Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):523-529
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100008
PURPOSE: To evaluate the adequacy of gestational weight gain and to determine its association with maternal socioeconomic, demographic and nutritional factors and health care, to estimate the prevalence of low birth weight, macrosomia, preterm birth and cesarean delivery and to identify the association of these outcomes with the adequacy of weight gain. METHODS: A cross-sectional study was performed in 2009/2010 to obtain socioeconomic, demographic, nutritional, dietary and physical activity data of pregnant women assisted by primary health care in a municipality of the state of São Paulo. Subsequently, data were collected from the medical records to evaluate gestational weight gain. Type of delivery, birth weight and gestational age at delivery were obtained from the Livebirths Information System. Gestational weight gain was evaluated according to the recommendations of the Institute of Medicine (2009). Associations were investigated by comparing the frequencies and by logistic regression, with excessive weight gain (yes, no) and insufficient gain (yes, no) being the dependent variables. RESULTS: A total of 212 pregnant women were studied: 50.5% had excessive gain and 19.8% insufficient weight gain. Only prepregnancy nutritional status was associated with adequacy of weight gain: compared with normal weight, prepregnancy overweight women had a four-fold higher chance to gain excessive weight (OR 4.66, 95%CI 2.19-9.4). Nearly a third of babies were born by caesarian section, 5.7% were premature, 7.1% were underweight and 4.7% were macrosomic. There was no association between adequacy of gestational weight gain and these outcomes. CONCLUSION: The proportion of inadequate gestational weight gain was high. Overweight pregnant women have a four-fold higher chance to gain excessive weight, and priority should be given to actions promoting adequate prenatal weight gain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):523-524
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):523-524
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(8):523-527
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000800007
Purpose: to study perinatal outcome in asthmatic pregnant patients who required hospital admission to control acute exacerbations. Patients and Method: retrospective study of 12 pregnant asthmatic patients admitted at the Hospital das Clínicas, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, FMRP-USP, during the period between 1992 and 1996. The analyzed data included: maternal age, prenatal care, length of hospitalization, gestational age at delivery, type of delivery, neonatal weight and Apgar score. Results: among the 12 asthmatic pregnant patients 7 did not have prenatal care for acute exacerbation treatment before hospitalization. Three of 12 developed preeclampsia (one with premature rupture of membranes and infection of the amniotic cavity and one with premature separation of the placenta); 2 of 12 were diagnosed with premature placental aging (one with premature labor and twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome and one with oligohydramnios); 1 of 12 was diagnosed with oligohydramnios and fetal death and had pneumonia, and 1 of 12 was diagnosed with polyhydramnios. Among the infants, 3 were small for gestational age. Conclusions: perinatal complications were more frequent in asthmatic pregnant patients who required hospital care for the acute exacerbations. Chronic asthmatic patients in reproductive age should be advised before pregnancy about the prophylactic measures to reduce the incidence of acute crises and exacerbations during pregnancy should be treated promptly.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):523-529
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000900004
PURPOSE: to determine the values of perineal muscular force (PMF) in the lying and seated positions and to identify the values of PMF between first pregnancy, according to type and the characteristics of the vaginal delivery and cesarean section. METHODS: study of the transversal type, performed in a maternity of Brazilian Public the Health System (SUS) in the city of São Paulo. The sample consisted of 95 primiparae at term. Evaluation occurred between the 40th and 45 th, day with an interview, physical examination and measurement of PMF using a perineometer of the Kegel type. The measurement was carried out in the lying and seated positions, muscular status (at rest and in maximum contraction), and the average of three measures for each position and muscular state were considered. RESULTS: 76.8% (73) of the women had vaginal delivery and 23.2% (22) cesarean section. After vaginal delivery, intact perineum in 18.9%, (18), perineal rupture in 24.2% (23), and episiotomy in 33.7% (32) were observed. Obtained values of the PMF were: lying position muscular rest 18. 9 mmHg, lying position maximum contraction: 30,7 mmHg, seated position muscular rest: 34.5 mmHg, seated positions maximum muscular contraction: 46.5 mmHg. CONCLUSION: there was association between the type and the characteristics of the delivery and PMF.
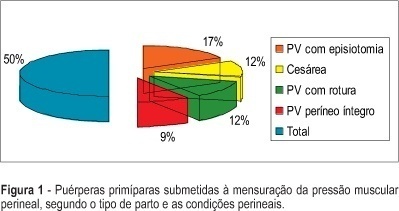
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):524-529
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100008
PURPOSE: To evaluate the concordance between polarization microscopy and confocal microscopy techniques in the evaluation of the meiotic spindle of human oocytes matured in vivo. METHODS: Prospective study that evaluated oocytes with the first polar extruded body obtained from infertile women who had undergone ovarian stimulation for intracytoplasmic sperm injection. The oocytes with the first polar extruded body were evaluated by polarization microscopy and were then immediately fixed and stained for microtubule and chromatin evaluation by high-performance confocal microscopy. We determined the correlation of polarization microscopy with confocal microscopy in the detection of meiotic oocyte anomalies, and we also evaluated the percentage of oocytes with a visible and non-visible cell spindle by polarization microscopy and with meiotic normality and abnormalities by confocal microscopy. Confidence intervals, Kappa's index and concordance between the methodologies were calculated, considering immunofluorescence microscopy analysis as the golden-standard for evaluating normal spindle and oocyte chromosome distribution. RESULTS: We observed that 72.7% of metaphase II oocytes with a nonvisible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy showed no meiotic abnormalities by confocal analysis and 55.6% of metaphase II oocytes with a visible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy were found to be abnormal oocytes by the confocal analysis. Only 44.4% of oocytes with a visible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy were found to be normal by confocal analysis. Concordance between the methods was 51.1% (Kappa: 0.11; 95%CI -0.0958 - 0.319). CONCLUSIONS: The low correlation between polarization microscopy and confocal microscopy in the assessment of oocyte meiotic spindle suggests that visualization of the meiotic spindle of human oocytes at metaphase II by polarization microscopy is not a good indicator of oocyte meiotic normality.
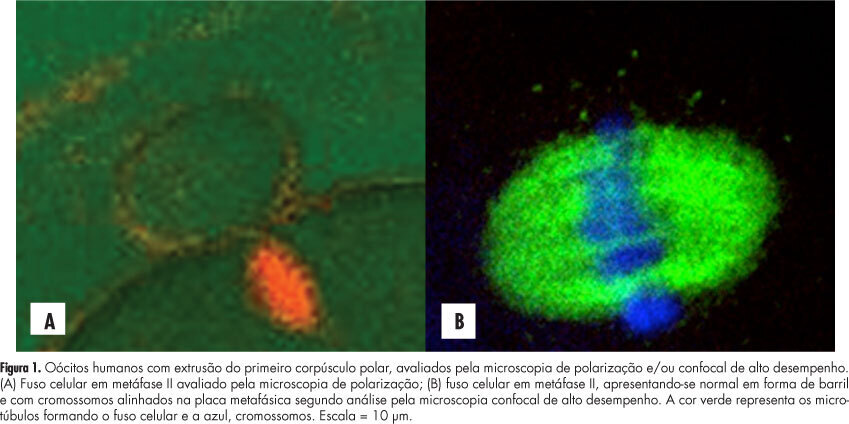
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):524-534
To assess the knowledge, attitude, and practice of Brazilian physicians about immediate postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion.
Cross-sectional online survey involving physicians on duty in public Brazilian hospitals. Participants answered an anonymous questionnaire with close-ended questions to assess their knowledge, attitude, and experience on the immediate postpartum and postabortion insertion of copper intrauterine devices.
One hundred twenty-seven physicians working in 23 hospitals in the 5 geographic regions of Brazil completed the questionnaire. Most were female (68.5%) and worked in teaching hospitals (95.3%). The mean (standard deviation) knowledge score (0–10 scale) was 5.3 (1.3); only 27.6% of the participants had overall scores ≥7.0. Most physicians (73.2%) would insert a postpartum intrauterine device in themselves/family members. About 42% of respondents stated that they had not received any training on postpartum or postabortion intrauterine device insertion. In the past 12 months, 19.7%, 22.8%, and 53.5% of respondents stated they had not inserted any intrauterine device during a cesarean section, immediately after a vaginal delivery, or after an abortion, respectively.
Most study participants have a positive attitude toward the insertion of intrauterine devices in the immediate postpartum period, but they have limited knowledge about the use of this contraceptive method. A large percentage of respondents did not have previous training on postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion and had not performed any such insertions in the last 12 months. Strategies are needed to improve the knowledge, training, and experience of Brazilian physicians on immediate postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):524-530
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000008
Detection of endometrial cancer in asymptomatic women has not proved to be a cost-effective procedure. Studies on this matter have shown that ultrasonography as a detecting method presents a high ratio of false-positive results and a negligible effect on the mortality rate. This way, the assistance strategy should be based on earlier diagnosis and appropriate treatment in women who present postmenopause bleeding. Being a non-invasive method, largely available and with high sensitivity, the transvaginal ultrasonography should be the initial investigative method. Though there is no consensus about the echographical endometrial thickness, above which the investigation is to proceed, diagnostic hysteroscopy should be the next step. The risk of neoplasia in endometriums with thickness under or equal to 3 mm is low enough to limit hysteroscopy to exceptional cases. Biopsy must be a necessary part of the hysteroscopy, because the diagnosis, made on visual basis, alone may lead to false results. Outpatient hysteroscopy can be done in more than 95% of the cases, even in menopausal women, rarely with severe complications. The adoption of "non-contact" examination techniques and the progressive reduction of the hysteroscope diameter have decreased the discomfort associated to small outpatient procedures.