Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):460-466
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005361
To evaluate the effectiveness of an illustrated home exercise guide targeting the pelvic floor muscles in promoting urinary continence during pregnancy.
A randomized clinical trial was performed with 87 participants, evaluated six times during pregnancy and divided into three groups: Gsup, supervised; Gobs, not supervised, and Gref, women who did not perform the home exercises program. A miction diary and perineometry were used to evaluate urinary incontinence (primary outcome) and pelvic floor muscle strength (secondary outcome), respectively. The Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn's and chi-square and Z tests with Bonferroni correction were used for continuous variables and proportions, respectively, with the level of significance set at 5%.
At the end of the study, 6.9% of pregnant women in the Gsup and Gobs had urinary incontinence, while 96.6% of Gref women were incontinent. Regarding pelvic floor muscle function, Gsup and Gobs had mean contractions of 10 and 8.9 cmH2O, respectively, while Gref had a value of 4.7 cmH2O. Both results were significant.
An illustrated home exercise guide targeting the pelvic floor muscles is effective in promoting urinary continence during pregnancy, even without permanent supervision.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):460-460
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):460-467
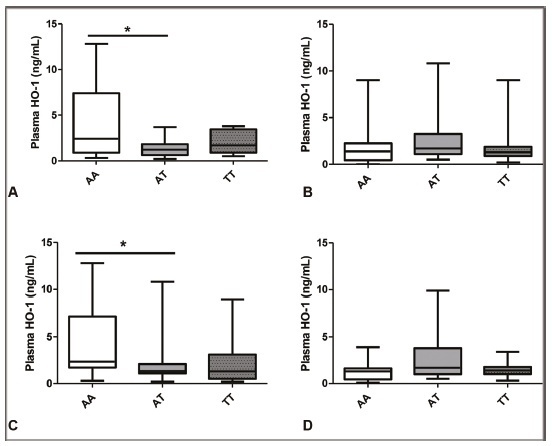
We examined the interaction of polymorphisms in the genes heme oxygenase- 1 (HMOX1) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS3) in patients with preeclampsia (PE) as well as the responsiveness to methyldopa and to total antihypertensive therapy.
The genes HMOX1 (rs2071746, A/T) and NOS3 (rs1799983, G/T) were genotyped using TaqMan allele discrimination assays (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA ), and the levels of enzyme heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
We found interactions between genotypes of the HMOX-1 and NOS3 genes and responsiveness tomethyldopa and that PE genotyped as AT presents lower levels of protein HO-1 compared with AA.
We found interactions between the HMOX-1 and NOS3 genes and responsiveness to methyldopa and that the HMOX1 polymorphism affects the levels of enzyme HO-1 in responsiveness to methyldopa and to total antihypertensive therapy. These data suggest impact of the combination of these two polymorphisms on antihypertensive responsiveness in PE.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):460-466
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800004
PURPOSE: to assess the performance of lamellar body count compared to the shake (Clements) test in the prediction of fetal lung maturity in diabetics. METHODS: prospective study of 62 patients who underwent amniocentesis between the 26th and 39th week of pregnancy. Immediately after collection, the amniotic fluid sample was submitted to the shake test and lamellar body count. Deliveries occurred within three days of amniocentesis. Immature test results (absence of a complete bubble ring in the third tube for the shake test and less than 50,000 lamellar bodies) were confronted with the occurrence of pulmonary immaturity in the neonate (respiratory distress syndrome). The performance of both tests was compared using the chi2 test and p<0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: seven infants had respiratory distress syndrome (11.3%). The lamellar body count and shake test were similar regarding sensitivity (100 vs 71.4%, respectively) and negative predictive value (100 vs 93.5%). Lamellar body count was superior as regards specificity (87.3 vs 52.7%, p=0.0001), positive predictive value (50 vs 16.1%, p=0.017), and accuracy (88.7 vs 54.8%, p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: lamellar body count is a simple and accurate method of assessing fetal lung maturity. It performs slightly better than the shake test in terms of specificity, positive predictive value and accuracy, with the advantage of not requiring manipulation or reagents. Similar to the shake test, lamellar body count has a high-negative predictive value: mature results (50,000 or more) indicate thar the infant will not have hyaline membrane.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):461-462
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700015
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):461-461
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700014
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(9):461-467
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000900007
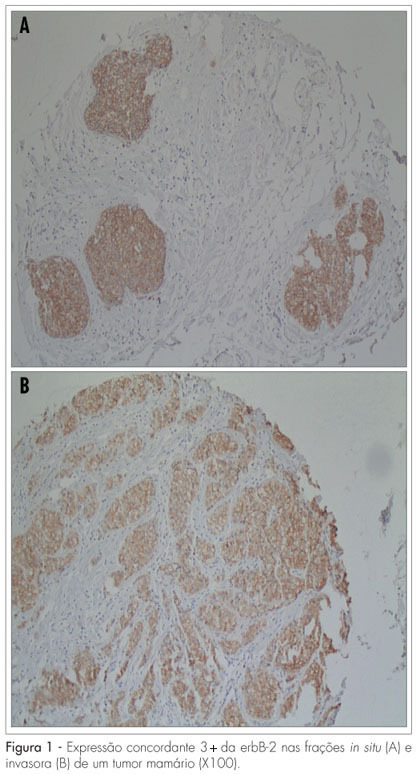
PURPOSE: to evaluate the expression of erbB-2 and of the estrogen and progesterone (ER/P) hormonal receptors in the transition regions between the in situ and the invasive fractions of ductal breast neoplasia (ISDC and IDC, respectively). METHODS: Eighty-five cases of breast neoplasia, containing contiguous ISDC and IDC areas, were selected. Histological specimens from the ISDC and the IDC areas were obtained through the tissue microarray (TMA) technique. The erbB-2 and the ER/PR expressions were evaluated through conventional immunohistochemistry. The McNemar's test was used for the comparative analysis of the expressions of erbB-2 protein and the ER/PR in the in situ and invasive regions of the tumors. The confidence intervals were set to 5% (p=0.05). Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated to assess the cross-tabulation agreement of the erbB-2 and the ER/PR expression in the ISDC and the IDC areas. RESULTS: the erbB-2 expression has not differed between the ISDC and the IDC areas (p=0.38). Comparing the two areas in each case, there was agreement in the expression of erbB-2 (ICC=0.64), PR (ICC=0.71) and ER (ICC=0.64). Restricting the analysis to tumors with the in situ component harboring necrosis (comedo), the ICC for erbB-2 was 0.4, compared to 0.6 for the whole sample. In this select group, the ICC for PR/ER did not differ substantially from those obtained with the complete dataset: as for the ER, ICC=0.7 (versus 0.7 for the entire sample) and for PR, ICC=0.7 (versus 0.6 for the entire sample). CONCLUSIONS: our findings suggest that the erbB-2 and the ER/PR expressions do not differ in the contiguous in situ and invasive components of breast ductal tumors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):461-466
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800005
PURPOSE: to compare the effectiveness of glibenclamide and acarbose with that of insulin for the treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), in regard to maternal glucose levels, newborn (NB) weight and neonatal hypoglycemia. METHODS: an open, randomized prospective study was carried out. Fifty-seven patients diagnosed with GDM were included. These patients required dietary control and additional therapy. Pregnant women were randomly alloted to one of three groups with different therapies: a control group making use of insulin therapy, a study group making use of glibenclamide and a study group making use of acarbose. The study took seven months (from October 1st 2003 to May 1st 2004). Assessed outcomes were maternal glucose levels in the prenatal period, the need for replacing therapy to achieve glucose level control, NB weight and neonatal hypoglycemia. Statistical analysis was determined by ANOVA with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: maternal characteristics were similar in all the three groups. Glucose level control was not obtained in three of the patients who used glibenclamide (15%) and in seven (38.8%) of the patients who used acarbose. Regarding fasting and postprandial glucose level rates and average NB weight no difference between the three groups was observed. No statistical difference was found for fasting or postprandial glucose levels and average NB weight in any of the three groups. The rate of large for gestational age fetuses was 5.2, 31.5 and 11.1% for the groups treated with insulin, glibenclamide and acarbose, respectively. Neonatal hypoglycemia was observed in six NB. Four of these were from the glibenclamide group (21.0%). CONCLUSIONS: glibenclamide was more effective for glucose level control than acarbose but neither were more efficient than insulin. NB children whose mothers had been alloted to the glibenclamide group showed a higher rate of macrosomia and neonatal hypoglycemia when compared to those newborns whose mothers were subjected to other therapies.