Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):534-540
The presence of bacteria in urine is called bacteriuria, which may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The manipulation of the urinary tract during urodynamic study (UDS), which is an invasive procedure, can result in urinary tract infection (UTI). Studies on the use of prophylactic antibiotics for UDSs are contradictory. Some investigators concluded that they were valuable and others did not. The objective of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis before UDS. This is a placebo-control randomized double-blind study.
Two-hundred and seventeen women affected by urinary incontinence were eligible for this study. All patients had presented negative urine culture previous to the UDS. They were randomized in four groups: group A received placebo, group B received 500 mg of levofloxacin, group C received 80 mg trimethoprim and 400 mg sulfamethoxazole and group D received 100 mg of nitrofurantoin. A urine culture was performed 14 days after the UDS.
We observed asymptomatic bacteriuria after the UDS in five patients in group A, one in group B, one in group C and one in group D. Only one patient on group A had symptomatic bacteriuria.We didn’t observe statistical difference between the groups. When we recategorized the patients in two groups, the incidence of bacteriuria was significantly higher in the placebo group compared with the antibiotic group.
The conclusion is that antibiotic prophylaxis before the UDS did not reduce the incidence of UTI in women within the target population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):534-534
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700014
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):534-540
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the role of morphological (12) and Doppler velocimetry (17) ultrasonographic features, in the detection of lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients. METHODS: 179 women (181 axillary cavities) were included in the study from January to December 2004. The ultrasonographic examinations were performed with a real-time linear probe (Toshiba-Power Vision-6000 (model SSA-370A)). The morphological parameters were studied with a frequency of 7.5-12 MHz. A frequency of 5 MHz was used for the Doppler velocimetry parameters. Subsequently, the women were submitted to level I, II and III axillary dissection (158), or to the sentinel lymph node technique (23). Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were calculated for each parameter. The decision tree test was used for parameter association. The cutoff points were established by the ROC curve. RESULTS: at least one lymph node was detected in 173 (96%) of the women by the ultrasonographic examinations. Histological examination detected lymph node metastases in 87 women (48%). The best sensitivity among the morphological paramenters was found with the volume (62%), the antero-posterior diameter (62%) and the fatty hilum placement (56%). Though the specificity of the extracapsular invasion (100%), border regularity (92%) and cortex echogenicity (99%) were high, the sensitivity of these features was too low. None of the Doppler velocimetry parameters reached 50% sensitivity. The decision tree test selected the ultrasonographic parametners: fatty hilum placement, border regularity and cortex echogenicity, as the best parameter association. CONCLUSION: the detection of axillary cavity lymph node stage by a noninvasive method still remains an unfulfilled goal in the treatment of patients with breast cancer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):535-541
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700005
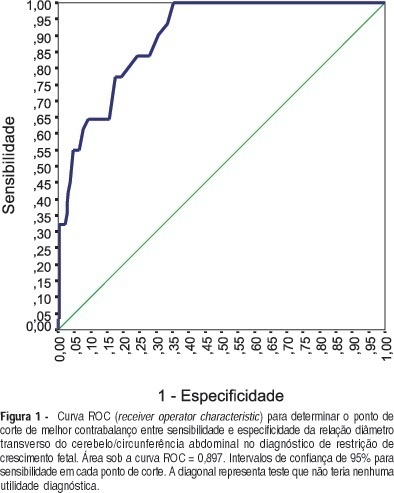
PURPOSE: to evaluate the validity of transverse cerebellar diameter (TCD)/abdominal circumference (AC) ratio in the diagnosis of fetal growth restriction (FGR), determining its best cutoff value and accuracy in symmetric and asymmetric FGR. METHOD: a prospective cross-sectional study, carried out in 250 pregnant women with singleton pregnancies, gestational age between 20 and 42 weeks, with ultrasound confirmation. The TCD measurement was obtained by placing the calipers at the outer margins of the cerebellum, after its localization in the posterior fossa, and slightly rotating the transducer below the plane of the thalami. The abdominal circumference was measured at the on junction of the left portal and umbilical veins. The best TCD/AC cutoff ratio was established by the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve. Neonates with TCD/AC ratio greater than the cutoff value were diagnosed as having FGR. We classified as gold standard for FGR the newborn infants who presented birth weight below the 10th percentile. Neonates showing FGR and Rohrer ponderal index between 2.2 and 3 were labeled as symmetric and below 2.2, asymmetric. RESULTS: the cutoff value calculated by the ROC curve for TCD/AC ratio was 16.15. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values, and likelihood ratio for positive and negative tests were 77.4, 82.6, 38.7, 96.3, 82, 4.5 and 3.7%, respectively. In the symmetric FGR, sensitivity and specificity were 80.8 and 81.7%, respectively. In the asymmetric FGR, sensitivity and specificity were 60 and 75%, respectively. CONCLUSION: TCD/AC ratio is an effective method in symmetric and asymmetric FGR diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):535-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700017
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):535-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700016
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):535-539
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800006
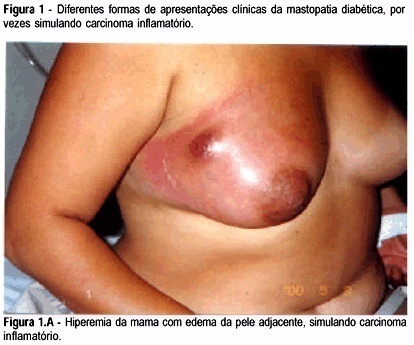
Purpose: to study the association between long-standing type 1 diabetes with bad glycemic control and breast inflammatory lesions which can simulate inflammatory carcinoma. Patients and Methods: eighteen patients were studied, retrospectively, in a mastology reference center from January 1998 to December 2001, presenting with breast inflammatory lesion with or without palpable mass. They were submitted to serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin determination, as well as image examination and histopathologic analysis, and diabetic mastopathy was diagnosed. Results: the patients' average age was 50.2 years, and all had insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, with average disease time of 14.9 years. All patients, with no exception, had a bad glycemic control; the average blood glucose was 329.6 mg/dL and the glycosilated hemoglobin average was 9.7%. NPH insulin dose being applied per day was 37.2 units. Patients underwent a clinical treatment with antibiotics and control of the glycemic levels with NPH insulin and had resolution of the symptoms in about five weeks. Conclusion: the professionals involved in women health care must be aware of this inflammatory pathology of the breast and its benign characteristics to avoid unnecessary procedures sometimes with patient injury.