenic phase of the fetus is more susceptible than its initial (embryogenic) or final (term) phases. The results call attention to the care which is to be taken when the use of this opioid is considered during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300004
To investigate the prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities in couples with two or more recurrent first trimester miscarriages of unknown cause.
The study was conducted on 151 women and 94 partners who had an obstetrical history of two or more consecutive first trimester abortions (1-12 weeks of gestation). The controls were 100 healthy women without a history of pregnancy loss. Chromosomal analysis was performed on peripheral blood lymphocytes cultured for 72 hours, using Trypsin-Giemsa (GTG) banding. In all cases, at least 30 metaphases were analyzed and 2 karyotypes were prepared, using light microscopy. The statistical analysis was performed using the Student t-test for normally distributed data and the Mann-Whitney test for non-parametric data. The Kruskal-Wallis test or Analysis of Variance was used to compare the mean values between three or more groups. The software used was Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), version 17.0.
The frequency of chromosomal abnormalities in women with recurrent miscarriages was 7.3%, including 4.7% with X-chromosome mosaicism, 2% with reciprocal translocations and 0.6% with Robertsonian translocations. A total of 2.1% of the partners of women with recurrent miscarriages had chromosomal abnormalities, including 1% with X-chromosome mosaicism and 1% with inversions. Among the controls, 1% had mosaicism.
An association between chromosomal abnormalities and recurrent miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy (OR=7.7; 95%CI 1.2--170.5) was observed in the present study. Etiologic identification of genetic factors represents important clinical information for genetic counseling and orientation of the couple about the risk for future pregnancies and decreases the number of investigations needed to elucidate the possible causes of miscarriages.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):113-120
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000001
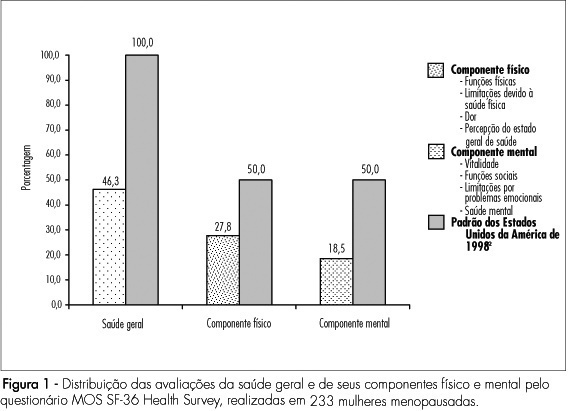
PURPOSE: to evaluate quality of life of climacteric women attended at a school hospital in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, adopting the Medical Outcome Study 36-item Short Form Health Survey (MOS SF-36 Health Survey) and the Women's Health Questionnaire (WHQ), as well as the modified Blatt-Kupperman index. METHODS: according to a descriptive, transversal study, 233 women, assisted from February to June 2006, were evaluated. Within a convenience sample, the inclusion criteria were age from 40 to 65 years old and agreement in participating of the research, excluding previous history of bilateral oophorectomy, hormonal therapy in the last semester and uncontrolled illnesses. The sample size was calculated admitting a prevalence of climacteric symptoms of 4% and a precision of 2.5%. The variables were: general health and physical and mental components based on the MOS SF-36 Health Survey; quality of health based on the WHQ and climacteric symptoms according to the modified Blatt-Kupperman index. Data were analyzed by the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 13.0 software. RESULTS: the quality of life was classified as bad. Based on the MOS SF-36 Health Survey, there was more damage in the mental component (18.53 versus 27.77% for physical components), higher losses in social functions (80.28%) and limitations for emotional problems (78.61%). According to WHQ, there were limitations due to sleep disturbances (69.77%), somatic (69.15%) and vasomotor symptoms (68.80%), considering regular sexual function and menstrual symptoms. Estrogenic deficiency symptoms were found in 53% of the women. The increase of hypoestrogenism symptoms were followed by worsening of general and menopausal health. CONCLUSIONS: it seemed reasonable to assume that menopause, for the researched women, was really configured as a biopsychosocial event, more than organic, derived predominantly from estrogenic deficiency.