Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(6):419-420
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000600013
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(6):419-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000600012
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):419-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the perinatal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by oligohydramnios, not due to premature rupture of membranes (PRM), diagnosed until the 26th week of gestation. PATIENTS AND METHODS: we analyzed retrospectively the cases of oligohydramnios that occurred from January 1994 to December 2000, and were diagnosed until the 26th week of gestation. Oligohydramnios was present when the amniotic fluid index was less or equal to 5.0 cm. After diagnosis the patients were followed-up with serial ultrasound evaluation, with emphasis on the maintenance of the oligohydramnios state. When remission of the oligohydramnios occurred, patients remained in the study. Cases due to PRM, fetal death detected on the first examination and the women who gave birth in another institution were excluded from the study. Concerning the patients, the presence of clinical and obstetric diseases was investigated. As regards the newborns, we evaluated birth weight, time of admission/death, occurrence of death or malformations. RESULTS: twenty-seven cases of oligohydramnios were analyzed. Thirteen fetuses had congenital anomalies, and among them, eight had anomalies of the urinary tract, four of the nervous system and one had cystic hygroma. Fourteen patients had a clinical or an obstetric disease, mainly hypertension (10 cases). In addition, we found three cases of placenta previa and one case of thyropathy. There were thirteen fetal deaths and fourteen neonatal deaths. CONCLUSION: oligohydramnios not due to PRM, occurring in the second trimester of gestation, independent of the etiology or the presence of congenital anomalies, was associated with a fatal perinatal result.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):419-421
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700009
Squamous cell carcinoma of the mammary tissue is a very rare neoplasm, representing less than 1% of all breast carcinomas. The present study reports a case of squamous cell carcinoma of the breast, treated at the Hospital Araújo Jorge/ACCG. The tumor diagnosis, treatment and prognosis are also discussed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):419-424
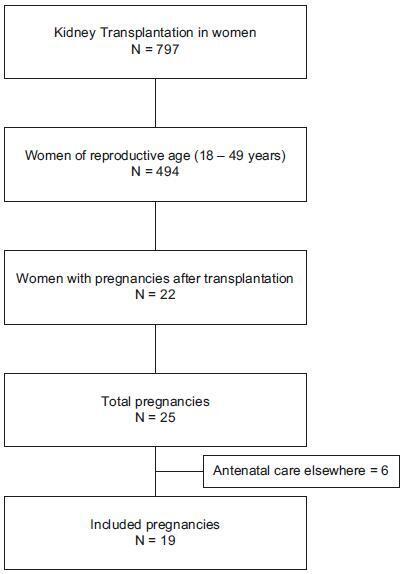
To assess maternal and perinatal outcomes in pregnancies after kidney transplantation in a tertiary center in Brazil.
Retrospective cohort of pregnancies in women with kidney transplantation at the Universidade Estadual de Campinas, from January 1995 until December 2017. Medical charts were reviewed, andmaternal and perinatal outcomes were described as means and frequencies. Renal function and blood pressure were evaluated during pregnancy and postpartum.
A total of 22 women had at least 1 pregnancy during the considered timeinterval, and 3 of them had > 1 pregnancy, totalizing 25 pregnancies. The mean age at transplantation was of 24.6 ± 4.2 years old, and the mean time interval until pregnancy was of 67.8 ± 46.3months. Themost frequent complication during pregnancywas hypertension, which affected 11 (64.7%)women. The gestational age at delivery was 34.7 ± 4weeks, and 47% of these pregnancies were preterm (< 37 weeks). A total of 88.2% of the women delivered by cesarean section. Renal function, measured by serum creatinine, remained stable during pregnancy, and the systolic blood pressure increased significantly, while the diastolic blood pressure did not differ during pregnancy.
Pregnancy after kidney transplantation is a rare event. Pre-eclampsia and prematurity were frequent complications, and cesarean section rates were very high. A specialized antenatal and postpartum care with a multiprofessional approach and continuous monitoring of graft function are essential for the early diagnosis of complications and improved outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):42-51
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005198
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) is the term to describe a set of malignant placental diseases, including invasive mole, choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor and epithelioid trophoblastic tumor. Both invasive mole and choriocarcinoma respond well to chemotherapy, and cure rates are greater than 90%. Since the advent of chemotherapy, low-risk GTN has been treated with a single agent, usually methotrexate or actinomycin D. Cases of high-risk GTN, however, should be treated with multiagent chemotherapy, and the regimen usually selected is EMA-CO, which combines etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide and vincristine. This study reviews the literature about GTN to discuss current knowledge about its diagnosis and treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):42-47
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100008
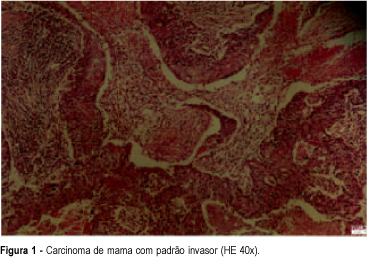
Breast cancer is the principal cause of death from cancer in women. Molecular studies of breast cancer, based in the identification of the molecular profiling techniques through cDNA microarray, had allowed defining at least five distinct sub-group: luminal A, luminal B, HER-2-overexpression, basal and " normal" type breast-like. The technique of tissue microarrays (TMA), described for the first time in 1998, allows to study, in some samples of breast cancer, distinguished by differences in their gene expression patterns, which provide a distinctive molecular portrait for each tumor and the basis for and improved breast cancer molecular taxonomy. Another important implication is that genetic profiling may lead to the identification of new target for therapy and better predictive markers are needed to guide difficult treatment decisions. Additionally, the current pathology classification system is suboptimal, since patients with identical tumor types and stage of disease present different responses to therapy and different overall outcomes. Basal breast tumor represents one of the most intriguing subtypes and is frequently associated with poor prognosis and absence of putative therapeutic targets. Then, the purpose of this review was to resume the most recent knowledge about the breast carcinoma classification and characterization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):420-426
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800008
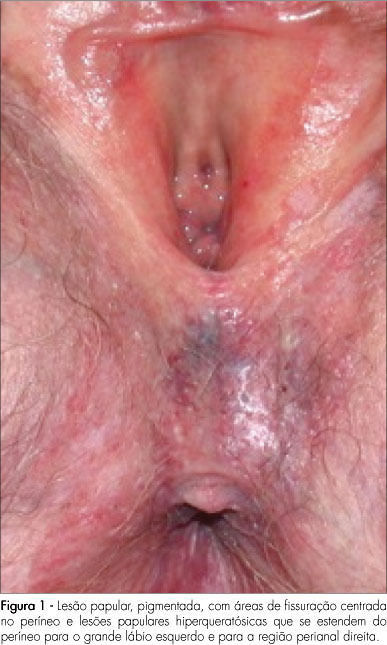
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is a pathological denomination coined by the International Society for Study of Vulvo-vaginal Diseases (ISSVD) and adopted by the International Society of Gynaecological Pathology (ISGYP) and by the World Health Organization. VIN is a heterogeneous pathological entity with a usual type (warty, basaloid and mixed) and a differentiated type. The incidence of the disease is increasing, especially in young women. The high-risk human papilomavirus (HR-HPV) infection, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, smoking, cervical, vaginal and rectal intraepithelial neoplasia are considered to be high risk factors for development of VIN. There are no specific symptoms or vulvar macroscopic aspects of VIN. However, a clinical lesion is always present. Liberal vulvar biopsies under colposcopy guidance should be done. Patients with diagnosis of VIN harbor an increased risk for vulvar invasive cancer. Surgical excision and laser CO2 vaporization are the most popular therapeutic modalities for VIN treatment, both with high rates of recurrence. A close follow-up of the patients is advised. Topical imiquimod seems to be a promising treatment option. Probably, prophylactic vaccination against HR-HPV will be an important tool for VIN prevention.