Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):436-441
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005105
Pregnant women have a 2-3 fold higher probability of developing restless legs syndrome (RLS – sleep-related movement disorders) than general population. This study aims to evaluate the behavior and locomotion of rats during pregnancy in order to verify if part of these animals exhibit some RLS-like features.
We used 14 female 80-day-old Wistar rats that weighed between 200 and 250 g. The rats were distributed into control (CTRL) and pregnant (PN) groups. After a baseline evaluation of their behavior and locomotor activity in an open-field environment, the PN group was inducted into pregnancy, and their behavior and locomotor activity were evaluated on days 3, 10 and 19 of pregnancy and in the post-lactation period in parallel with the CTRL group. The serum iron and transferrin levels in the CTRL and PN groups were analyzed in blood collected after euthanasia by decapitation.
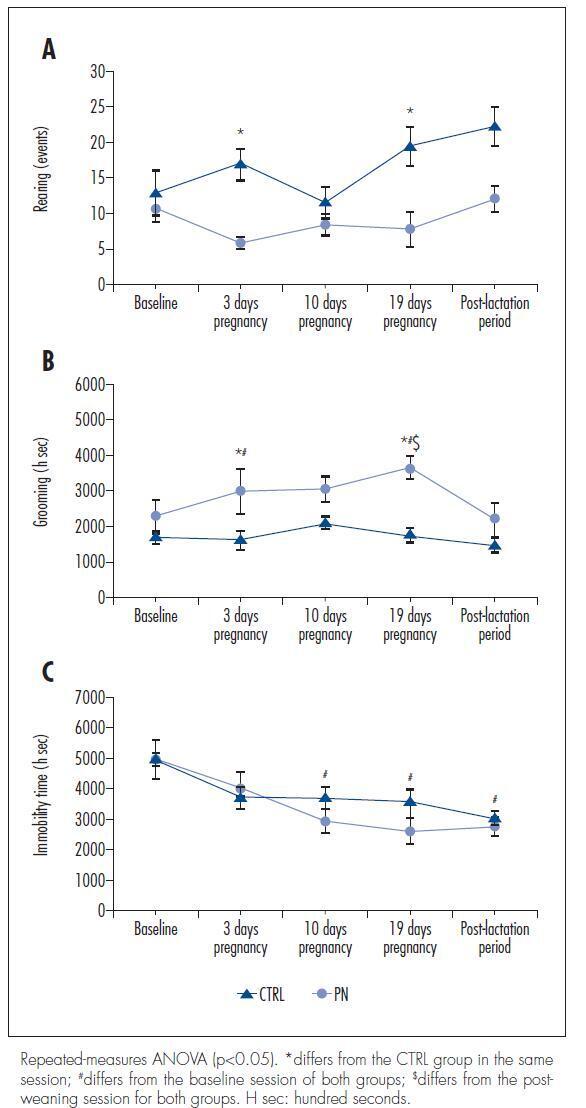
There were no significant differences in the total ambulation, grooming events, fecal boli or urine pools between the CTRL and PN groups. However, the PN group exhibited fewer rearing events, increased grooming time and reduced immobilization time than the CTRL group (ANOVA, p<0.05).
These results suggest that pregnant rats show behavioral and locomotor alterations similar to those observed in animal models of RLS, demonstrating to be a possible animal model of this sleep disorder.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):436-440
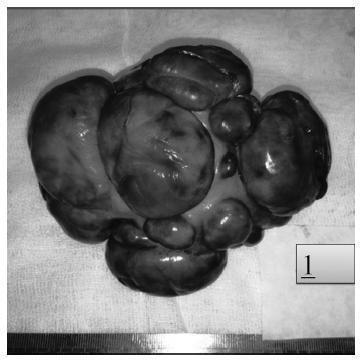
Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma is a leiomyoma variant exhibiting unusual growth patterns. We aimed to demonstrate this, as well as to point out another feature that has not been previously reported.
A congested, multinodular myomectomy specimen was resected. Histologically, smoothmuscle fascicles with marked vascularity and extensive hydropic degeneration were detected. A total of 2 mitoses per 10 high power fields were counted, and the Ki-67 index was of 2-3%. We encountered atypical bizarre cells that have not been previously reported. Coagulative necrosis was not present. The patient was alive and well 36 months after surgery, with no evidence of recurrence.
Albeit the gross aggressive appearance, cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyomas are benign in nature. To this day, atypical cells have not been reported in this type of tumor. Despite the presence of symplastic features, cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyomas are clinically benign entities. Surgeons and pathologists should be acquainted with this variant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):436-436
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):436-436
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(10):436-441
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001000002
PURPOSE: To evaluate the association between central nervous system (CNS) malformations and the C677T-MTHFR mutation in fetal blood. METHODS: A case-control study was conducted to compare the MTHFR-C677T mutation detected in 78 fetuses with CNS malformations and with 100 morphologically normal fetuses. Genomic DNA was extracted and purified from fetal blood using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA) according to manufacturer's protocol. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to assay the thermolabile MTHFR-C677T mutation. The γ² and the Fisher's exact tests were used for descriptive analysis and the Wilcoxon test was used for univariate analysis. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify which variables were predictors of CNS malformation. RESULTS: Cases and controls were similar regarding maternal characteristics such as age and number of deliveries and abortions. The MTHFR-C677T mutation was detected in 20 cases (25.6%) and in 6 controls in its heterozygous form (OR 10.3; 95%CI 3.3-32.2) and in 6 cases (7.7%) and in 1 control in its homozygous form (OR 12.3; 95%CI 1.3-111.1), and the differences were statistically significant. CONCLUSION: The presence of the MTHFR-C677T mutation in fetal blood was consistent with a higher risk of CNS malformations, both in the heterozygous and homozygous forms.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):436-441
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the risk factors for cesarean section (C-section) in low-risk multiparous women with a history of vaginal birth.
The present retrospective study included low-risk multiparous women with a history of vaginal birth who gave birth at between 37 and 42 gestational weeks. The subjects were divided into 2 groups according to the mode of delivery, as C-section Group and vaginal delivery Group. Risk factors for C-section such as demographic characteristics, ultrasonographic measurements, smoking, weight gain during pregnancy (WGDP), interval time between prior birth, history of macrosomic birth, and cervical dilatation at the admission to the hospital were obtained fromthe charts of the patients. Obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared between groups.
The most common C-section indications were fetal distress and macrosomia (33.9% [n=77 and 20.7% [n=47] respectively). A bivariate correlation analysis demonstrated that mothers aged>30 years old (odds ratio [OR]: 2.09; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.30-3.34; p=0.002), parity >1 (OR: 1.81; 95%CI: 1.18-2.71; p=0.006), fetal abdominal circumference (FAC) measurement>360mm (OR: 34.20; 95%CI: 8.04 -145.56; p<0.001)) and<345mm (OR: 3.06; 95%CI: 1.88-5; p<0.001), presence of large for gestational age (LGA) fetus (OR: 5.09; 95%CI: 1.35-19.21; p=0.016), premature rupture of membranes (PROM) (OR: 1.52; 95%CI: 1-2.33; p=0.041), and cervical dilatation<5cm at admission (OR: 2.12; 95%CI: 1.34-3.34; p=0.001) were associated with the group requiring a C-section.
This is the first study evaluating the risk factors for C-section in low-risk multiparous women with a history of vaginal birth according to the Robson classification 3 and 4. Fetal distress and suspected fetal macrosomia constituted most of the Csection indications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):436-437
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):437-442
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600009
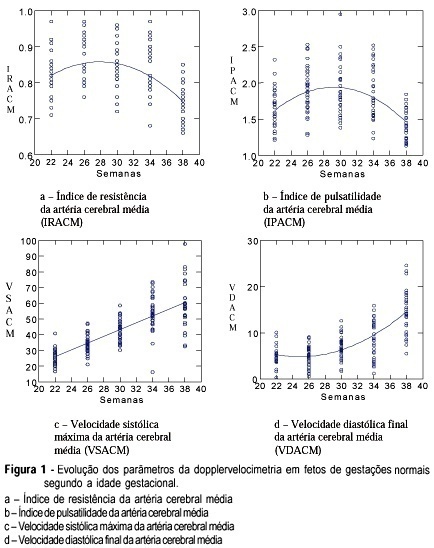
PURPOSE: to study the evolution of the resistance and pulsatility indices, maximum velocity, final diastolic velocity and time of acceleration of the middle cerebral artery of fetuses between 22 and 38 weeks of gestation. METHODS: a prospective and longitudinal observational study was conducted on 33 fetuses of normal pregnant women evaluated between 22 and 38 weeks of pregnancy. The gestational age was determined on the basis of the date of the last menstruation and/or by ultrasound examination during the first trimester. Doppler ultrasound examination was performed by a single observer using an Image Point 1800 (Hewlett Packard) apparatus equipped with a multiple frequency transducer. For the acquisition of the Doppler tracing of the middle cerebral artery, the sample indicator was calibrated for a sample volume of 1 mm³ and placed on the anterior middle cerebral artery as close as possible to the skullcap. The insonation angle was kept between 5º and 19º and the filter was adjusted to a frequency of 50-100 Hz. The newborn infants were evaluated in order to confirm that the fetuses were vigorous and adequate for gestational age. RESULTS: the results obtained for the resistance and pulsatility indices revealed a 2nd-degree equation, representing a parabola whose values for the resistance index were 0.81 during the 22nd week and 0.75 during the 38th week. The pulsatility index was 1.59 during the 22nd week and 1.45 during the 38th week. Maximum systolic velocity increased progressively along pregnancy, with values of 26.3 cm/s during the 22nd week and 57.7 cm/s during the 38th week. Final diastolic velocity increased progressively from the 26th week (5.21 cm/s) to term (14.6 cm/s). Acceleration time increased significantly only between 26 and 30 weeks, with values of 0.04 s during the 26th week and 0.05 s during the 30th week. CONCLUSION: it was concluded that the evolution of the resistance and pulsatility indices and of maximum systolic velocity were similar to those of most studies described in the literature. Acceleration time presented few modifications during the evaluated gestational weeks.