You searched for:"Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral"
We found (23) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(12):584-590
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001200004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the differences between the maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, according to the classification as the severe/mild form, and the early/late onset form. METHODS: a retrospective study with 211 pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, assessed at a university reference center from 2000 to 2010. The diagnosis and disease severity were based on the values of blood pressure, proteinuria, and clinical and laboratory findings. The pregnant's age, skin color, parity, blood pressure, urine protein semiquantitative values, presence of bilateral notch in the uterine artery dopplervelocimetry and birth conditions were compared between patients with mild and severe disease, as well as between those of early/late onset. The disease was considered to be of early onset when diagnosed at less than 34 weeks of gestational age. RESULTS: most patients had the severe form of preeclampsia (82.8%), and the onset of the condition was early in 50.7%. Blood pressure values (133.6±14.8 versus 115.4 mmHg, p=0.0004 and 132.2±16.5 versus 125.7 mmHg, p=0.0004) and semiquantitative proteinuria (p=0.0003 and p=0.0005) were higher in the early and severe forms compared to mild and late forms. Infant birth weight (1,435.4±521.6 versus 2,710±605.0 g, 1,923.7±807.9 versus 2,415.0±925.0 g, p<0.0001 for both) and Apgar score (p=0.01 for both) were smaller for severe and early preeclampsia compared to mild and late preeclampsia. On the other hand, the presence of a bilateral notch in the uterine arteries was linked to the forms of early onset (69.2 versus 47.9%, p=0.02), whereas fetal growth restriction was more frequent in the severe forms of preeclampsia (30 versus 4.4%, p=0.008). CONCLUSION: the preeclampsia classification based on maternal clinical parameters better reflected the conditions of fetal nutrition, while the early onset of the condition was associated with placental vasculopathy detected by dopplervelocimetry.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(12):614-618
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200003
PURPOSE: to determine the variation of the number of ovarian follicles during fetal life. METHODS: twelve ovaries donated for research were included in our study, nine from fetuses and three from newborn babies who died in the first hour after being delivered with 39 weeks of pregnancy. Fetal age was confirmed both by the last menstrual period of the woman and by ultrasonography. Ovaries were fixed in formaldehyde, included in paraffin and serially sliced at 7 mm. At every 50 cuts, the obtained material was haematoxilin-eosin stained and evaluated with an optical microscope (400 X). The follicles were counted in ten different regions of the ovarian cortex, each region with an area of 625 mm². The presence of a nucleus was considered the parameter for counting. Follicular density, per 1 mm³ was calculated using the formula Nt=(No x St x t)/do, where Nt is the number of follicles; No is the mean number of follicles in 1 mm²; St is the total number of slices in 1 mm³; t is the slice thickness and do is the nuclei mean diameter. RESULTS: the gestational age of fetuses ranged from 24 to 39 weeks. The number of follicles per 0.25 mm² ranged from 10.9 ± 4.8 in a newborn to 34.7 ± 10.6 in another newborn. Among the fetuses, the least value was obtained in a 36 week-old fetus (11.1 ± 6.2) and the highest in a 28 week-old fetus (25.3 ± 9.6). The total number of slices per ovary ranged from six to 13, corresponding to follicles counted in areas from 15 to 32.5 mm². The total number of follicles ranged from 500,000 at the age of 22 weeks to > 1,000,000 at the age of 39 weeks. CONCLUSIONS: our results demonstrate different (increasing) densities of ovarian follicles along the gestational period, providing more knowledge about this still not well-known subject.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(8):649-653
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800009
PURPOSE: to assess the correlation between middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity and umbilical cord blood hemoglobin concentration and to determine its diagnostic value. PATIENTS AND METHODS: a cross-sectional prospective study was performed from January 2000 to May 2003. Forty-four isoimmunized pregnant women underwent a protocol for the identification of fetal hemolysis. When intrauterine transfusions were indicated, the umbilical cord blood hemoglobin concentration was measured at the beginning of the procedure. Each intrauterine transfusion preceded by Doppler velocimetry of the middle cerebral artery was regarded as one case, summing up eighty-three procedures. In all cases, the middle cerebral artery Doppler examinations were performed within the three hours preceding fetal blood sample collection. The systolic velocity peak was recorded and considered abnormal when its value was above 1.5 times the median for the corresponding gestational age. Hemocue® (B-Hemoglobin Photometer Hemocue AB; Angelholm, Sweden) was the device used to measure fetal hemoglobin concentration. The relationship between middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity and cord blood hemoglobin was obtained by the chi2 test, considered significant at p<0.05. RESULTS: in thirty-three cases the cord blood hemoglobin concentration was below 10.0 g/dL. There was a strong correlation between the two measured variables (p<0.001). The middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity with values above 1.5 times the median was associated with cord blood hemoglobin concentration below 10 g/mL (p<0,001). The sensitivity of an increased middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity was 75.8% for the detection of a cord blood hemoglobin level of 10 g/dL or lower. CONCLUSION: the middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity can be used as a noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(10):653-657
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001001000007
Purpose: to verify if there is an association between the mean blood velocity in the descending thoracic aorta and fetal anemia diagnosis. Methods: this is a prospective, cross-sectional study in which the mean blood velocities in the fetal aorta, in 66 fetuses at risk for severe anemia due to severe Rh immunization, and cord blood hemoglobin levels were analyzed comparatively. The hemoglobin level was obtained by cordocentesis if an intravascular transfusion was performed for severe anemia, however, if the fetus received an intrauterine transfusion by the intraperitoneal route or if the fetus did not receive a transfusion at all, hemoglobin level was measured at the time of pregnancy termination by umbilical cord puncture. The authors made a statistical association between the mean blood velocity in fetal descending thoracic aorta and the diagnosis of fetal anemia. The c² test was used for statistical analysis and a p value <0,05 was used to indicate significance. Results: there was a significant and indirect association between the mean blood velocity in the descending thoracic aorta and the detection of fetal anemia. The mean blood velocity in fetal thoracic aorta had a sensitivity of 47.4% for the diagnosis of moderate fetal anemia (Hg<10.0 g/dL), with a p value <0.01 by the Fisher exact test, and a sensitivity of 54.5% for severe Rh isoimmunization (Hg<7.0 g/dL), with a p value =0.01. Conclusion: this study revealed a significant indirect correlation between mean blood velocity in the descending thoracic aorta and the detection of fetal anemia due to Rh isoimmunization.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(2):66-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200003
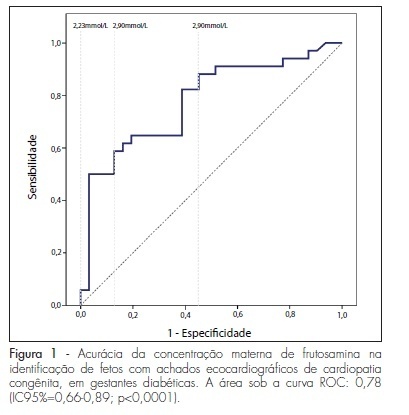
PURPOSE: to evaluate the importance of maternal plasma concentration of fructosamine as an indicator of fetal congenital cardiopathies in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus. METHODS: this was a retrospective study conducted on 91 pregnant women with diabetes mellitus who underwent routine fetal echocardiography at a university reference center in fetal medicine. Sixty-five patientes who presented pre-gestational diabetes mellitus and plasma fructosamine level were registered in the medical records prior to the ultrasound exam. The first measurement recorded was compared with the result of routine fetal echocardiography, carried out by a specialist physician of the service. The presence or absence of echocardiographic findings of congenital cardiopathies (EFCC) was related to plasma levels of fructosamine by the mean t-test and its accuracy for EFCC was verified by the ROC curve. Plsama fructosamine concentrations of 2.68, 2.9 and 2.23 mmol/L, which are, respectively, the local reference laboratory values, the value of the kit employed for measurement and the one of highest overall accuracy, were discussed as the cut-off values. RESULTS: EFCC was found in 52.3% of the fetuses. The first measurement of fructosamine, during the prenatal care period, was performed, on average, at 20.4±8.0 weeks of pregnancy. The maternal concentration ability of the fructosamine to identify fetuses with EFCC was significant (p<0.0001) and had an area under the ROC curve of 0.78 (95%CI=0.66-0.89). The 2.9 mmol/L plasma concentration of fructosamine revealed EFCC with better specificity, but with a higher percentage of false-negative results (96.8 and 55.9%). Values above 2.68 mmol/L were associated with a probability of 4.6 to identify fetuses with EFCC compared with lower values, with 58.8% of sensitivity and 87.1%, specificity. The value of 2.23 mmol/L proved to be the most overall accurate of the three values suggested, with a sensitivity of 88.2% in the identification of fetuses with echocardiographic abnormalities. CONCLUSIONS: it is possible to use a second trimester plasma fructosamine level to refer high risk pregnant women to a reference center of fetal echocardiography. These findings are important for the management of women with diabetes mellitus who initiate late prenatal care.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(10):663-668
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of intravascular transfusion on ductus venosus and inferior vena cava Doppler ultrasound indexes (SV/CA) and to relate it to hemoglobin levels before transfusion. METHODS: this is a transversal prospective study. A total of 62 intravascular transfusions were performed in 27 fetuses from pregnancies with red blood cell isoimmunization. The 62 cases were divided into two groups: (1) fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion £10 g/dL and (2) fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion >10 g/dL. The SV/CA and CA/SV indexes were measured using color Doppler ultrasound 6 h before and 12 h after intravascular transfusion. The index values before and after transfusion in all 62 cases were compared. Thereafter we compared these indexes before and after transfusion regarding each group. The Wilcoxon test was used and the results were considered statiscally significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: when we studied the whole group (62 cases) no significant difference was observed between the CA/SV index before and after transfusion (p=0.775). On the other hand, a significant increase in the SV/CA index was observed after transfusion (p=0.004). No significant differences were observed in both the SV/CA and CA/SV indexes before and after transfusion in the group of fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion £10 g/dL (p=0.061 and p=0.345, respectively). There was a significant increase in the CA/SV index after transfusion in fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion >10 g/dL (p=0.049), but the SV/CA index did not change in this group (p=0.086). CONCLUSION: venous Doppler study may be useful to understand fetal hemodynamic adjustment after intravascular transfusion. An increase in SV/CA without change in CA/SV after transfusion in anemic fetuses may be an important compensatory mechanism to increase intravascular volume. The increase in CA/SV index in fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion <10 g/dL suggests a state of fetal hypervolemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(9):691-695
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the importance of circulating maternal and fetal leptin in the healthy gestation, using its association with maternal, placental and fetal anthropometric variables, obtained at birth, and the relationship between the evaluated compartments. METHODS: in a transversal study a population of 33 single, healthy and term gestations was studied. The evaluated variables were maternal age, maternal weight, body mass index (BMF), weight of the newborn, placental weight, and placental index. Samples of maternal blood were immediately obtained before birth and from fetal umbilical cord blood at birth. Determination of serum leptin was performed using conventional radioimmunoassay. The relationships between serum leptin concentrations in maternal blood, umbilical artery and vein and the studied variables were assessed through linear regression. RESULTS: leptin levels were detected in the blood of all 33 pregnant women and their respective newborns, with maternal blood concentration (17.1±1.77 ng/mL) higher than that of umbilical vessels (vein: 9.0±1.16 ng/mL; artery: 8.23±1.02 ng/mL), p<0.0001. Leptin concentrations in the maternal blood were correlated with leptin concentrations in fetal blood (artery: coef. 0.63, p=0.037; vein: coef. 0.72, p=0.006). Regarding the anthropometric variables, leptin measured in the maternal blood was associated with initial and final maternal BMF (coef. 1.13; p=0.002; coef. 1,18, p=0.001) and cord leptin levels were correlated with the fetal weight at birth (vein: coef. 0.007, p=0.02; artery: coef. 0.006, p=0.02). CONCLUSION: there was a correlation between maternal and fetal leptin production and probably by the action of similar stimuli during gestation. Serum leptin was associated with the weight of the compartment where it circulates.