Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):536-540
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of body mass index (BMI) on in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) outcomes performed at the Human Reproduction Center of Faculdade de Medicina do ABC. METHODS: retrospective data from 488 IVF cycles of 385 patients. Patients were classified into two groups according to BMI: normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m²) and overweight/obesity (>25 kg/m²). We evaluated the dose of recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (FSHr), the cancellation rates for ovarian cycle response, and the results of the assisted reproduction laboratory such as number of oocytes, number of good quality embryos, number of embryos transferred, and pregnancy rates, chemical pregnancy rates, miscarriage rate and live birth rate. The t test was used for comparison of quantitative variables between groups, and the χ2 test for comparison between qualitative variables. P values <0.05 were considered significant. RESULTS: considering ovulation induction characteristics, there was no statistically significant difference between groups regarding the FSHr dose administered or the cancellation rates, p=0.47 and p=0.85, respectively. Regarding laboratory findings, the number of oocytes retrieved per cycle was similar for both groups (p=0.09), as also was the number of good quality embryos obtained and transferred (p=0.7 and p=0.6). The pregnancy rate per embryo transfer was 27.6% for the group of normal weight and 29.6% for the overweight/obese group (p=0.76). Miscarriage rates and birth rates were similar for both groups, p=0.54 and p=0.94. CONCLUSION: BMI did not influence IVF/ICSI outcomes evaluated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):536-544
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000900006
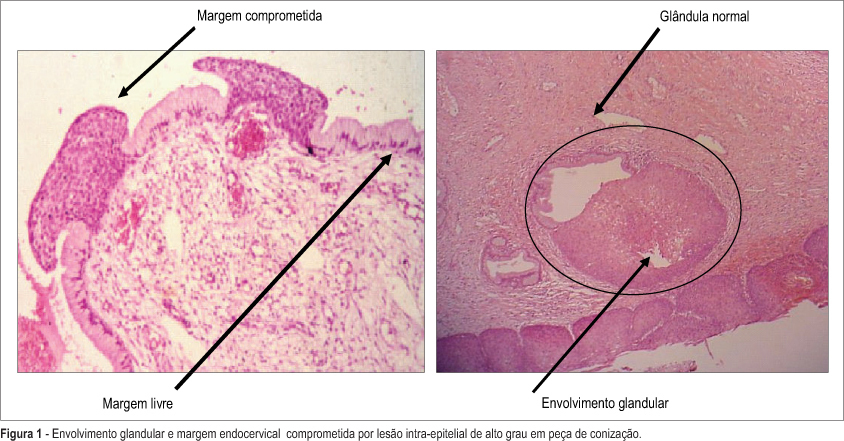
PURPOSE: to evaluate risk factors associated with cervical intraepithelial lesion recurrence after LEEP conization. METHODS: nested case-control study in a cohort of 201 patients with cervical intraepithelial lesion, that were submitted to LEEP conization. Average follow-up of these patients was 2 years. Ninety-four HIV-infected women and 107 non-infected were enrolled. Cervical conization was achieved by the Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP). Evaluated surgical biopsy histopathological characteristics were lesion grade, lesion borders and glandular involvement. After surgery all patients were submitted to a colposcopy and cytological evaluation every six months. Recurrent lesions were defined it confirmed by biopsy after surgery. Cases were patients with and controls patients without recurrence. chi2 test and multivariable analysis by logistic regression were used for group comparisons. Kaplan Meier's method was performed for the survival analyses (log-rank test). RESULTS: 40 patients had lesion recurrence. Initially, significant variables were: partner number, HIV-infection, lesion borders and glandular involvement. The most frequent recurrence occurred when there were simultaneous association between positive margins and glandular involvement as indicator for recurrence risk. After logistic regression analysis the main factors associated with lesion recurrence were: glandular involvement (OR-9.1; 95% CI:13.0- 27.5); HIV-infection (OR-4.6; 95% IC:1.1-6.3); compromised margins (OR-2.6; 95% IC:1.9-11.2). CONCLUSIONS: risk factors associated with cervical intraepitelial lesion recurrence were HIV-infection, glandular involvement and compromised margins.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):537-540
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900008
Purpose: the laparoscope can be used to convert an abdominal into a vaginal hysterectomy when there are contraindications for the vaginal approach, and not as a substitute for simple vaginal hysterectomy. The purpose of the present study is to discuss the role of laparoscopy in vaginal hysterectomy. Methods: between February 1995 and September 1998, 400 patients were considered candidates for vaginal hysterectomy.Exclusion criteria included uterine prolapse, adnexal tumor and uterine immobility. The Heaney technique was used, and different morcellation procedures were employed for the removal of enlarged uteri. Results: the mean age and parity was 46.9 years and 3.2 deliveries, respectively. Twenty-nine patients (7.2%) were nulliparous, and 104 (26.0%) had never delivered vaginally. Three hundred and three patients (75.7%) had a history of previous pelvic surgery, the most common being cesarean section (48.7%). The most frequent indication was leiomyoma (61.2%), and the mean uterine volume was 239.9 cm³ (30-1228 cm³). Vaginal hysterectomy was successfully performed in 396 patients (99.0%), and 73 surgeries (18.2%) were done by residents. The mean operative time was 45 min. Diagnostic/operative laparoscopy was performed in 16 patients (4.0%). Intraoperative complications included 6 cystotomies (1.5%) and one rectal laceration (0.2%). There were four conversions (1.0%) to the abdominal route. Postoperative complications occurred in 24 patients (6.0%). Two hundred and eighty-one patients (70.2%) were discharged 24 h after surgery. Conclusions: the laparoscope does not seem to be necessary in cases were the uterus is mobile and there is no adnexal tumor. The main role of the laparoscope may be to increase the awareness of gynecologists to the possibility of a simple vaginal hysterectomy in the majority of cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of tibolone use on dopplervelocimetric parameters of ophthalmic and retinal arteries. METHODS: clinical, prospective, longitudinal, randomized, placebo-controlled, triple-blind study, in which among 100 menopausal women, 50 have used 2.5 mg of the active principle tibolone (Tib Group) and 50, placebo as a means to form the control-group (Plac Group). In the Tib Group, 44 of the 50 women returned after 84 days to finish the exams, and in the Plac Group, 47. The ophthalmic and retinal arteries were studied to determine the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole ratio (S/D). Assessments have been done before and 84 days after medication. The t-Student test has been used for the comparison of means between the groups in independent samples, as well as for within-group comparisons in dependent samples. RESULTS: in both groups, the women's characteristics were similar in age, menopause duration, body mass index, arterial blood pressure, deliveries and cardiac rate. The Tib Group presented the following values in the ophthalmic artery: RI(pre)=0.71±0.05, RI(post)0.72±0.08 (p=0.43); PI(pre)=1.29±0.22, PI(post)=1.30±0.25 (p=0.4) and S/D(pre)=3.49±0.77, SD(post)=3.65±0.94 (p=0.32). In the retinal artery, the following values have been found: RI(pre)=0.67±0.09, RI(post)=0.69±0.10 (p=0.7); PI(pre)=1.20±0.29, PI(post)=1.22±0.3 (p=0.2) and SD(pre)=3.29±0.95, SD(post)=3.30±1.07 (p=0.3). Also, the tibolone and control groups did not show any significant difference in regard to the above indexes in the end of the study. CONCLUSIONS: the 2.5 mg dose of tibolone had no effect on the Doppler velocimetry indexes of the ophthalmic and retinal arteries.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(10):538-547
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000008
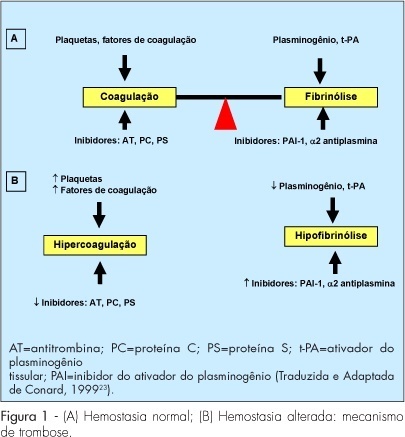
Exogenous female hormones used for contraception or postmenopausal hormonal replacement therapy are associated with an increase of venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk, mainly because they cause a hypercoagulable state. The risk is highest during the first year of use and it is not cumulative. The dose of estrogen, the type of estrogen and progestogen, the route of administration of female sex steroid hormones, and the hereditary risk factors for VTE of each patient can interfere on the final risk for VTE. The knowledge of their effect on hemostasis is essential for a correct prescription.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(11):538-544
Toxoplasmosis a parasitic zoonosis of global distribution, responsible for disorders during gestation can cause fetal death or congenital anomalies.
To evaluate the knowledge of toxoplasmosis among pregnant and postpartum women treated at the University Hospital of the city of Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
This was a cross-sectional study of 100 pregnant and postpartum women at the University Hospital. Participants answered a self-administered questionnaire and gave consent for data relating to serological examinations to be abstracted from their medical records.
The proportion of women who received information about toxoplasmosis was higher among those who received care in the private health care system (52.9%) than among those cared for in the public health care system (25.0%). Only 55.7% of women reported having some knowledge about toxoplasmosis. Of these, 53.7% received information during the prenatal period. However, most participants were unable to answer questions about preventive measures and modes of infection. Of the 100 patients in the study, only 46 underwent serologic testing for toxoplasmosis, 65.2% of whom tested negative (IgG).
Findings from this study are relevant to the training of health professionals regarding toxoplasmosis education and prevention. Improved education for health care providers and patients can lead to earlier diagnoses and reductions in adverse outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):539-544
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900007
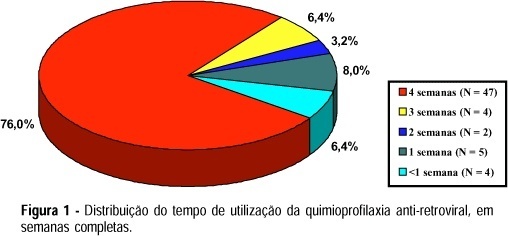
Purpose: some medical institutions have been prophylactically ministrating anti-HIV therapy in cases of sexual violence, although there are no appropriate basic facts to establish its efficacy. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the acceptance, tolerance and adhesion of these women under a chemoprophylaxis plan for HIV. Methods: sixty-two women victims of rape and/or anal intercourse with unknown aggressors have been evaluated. Prophylaxis has been started within the first 48 h after violence and maintained for 4 weeks, with daily administration of zidovudine, 600 mg; indinavir, 2,400 mg and lamivudine, 300 mg. Results: the discontinuance rate was 24.2%, withe 12 cases (80%) due to gastric intolerance. The side effects were present in 43 cases (69.4%), including nausea and vomitting as the most frequent. Complex dosage and time of administration were factors possibly related to the inadequate use of the drugs in 10.6% of the cases. Conclusion: the authors concluded that the chemoprophylaxis discontinuance rate was similar to that observed in other indications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):539-547
To describe a population of pregnant women diagnosed with toxoplasmosis and their respective newborns, describing the hospital protocol for treatment and follow-up.
Retrospective cohort of pregnant women with acute toxoplasmosis infection and risk of transplacental transmission who were sent to the Fetal Medicine Group of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA) between - January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2016. All patients with confirmed disease were included. The diagnostic protocol and treatment were applied; a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of the amniotic fluid was used to diagnose toxoplasmosis and determine the treatment. The newborns were followed up at the pediatric outpatient clinic specializing in congenital infection. The patients who were not followed up or were not born in the HCPA were excluded.
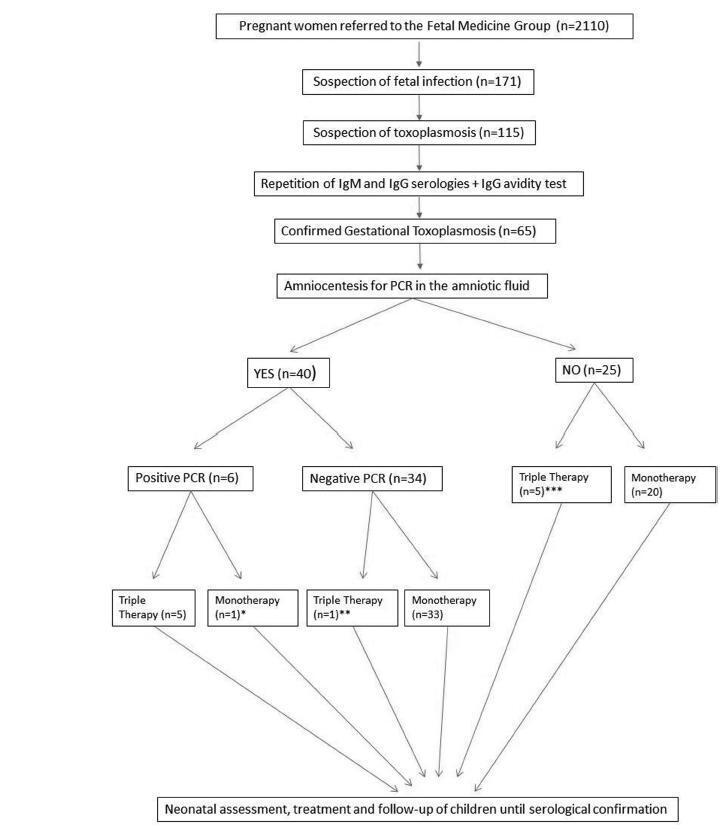
A total of 65 patients were confirmed to have gestational toxoplasmosis; 40 performed amniocentesis, and 6 (15%) were identified as having positive PCR in the amniotic fluid. In five of those cases, this result associated with the gestational age defined the triple therapy during pregnancy, and in one case, it defined the monotherapy (advanced gestational age). A total of 4 of these newborns were treated from birth with triple therapy for 10months, 1 was not treated (due to maternal refusal), and 1 progressed to death within the first 54 hours of life due to complications of congenital toxoplasmosis. Of the 34 remaining cases with a negative PCR, 33 were treated with monotherapy and 1 was treated with triple therapy (ultrasound findings); of these children, 9 (26.5%) presented negative immunoglobulin G (IgG), 24 (70.6%) presented positive IgG (but none presented positive immunoglobulin M [IgM]), and 1 (2,9%) presented alterations compatible with congenital disease and started treatment with the triple therapy soon after birth. Out of the total sample of 60 patients, among the 25 who did not perform amniotic fluid PCR, 5 were treated with triple therapy (ultrasound findings/prior treatment) and 20 patients were submitted to monotherapy; only two newborns underwent treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis. Among the 65 cases of gestational toxoplasmosis, 6 (9,2%) children had a diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis, and 2 patients with triple therapy felt severe adverse effects of the medications.
The present study suggests that research on PCR screening of the amniotic fluid may be useful to identify patients with a higher potential for fetal complications, who may benefit from the poly-antimicrobial treatment. Patients with negative PCR results must continue to prevent fetal infection with monotherapy, without risk of fetal or maternal impairment.