You searched for:"Luiz Kulay Júnior"
We found (21) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1999;21(9):533-538
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900006
Purpose: to develop an animal model for the study of, and training in, bovine biopsies. Methods: cow ovaries were obtained from a slaughterhouse and transported to the laboratory where the oocytes were aspirated, maturated and submitted to in vitro fertilization. On the 5th day after fertilization, the embryos were biopsied, with the zona pellucida being opened with a cutting blade fitted to the light microscope. One or two blastomeres were removed from the embryos and left in coculture for three additional days. After this time, embryo development was evaluated in comparison to a control group by morphological study and cell counts using specific staining for nuclei. Results: forty of the 57 biopsied embryos reached the blastocyst stage (70.2%) and hatching was observed in 11 (27.5%). Forty-two blastocysts were obtained in the control group (73.7%) and 11 of them hatched (26.2%). Cell counts showed no significant differences between groups. Conclusions: we conclude that the proposed protocol is technically feasible and supplies a good number of embryos because of the easy technique for obtaining bovine oocytes, thus representing a method that could be adopted for training.
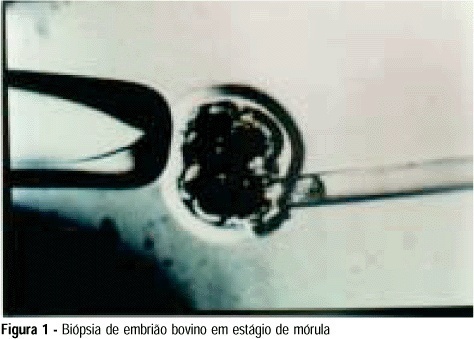
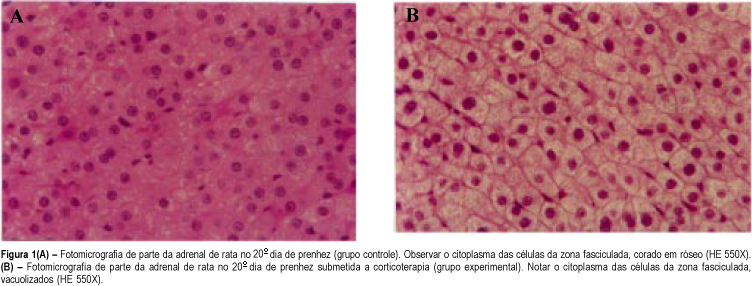
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(8):641-647
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800008
OBJECTIVE: to investigate whether it is possible to predict acidemia at birth in pregnancies with placental insufficiency using venous-arterial indices: pulsatility index for vein (PIV) of the ductus venosus (DV) over PI of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) and PIV of the DV over PI of the umbilical artery, and establish cut-off values for this prediction. PATIENTS AND METHODS: this was a prospective cross-sectional study involving forty-seven patients with placental insufficiency (umbilical artery resistance and pulsatility indices above the 95th percentile for gestational age) who were submitted to Dopplervelocimetry in the last 24 hours before delivery. All pregnancies were singleton, over 26 weeks of age and without structural or chromosome anomalies. Arterial cord blood was obtained for gasometry immediately after birth. Acidemia was defined as umbilical arterial pH < 7.20 in the absence of uterine contractions and pH < 7.15 in the presence of contractions. Metabolic or mixed acidemia at birth were considered pathological. A ROC curve was calculated for the venous-arterial indices: PIV DV/PI umbilical artery (UA) and PIV DV/PI MCA. A cut-off value was established and sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values and positive and negative likelihood ratios were calculated. RESULTS: The DV/UA PI index was not a good predictor of acidemia at birth. The DV/MCA PI index was related to acidemia at birth (area under the curve 0,785, p = 0,004). The cut-off value was: 0,582, sensitivity 66,7%, specificity 77,1 and accuracy 74,5%. CONCLUSION: the PIV DV/PI MCA ratio is adequate for predicting acidemia at birth in pregnancies with placental insufficiency. The cut-off value was: 0,582.
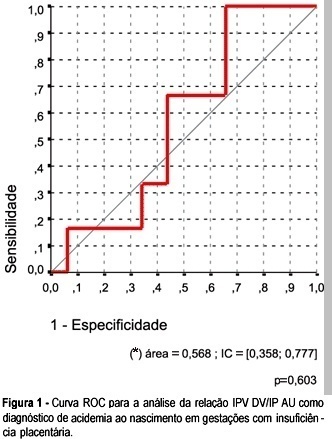
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(10):667-673
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001001000009
Purpose: the repetitive use of antenatal corticosteroid therapy for acceleration of fetal lung maturation has been common in cases at risk of preterm delivery. We studied the corticosterone levels at term and the morphologic aspects in the maternal and fetal adrenal glands submitted to the effect of betamethasone in the second half of rat pregnancy in order to verify its consequences. Methods: thirty female pregnant rats were divided into three groups of ten animals each. Group I received betamethasone on the 11th, 12th, 18th and 19th day of pregnancy. Group II received distilled water on the same days (control group). Group III did not receive any drug (stress control group). All rats were sacrificed on the 20th day of pregnancy when plasma corticosterone levels of dams were assessed and the maternal and fetal adrenal glands were studied by light microscopy. Results: plasma corticosterone level of dams was lower in the group treated with betamethasone (4.8 mg/dL) when compared with the control groups (17.7 and 26.8 mg/dL). The light microscopy study revealed cytoplasmatic vacuolation in the fasciculate zone in the maternal and fetal adrenal glands, which indicates adrenal suppression. Conclusions: the antenatal repetitive and prolonged use of corticosteroids in pregnant rats for acceleration of lung fetal maturation causes maternal and fetal adrenal suppression.
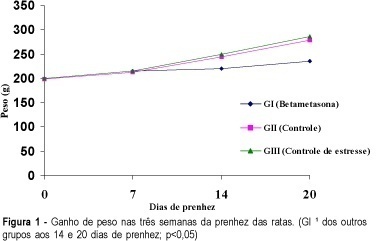
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(2):93-97
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200006
Purpose: to analyze the effect of betamethasone on the pregnancy of rats. Methods: thirty pregnant rats were divided into three groups of ten animals each. Group I -- the animals received betamethasone IM (1 mg/kg body weight, in 0.5 ml distilled water) on the 11th, 12th, 18th and 19th day of pregnancy. Group II -- the rats received distilled water (0.5 ml) IM on the 11th, 12th, 18th and 19th day of pregnancy. Group III - the rats did not receive any drug or vehicle. The animals were weighed on days 0, 7, 14 and on the 20th of pregnancy, and on the last day of weighing, the animals were sacrificed. The number of implantations, resorptions, fetuses, placentas, malformations, maternal and fetal mortality as well as the weight of the fetuses and placentas were obtained and analyzed. Results: our results show that the rats treated with betamethasone gained significantly less weight. Their fetuses had an average weight of 3.2 g compared with 3.75 g in the control group. The results regarding placental weight were 0.36 g vs 0.48 g, respectively. All these differences were statistically significant. Conclusions: betamethasone had a negative effect on the gain of weight of matrices, fetuses and placentas when administered repeatedly and continuousy after the second half of pregnancy.