Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(9):478-483
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900007
PURPOSE: to quantify the presence of antithyroperoxidase (anti-TPO) and antithyroglobulin (anti-TG) antibodies, and the plasmatic concentrations of thyrotropin (TSH) and free thyroxine (FT4) in normal pregnant women. METHODS: a hundred twenty-seven pregnant women, residing in São Paulo, aged from 14 to 44 years old and gestational age > 16 weeks, determined by ultrasound performed before the 20th week of pregnancy were included in a transversal study performed in the prenatal clinic of Santa Casa de Misericórdia de São Paulo, from January 2003 to September 2004. Pregnant women using medicines or with thyroidopathy history were excluded. Antithyroperoxidase and antithyroglobulin antibodies were quantified by chemiluminescence immunoassay. The immunofluorimetry technique by time-resolved was used for determining the thyrotrophin and free thyroxine. The Student's t test, with significance of 5%, was used for analyzing the results. RESULTS: the frequency of antithyroid antibodies was 12.6% (8.6% of anti-TPO antibodies, and 4.6% of anti-TG antibodies). The average of TSH concentrations was 2.13±1.0 µU/ml, and the average of T4L was 0.9±0.5 ng/dl. It was observed alteration of the thyroid function in ten pregnant women (8%). Three of them had diagnosis of hypothyroidism: one in the clinical form of the disease, with increased TSH and decreased FT4; two in the subclinical form with increased TSH and normal FT4. Five presented decreased TSH and increased FT4, consistent with clinical hyperthyroidism and two were diagnosed with subclinical hyperthyroidism, with decreased TSH concentrations only. CONCLUSIONS: the frequency of antithyroid antibodies was 12.6% in pregnant women, the antithyroperoxidase antibodies being predominant over the antithyroglobulin antibodies. It was observed some thyroid dysfunction in 8% of the cases with alterations of TSH and/or T4L.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):479-481
Summary
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):479-484
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800008
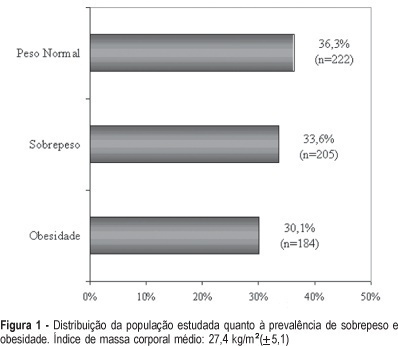
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of overweight and obesity among climacteric women. METHODS: this cross-sectional study included 611 women aged between 45 and 60 years attended at a climacteric clinic from January to June 2003. The prevalence of overweight and obesity was evaluated through the body mass index (BMI). Overweight or obesity was considered when there was a BMI equal or higher than 25 kg/m². Sociodemographic and reproductive variables as well as life style were also evaluated. The chi2 test followed by logistic regression was performed for statistical analysis. RESULTS: the average age of the studied women was 51.4 (±4.4) years, whereas 52.9% of them were postmenopausal. About 63.7% of them had a BMI equal or higher than 25 kg/m². The prevalence of overweight and obesity was 33.6 and 30.1%, respectively. The prevalence of overweight and obesity was higher among older women (OR=1.2; 95%IC: 1.1-1.4) or non hormonal therapy users (OR=1.8; 95%IC: 1.2-2.8). The opposite was observed among the women without a professional occupation (OR=0.6; 95%IC: 0.5-0.9) or a steady partner (OR=0.7; 95%IC: 0,4-0,9). CONCLUSIONS: in this study, the prevalence of overweight and obesity was influenced by age, but not by the menopausal status. The association between the marital status and occupation and the BMI strengthens the hypothesis that the health of the climacteric women may be influenced by biological factors as well as by psychosocial factors and life style. The lowest prevalence of overweight and obesity among the users of hormonal therapy may be explained by possible restrictions in relation to its prescription for women with previous overweight or obesity. Further studies are necessary to get more conclusive results, in particular with longitudinal studies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):479-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800007
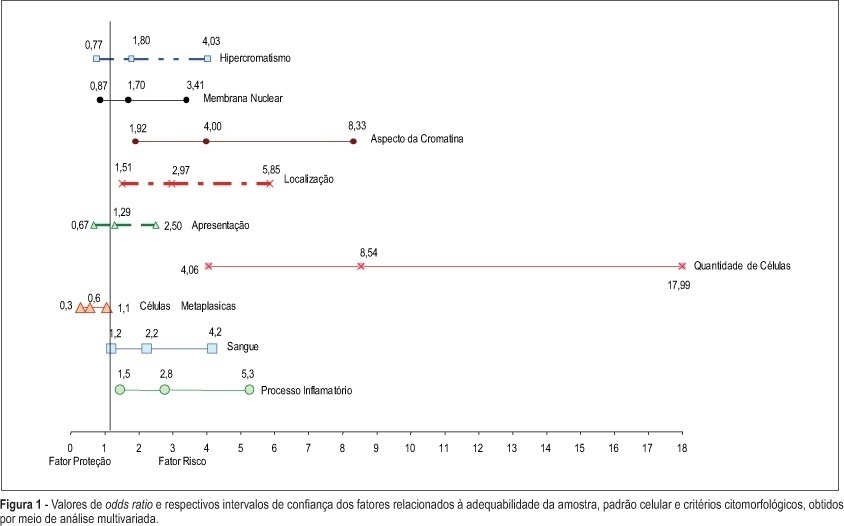
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether factors related to the adequacy of the sample, cell pattern and cytomorphological criteria are associated with false-negative (FN) results of cervical cytopathology during routine examinations. METHODS: this is a case-control study in which the study group included 100 cytopathologic smears with FN results detected during systematic internal quality control consisting of 100% rapid review. For each FN result detected, two smears with a true-positive diagnosis were identified by the same cytotechnician and these constituted the control group, making a total sample size of 300 smears. The variables were established in accordance with the criteria defined for the analysis of sample adequacy, cell pattern and cytomorphological analyzed criteria. The results were evaluated using bivariate analysis and logistic regression with stepwise variable selection criteria expressed in OR (95%). RESULTS: the number of atypical cells, the appearance of nuclear chromatin, and the distribution and presentation of atypical cells in the smear were the variables that showed the greatest risk for FN results with OR of 9.6, 4.2, 4.4, and 3.6, respectively. Inflammatory processes and the presence of blood in the smear were also identified as variables that influence the risk of FN results. CONCLUSIONS: the majority of the factors associated with FN results are dependent on the conditions and techniques of sample collection, since in the majority of cases, the lesion may not be adequately represented in the smear. Confounding factors such as blood and inflammatory processes may also impair analysis. With respect to cytomorphological alterations, thin chromatin strand was the variable that indicated the greatest risk of FN results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(1):48-55
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000100008
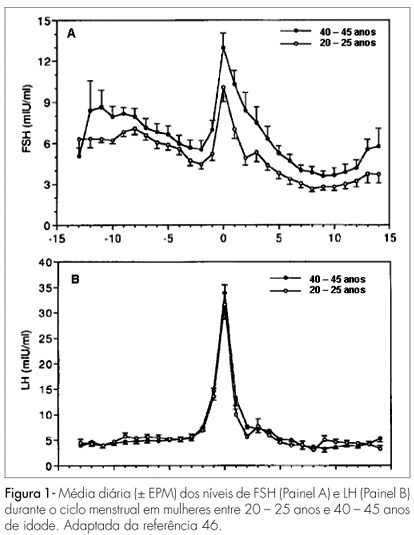
Changes in the levels of gonadotropins throughout the reproductive life depend on a fine tuned functional development of neural pathways and GnRH-neurones, pituitary gonadotrophs and granulosa-theca cells of the follicular wall. Both, LH and FSH levels change according to the day-time, menstrual cycle phase, and gynecological age. Initiating the puberty, changes in LH pulses are remarkable, showing higher frequency and amplitude at night. Later in puberty, the pulses of LH are also maintained during the day, remaining its levels with very little variation within the 24 hours period. During the menstrual cycle, the FSH levels increase at the end of the luteal phase, decrease during the medium and late follicular phase, increase rapidly in the ovulatory phase and remain at low basal levels until the late luteal phase. The levels of LH remain unaltered during the whole follicular phase, increase in the ovulatory surge, and decrease to the basal levels in the luteal phase. At the forth decade of life, the GnRH secretion changes, with hypothalamic loss of sensitivy to the estradiol positive feedback and decrease in frequency and prolongation of the GnRH pulses. The pituitary response is atenuated due to decrease in the density of GnRH receptors on gonadotroph cells, loss of gonadotroph sensitivity, secretion of more basic FSH and LH molecules, decrease in frequency and increase in amplitude of LH and FSH pulses. These modifications result in monotropic increase of the FSH secretion. Current studies show that the selective increase in the FSH levels in the early follicular phase is gradual, beginning as early as the third decade of life. These alterations in FSH are associated with an accelerated follicular depletion in women after 37-38 years old. On the other side, the LH levels remain almost constant up to the end of reproductive life. The different levels of FSH and LH seen throughout the reproductive years may be due to yet unknown regulatory mechanisms in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis.