Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):502-502
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):503-510
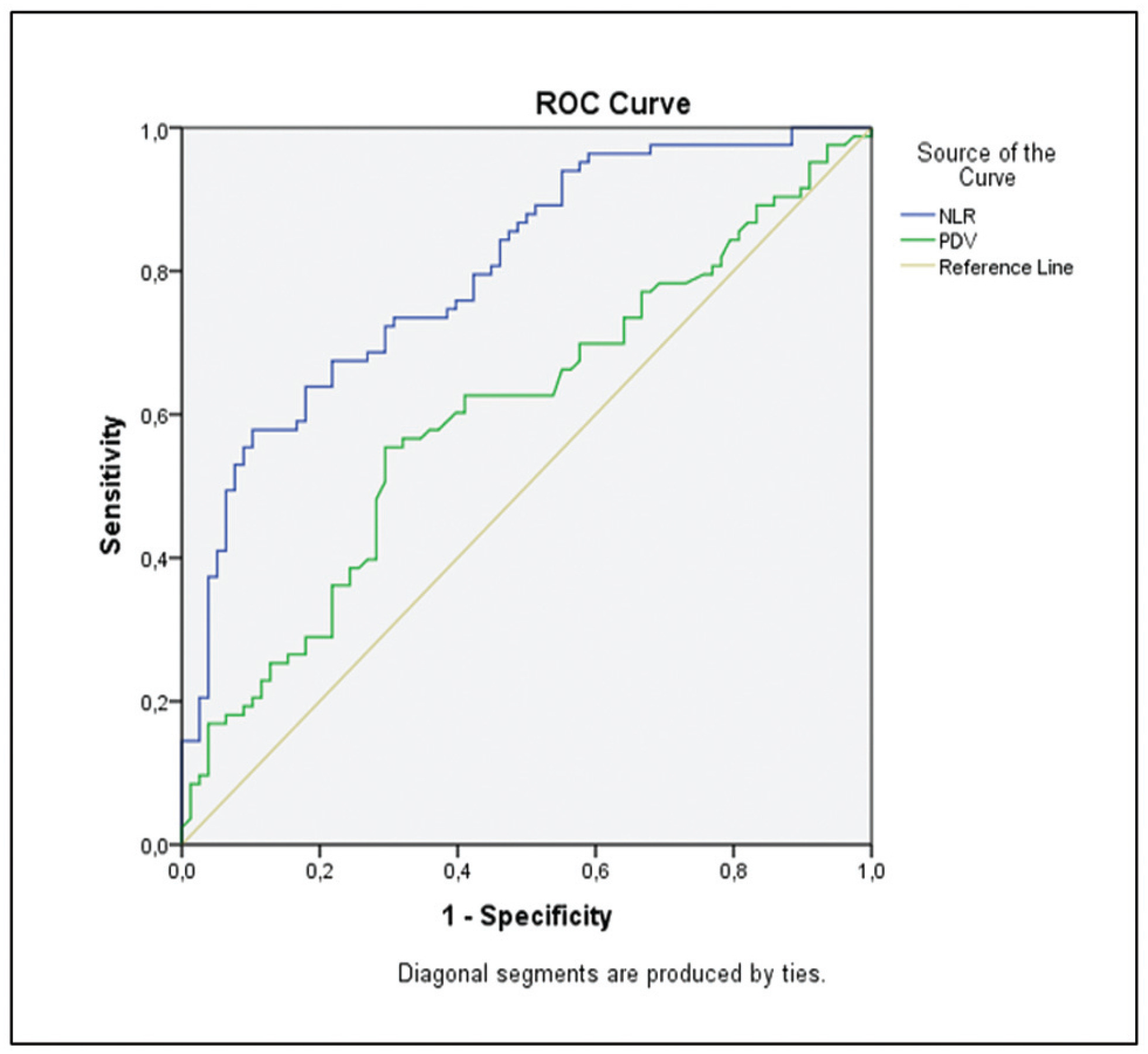
The availability of reliable and inexpensive markers that can be used to determine the risk of rupture during methotrexate (MTX) treatment in ectopic pregnancies (EPs) is considerable. The aim of the present study is to investigate the role of systemic inflammatory markers such as leukocytes (or white blood cells, WBCs), the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet distribution width (PDW), which are among the parameters of the complete blood count (CBC), in the prediction of rupture of EPs under MTX treatment.
A total of 161 patients with tubal EP who underwent a single-dose methotrexate (MTX) protocol were retrospectively analyzed, and the control group (n = 83) included patients cured by MTX, while the ruptured group (n = 78) included patients who were operated on for tubal rupture during the MTX treatment. The features of EP, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels, sonographic findings, and CBC-derived markers such as WBC, NLR, and PDW, were investigated by comparing both groups.
The NLR was found to be higher in the ruptured group, of 2.92 ± 0.86%, and significantly lower in the control group, of 2.09 ± 0.6%. Similarly, the PDW was higher (51 ± 9%) in the ruptured group, and it was significantly lower a (47 ± 13%) in the control group (p < 0.05). Other CBC parameters were similar in both groups (p > 0.05).
Systemic inflammation markers derived from CBC can be easily applied to predict the risk of tubal rupture in Eps, since the CBC is an inexpensive and easy-to-apply test, which is first requested from each patient during hospitalization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):503-510
To evaluate the impact of surgical treatment of deep infiltrative endometriosis (DIE) on pelvic floor dysfunction (urinary incontinence [UI], pelvic organ prolapse [POP], fecal incontinence [FI)] or constipation, and sexual function [dyspareunia]).
The present systematic review was performed in the PubMed database. For the selection of studies, articles should be published by January 5, 2021, without language restriction.
Six randomized controlled studies that evaluated surgical treatment for DIE and the comparison of different surgical techniques were included.
The studies were selected independently by title and abstract by two authors. Disagreements were resolved by a third author. All included studies were also evaluated according to the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the quality of the evidence was analyzed using the GRADE criteria. Subgroup analysis by different treatments and follow-up periods was also performed.
Six studies were included in the quantitative analysis. The risk of bias between studies showed an uncertain risk of bias for most studies, with concealment of allocation being the least reported category. The quality of the evidence was considered low. High heterogeneity was found between the studies. No study has evaluated UI or POP comparatively before and after surgery.
Dyspareunia and FI have improved after the surgical procedure, but it was not possible to demonstratewhich surgical technique was related to these outcomes as there was surgical heterogeneity. This diversity was found across data, with the recommendation of future prospective studies addressing pelvic floor disorders withDIE.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(10):503-507
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001000006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of hysterectomy on the sexuality of women with uterine leiomyoma. METHODS: prospective study including 33 sexually active women, with ages from 35 to 50 years old, with orgasmic experience and with a fit stable partner. All the women were submitted to two instruments for the evaluation or their sexuality: Sexual Quotient - Female Version (SQF) and Sexual Satisfaction Inventory - Female Version (SSIF). Both instruments were applied by the same examiner, before and six months after the hysterectomy. RESULTS: the SQF has shown that 39.4% of the patients presented deterioration in the sexual intercourse, even though there has not been found an association between the SQF results before and after hysterectomy (χ2= 0.6; degree of freedom=12; p=0.05). The mean scores obtained after the application of the SSIF have shown significant deterioration in the following parameters: sexual satisfaction (p=0.03); expression of feminine sensuality (p=0.01); vaginismus/dyspareunia (p=0.02) and anorgasmia (p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: it seems that hysterectomy has a negative impact on women's sexual life, with reports of decreased libido, arousal and orgasmic capacity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):503-508
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005081
To evaluate variations in the body mass index in patients undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer, and to associate these changes with patient's age and adjuvant chemotherapy regimen.
We performed a retrospective cohort study in order to correlate any variation in the body mass index before and after adjuvant chemotherapy with patient's age and adjuvant chemotherapy regimen. Patients who received any form of prior hormone therapy, such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors, were excluded. We selected data for 196 patients with stage I to III breast cancer who were treated by radical or conservative surgery and received adjuvant chemotherapy at the Cancer Institute of the State of São Paulo, Brazil.
Before adjuvant chemotherapy, 67.8% of patients were classified as overweight or obese according to their body mass indices. Around 66.3% (95% CI 59.7–73.0) of the patients exhibited an increase in the body mass index after adjuvant chemotherapy. The average age of all patients was 56.3±11.3 years. Participants whose body mass index increased were younger than those with no increase (54.7±11.1 versus 59.3±11.2 years; p=0.007). Patients were treated with the following adjuvant chemotherapy regimens: doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel (AC-T, 129 patients, 65.8%); 5-fluoracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (36 patients, 18.4%); cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluoracil (16 patients, 8.2%); docetaxel and cyclophosphamide (7 patients, 3.6%); and other regimen (8 patients, 4.1%). The AC-T regimen showed a statistically significant association with increase in the body mass index (p<0.001 by ANOVA).
Most patients with breast cancer showed an increase in the body mass index after adjuvant chemotherapy, especially after the AC-T chemotherapy regimen.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):503-506
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):503-510
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100005
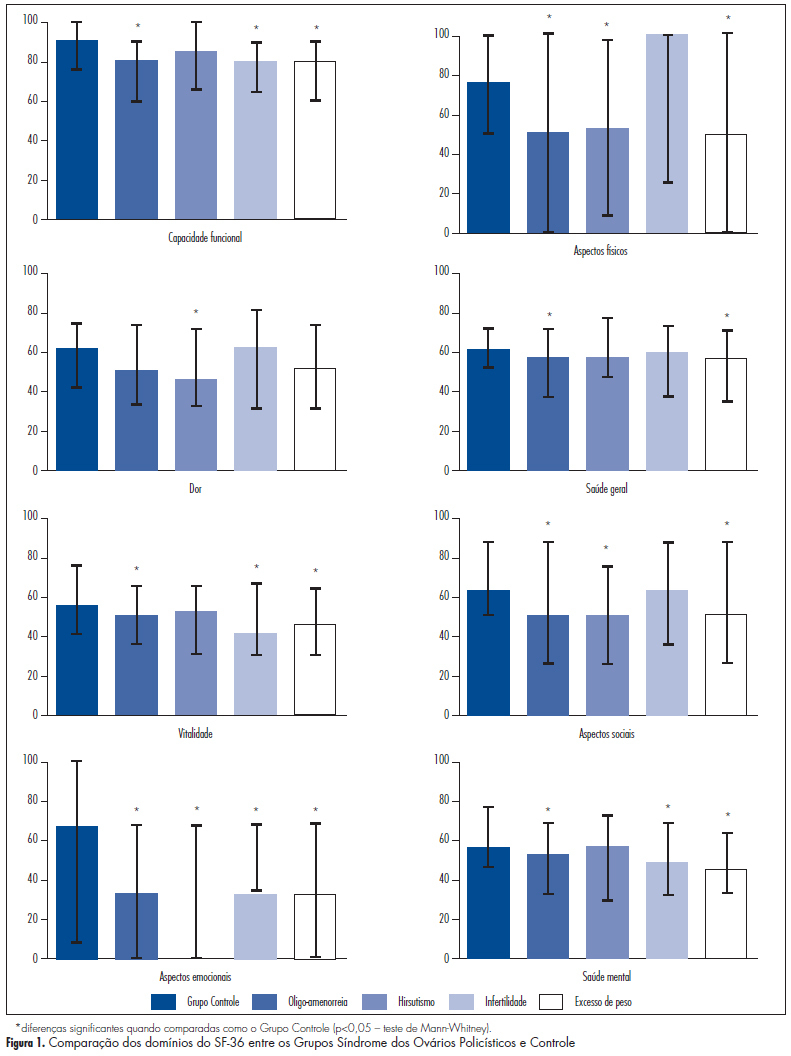
PURPOSE: To evaluate the quality of life of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (POS) and to learn about the experience of these women regarding the symptoms of their disease. METHODS: The study complementarily employed two methodological approaches - quantitative and qualitative ones. The quality of life of 213 women was evaluated (quantitative approach) using the SF-36 questionnaire. Of these, 109 had POS (Case Group: 26.8±5.4 years of age) and 104 were healthy (Control Group: 23.9±6.7 years of age). Data were analyzed statistically by the Student t-test, the chi-square test and the Pearson correlation test, with the level of significance set at 5%. Fifteen women with POS participated in the quantitative study and were interviewed using a semi-structured questionnaire. The qualitative data were analyzed by the technique of categorical thematic analysis. RESULTS: The women with POS showed impaired quality of life compared to Control (functional capacity: 76.5±20.5 and 84.6±15.9, respectively; physical aspects 56.4±43.3 and 72.6±33.3; general health status: 55.2±21.0 and 62.5±17.2; vitality: 49.6±21.3 and 55.3±21.3; social aspects: 55.3±32.4 and 66.2±26.7; emotional aspects: 34.2±39.7 and 52.9±38.2; mental health: 50.6±22.8 and 59.2±20.2). Regarding the qualitative data, thematic categorical analysis revealed that feelings of "abnormality", sadness, fear and anxiety were associated with the main symptoms of POS, i.e., hirsutism, menstrual irregularity, infertility and obesity. These symptoms affected the social, professional and marital life of these women. CONCLUSION: POS compromises the quality of life of affected women, causing them to feel that they are different from other women. Thus, women with POS do not simply require medical treatment regarding the reproductive, aesthetic and metabolic effects of the disease, but also need multiprofessional care.
Summary
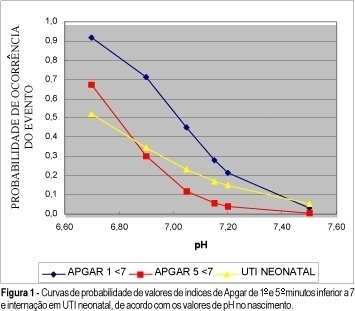
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):503-510
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800006
Purpose: to analyze the relationship between the values of pH at birth, fetal surveillance examinatios and neonatal results. Methods: one thousand, three hundred and forty-six high-risk pregnancies were evaluated at the Fetal Surveillance Unit. The assessment of fetal well-being included cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile and amniotic fluid index. After birth, the perinatal results (gestational age at birth, birth weight, Apgar scores at 1st and 5th minutes, umbilical cord pH at birth) were collected. To study the results, the patients were divided into four groups: G1 (pH <7.05), G2 (pH between 7.05 and 7.14), G3 (pH between 7.15 and 7.19) and G4 (pH > or = 7.20). Results: the abnormal patterns of cardiotocography were associated with pH at birth inferior to 7.20 (p = 0.001). Abnormal results of the fetal biophysical profile (<=4) were related to decrease in pH values at birth (p<0.001). The adverse neonatal outcomes were associated with acidosis at birth, and they were selected to be analyzed by the logistic regression model, showing that the odds ratio of each adverse neonatal outcome increases significantly when the values of pH at birth decrease. Conclusions: significant correlation was found between the values of pH at birth and adverse neonatal results, providing the possibility to estimate the risk of neonatal complications according to the pH values at birth.