Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(8):529-533
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000800008
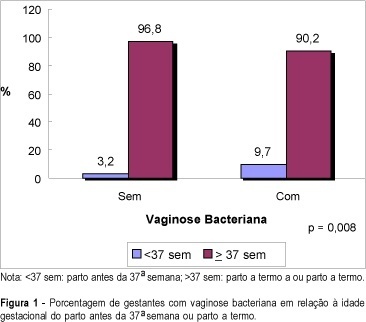
Purpose: to evaluate the relationship between bacterial vaginosis (BV) and spontaneous preterm delivery. Method: a total of 611 pregnant women from the general antenatal clinic of the "Clínica Obstétrica do Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade de São Paulo" were enrolled in this study. All pregnancies were dated by an early scan. Iatrogenic preterm deliveries were excluded. The presence of bacterial vaginosis was evaluated between 23 and 24 weeks of pregnancy by a Gram stain of the vaginal smear collected from the posterior vaginal wall using a sterile swab. Vaginal pH was also assessed from the lateral vaginal wall by a Universal 0-14 pH strip produced by Merck. Result: a complete follow-up was obtained in 551 patients and bacterial vaginosis was diagnosed in 103 (19%) cases. Among the patients with BV in the vaginal smear, 9.7% delivered before 37 weeks against only 3.2% in the group with normal vaginal smear (p=0.008). The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and false-positive rate for preterm delivery in the presence of bacterial vaginosis on Gram stain of the vaginal smear were 41.7, 82, 80.2 and 18%, respectively, with a relative risk of 1.8 for preterm delivery. The mean vaginal pH in the group of positive BV was 4.9 and in the group with normal smear it was 4.3 (p=0.0001). Conclusion: bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy increases the risk for spontaneous preterm delivery, with a relative risk of 1.8.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):53-58
The gestational complication most associated with perinatalmortality and morbidity is spontaneous preterm birth with gestational age < 37 weeks. Therefore, it is necessary to identify its risk factors and attempt its prevention. The benefits of the pessary in prematurity are under investigation. Our objective was to analyze the use of the pessary in the prevention of preterm births in published studies, and to compare its efficacy with other methods.
Randomized clinical trials published between 2010 and 2018 were selected from electronic databases. Studies on multiple gestations were excluded.
Two studies were in favor of the pessary as a preventive method, one study was contrary to the method and another two showed no statistically significant difference. Themeta-analysis showed no statistical difference with the use of a cervical pessary in the reduction of births < 37 (odds ratio [OR]: 0.63; confidence interval [95% CI]: 0.38-1.06) and < 34 weeks (OR: 0.74; 95% CI: 0.35-1.57)
The pooled data available to date seems to show a lack of efficacy of the cervical pessary in the prevention of preterm birth, although the heterogeneity of the studies made comparisons more difficult.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):53-53
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100011
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):53-53
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100010
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):53-58
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100008
PURPOSE: to correlate endometrial thickening diagnosed by ultrasonography with hysteroscopic findings in postmenopausal women. METHODS: a transversal study with hysteroscopic evaluation was performed in 121 postmenopausal women, with endometrial thickening diagnosed through transvaginal ultrasonography. In 98 women there was no history of hormonal replacement therapy, while the remaining 23 received different types of hormone; 55 patients complained of vaginal bleeding and the remaining did not present this condition. The endoscopic examinations were performed in the outpatient clinic, using a 4 mm rigid hysteroscope. For uterine cavity distention carbon dioxide (CO2) was used. Biopsy was performed in all patients, with a 3 mm Novak type curette, and the collected material was submitted to a histopathological study. RESULTS: endometrial thickening varied from 6 to 38 mm, with a mean of 10.7 ± 5.3 mm. The hysteroscopic findings were: polypoid lesion in 51 patients (42.1%); atrophic endometrium in 15 patients (12.4%); senile synechia in 15 patients (12.4%), focal thickening in 13 patients (10.7%); cerebroid lesion in 6 patients (5.0%); proliferative endometrium in 5 patients (4.1%); mucus in 5 patients (4.1%); myoma in 4 patients (3.3%); secreting endometrium in 3 patients (2.5%); endometrial hyperplasia in 3 patients (2.5%); and cystic atrophy in 1 patient (0.8%). Correlation between hysteroscopic findings and cytopathology was observed in 30 of 51 cases of polypoid lesion, in 12 of 15 cases of atrophic endometrium and in all cases in which the diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia or adenocarcinoma was suspected. CONCLUSION: in the majority of the patients, the hysteroscopic examinations revealed that there was no genuine endometrial thickening but rather other types of lesion in the uterine cavity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):53-55
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):53-58
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004963
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):53-53