Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):401-406
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the agreement between noninvasive methods - pelvic pain, transvaginal ultrasound and hysterosalpingography - and the gynecologic endoscopy approach for the diagnosis of tuboperitoneal factors responsible for conjugal infertility. METHODS: this is a cross-sectional study including 149 infertile patients who were submitted to clinical evaluation, transvaginal ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, and laparoscopy. In the evaluation of pelvic pain, the following complaints were considered to be abnormal: pelvic pain of the dyspareunia type, dysmenorrhea or acyclic pain, and pain upon mobilization of the cervix and palpation of the adnexa. Ultrasonographic examination was considered to be altered when adnexal or uterine morphological changes (hydrosalpinx, myomas or uterine malformations) were detected. Hysterosalpingography was considered to be abnormal in the presence of anatomical tubal changes and unilateral or bilateral obstruction. The agreement between noninvasive methods and endoscopy was evaluated by kappa statistics. RESULTS: the agreements between pelvic pain, transvaginal ultrasound, and hysterosalpingography and the endoscopic approach were 46.3% (kappa=0.092; CI 95%: -0.043 to 0.228), 24% (kappa=-0.052; CI 95%: -0.148 to 0.043), and 46% (kappa=0.092; CI 95%: -0.043 to 0.228), respectively. When at least one alteration detected by noninvasive methods was considered, the agreement with endoscopic approach was 63% (kappa=-0.014; CI 95%: -0.227 to 0.199). Sensitivity and specificity in predicting alterations on endoscopic approach were 39.5 and 80% in the presence of pelvic pain, 14.5 and 72% in the presence of alteration on transvaginal ultrasound, 39.5 and 80% in the presence of alteration on hysterosalpingography, and 70.2 and 28% in the presence of at least one alteration by noninvasive methods. CONCLUSION: there is a poor diagnostic agreement between the several noninvasive methods and endoscopy in the investigation of conjugal infertility secondary to tuboperitoneal factors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(6):401-406
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000600007
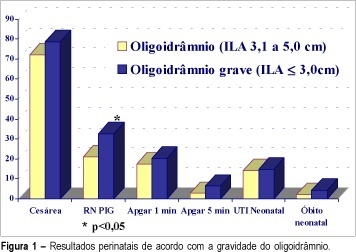
Purpose: to evaluate, in the high-risk pregnancies with oligohydramnios, the assessment tools for fetal well-being and perinatal results. Methods: five hundred seventy-two high-risk pregnancies were retrospectively analyzed. All of them presented with oligohydramnios established by AFI <=5.0 cm. Severe oligohydramnios was detected in 220 cases (AFI<=3,0 cm). The fetal well-being tests included: antepartum cardiotocography, biophysical profile score (BPS) and dopplervelocimetry of umbilical and middle cerebral arteries. Multiple gestation, fetal anomalies and premature rupture of membrane cases were excluded. Results: severe oligohydramnios was significantlly associated with abnormal and suspected cardiotocography results (23.2%), abnormal biophysical profile score (10.5%), abnormal results of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry (54.5%), small for gestational age infants (32.7%) and meconial amniotic fluid (27.9%) when compared to pregnancies with AFI between 3.1 and 5.0 cm. This group presented: abnormal or suspected cardiotocography results (13.9%), abnormal biophysical profile score (4.3%), abnormal results of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry (33.9%), small for gestational age infants (21.0%) and meconial amniotic fluid (16.8%). Conclusion: the oligohydramnios severity in high-risk pregnancies allows to discriminate the cases that are related to adverse perinatal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):401-411
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700002
Purpose: to analyze the relationship between White's classification and the histopathological, changes occurring in the placentas of diabetic pregnant women, performing a qualitative comparison of histopathological changes in the placentas of nondiabetic pregnant women with those in diabetic ones (classes A and A/B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH), studying the influence of the quality of glycemic control and of gestational age on placental changes in the three groups of diabetic pregnant women. Patients and methods: specimens of placentas were collected from all diabetic pregnant women seen between 1991 and 1996 in the Maternity Section of the Hospital das Clínicas, Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, stained using the hematoxylin-eosin technique, and submitted to a histopathological examination. The quality of glycemic control was analyzed by the glycemia average of gestation and classified as adequate or inadequate, with a limit of 120 mg/dl. Gestational age was individualized as term and preterm. Results: forty-two newborns (43.3%) were born at term and the remaining were preterm (56.7%). The prematurity rate was higher for women with clinical diabetes (classes B and C; D to FRH). Some histopathological alterations were observed only in placentas from diabetic pregnant women: cystoid degeneration, chorial edema, intima edema, dysmaturity, Hofbauer cell hyperplasia, villitis, ghost cells, two vessels in the umbilical cord, and endarteritis. Conclusions: histopathological changes in the placentas of pregnant women with gestational diabetes (classes A and A/B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH) were similar to those in the nondiabetic ones, and, therefore, were independent of White's clinical classification. The histopathological changes in the placentas of pregnant women with gestational diabetes (classes A and A and B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH) were not related to gestational age at birth and to the quality of glycemic control of the mother. The comparison between histopathological changes and the increased number of preterm newborns in clinical diabetes, class D to FRH, suggest early placental ageing in clinical diabetes patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):401-405
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700006
Purpose: to investigate if the addition of a cotton "swab" to the Ayre spatula and its previous moistening with physiologic saline solution increase the obtention of endocervical cells in colpocytologic smears. Methods: a random and single-blind diagnostic study was performed, involving three techniques of collection (Ayre spatula, combination of Ayre-dry cotton swab spatula and combination of Ayre-moist cotton swab spatula). A total of 307 smears prepared by Medicine students and residents of Gynecology and Obstetrics were evaluated. Results: there was no significant increase in the number of endocervical cells (columnar and/or metaplastic), obtained with the addition of dry swab (p = 0.2) or with the addition of a moistened swab (p = 0.8). Conclusions: the author concluded that mainly when the collections were performed by trainee professionals and in the absence of other more effective endocervical collecting device, it is more economical to use only the Ayre spatula to prepare the smear.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):401-408
To analyze the outcomes of a cohort of patients with high-risk histologies of endometrial cancer (EC) treated at Instituto Nacional de Câncer (National Cancer Institute, INCA, in Portuguese), in Brazil.
We reviewed the medical records of patients with high-risk histologies of EC in any stage registered at INCA between 2010 and 2016 to perform a clinical and demographic descriptive analysis and to evaluate the outcomes in terms of recurrence and survival.
From 2010 to 2016, 2,145 EC patients were registered and treated at INCA, and 466 had high-grade histologies that met the inclusion criteria. The mean age of the patients was 65 years, 44.6% were Caucasian, and 90% had a performance status of 0 or 1. The most common histology was high-grade endometrioid (31.1%), followed by serous carcinoma (25.3%), mixed (20.0%), carcinosarcoma (13.5%), and clear cell carcinoma (9.4%). Considering the 2018 Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics, FIGO, in French) staging system, 44.8%, 12.4%, 29.8%, and 12.9% of the patient were in stages I, II, III or IV respectively. Age (> 60 years), more than 50% of myoinvasion, higher stage, poor performance status, serous and carcinosarcoma histologies, and adjuvant treatment were independent factors associated with recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) in the multivariate analysis.
The current findings reinforced the international data showing poor outcomes of these tumors, especially for serous and carcinosarcomas and tumors with advanced stages, with shorter survival and high recurrence rates in distant sites, independently of the FIGO stage. Adjuvant therapy was associated with better survival.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):402-407
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800004
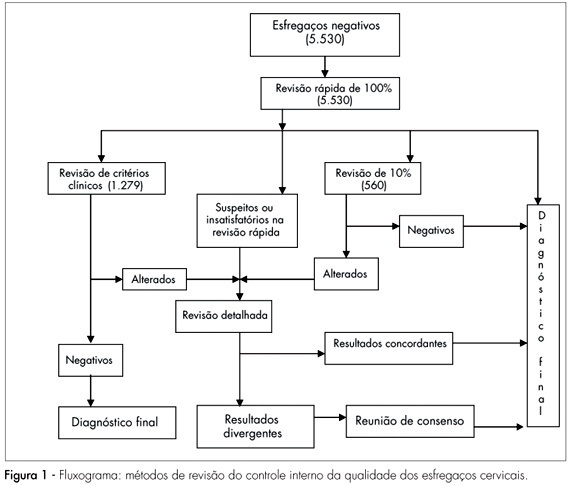
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficiency of the 100% rapid rescreening in the detection of false-negative results and to verify whether the results vary according to the adequacy of the sample and the woman’s age group. METHODS: to evaluate the efficiency of the rapid rescreening, the 5,530 smears classified as negative by the routine screening, after being submitted to the rapid rescreening of 100%, were compared with the rescreening of the smears on the basis of clinical criteria and 10% random rescreening. For statistical analysis, the variables were evaluated descriptively and the c² test and the Cochran-Armitage test were applied to compare results. RESULTS: of the 141 smears identified as suspicious according to the rapid rescreening method, 84 (59.6%) cases were confirmed in the final diagnosis, of which 36 (25.5%) were classified as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, five (3.5%) as atypical squamous cells that cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, 34 (24.1%) as low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, six (4.3%) as high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, and three (2.1%) as atypical glandular cells. Of the 84 suspect smears confirmed in the final diagnosis, 62 (73.8%) smears were classified as adequate and 22 (26.2%) as adequate but with some limitation, but no significant difference was observed with the woman’s age. CONCLUSIONS: the results of this study show that rapid rescreening is an efficient option for internal quality control for the detection of false-negative cervical smear results. In addition, it should be noted that rapid rescreening performed better when the sample was classified as adequate for analysis; however, it did not vary according to the woman’s age group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):403-408
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900003
PURPOSE: To identify the causes of fetal death in the studied population and to measure their contribution in identifying the cause of this outcome. To propose the use of the system Relevant Condition of Death (ReCoDe) in elucidating the causes of fetal death to minimize the number of unknown causes. METHODS: Cross-sectional study related to fetal deaths seen at a specialized academic hospital in the South of Brazil, from January 2000 to December 2009. The data were collected in the death certificates, maternal medical records and the reports of study of fetuses and attachments, and the findings were compared. Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 17.0. RESULTS: Were included 111 fetuses and their respective mothers in this study. The comparison between the diagnostic causes in the pathology and clinical evaluation showed 74 (66.7%) and 73 (65.8%), respectively. Together, they found a potential cause in 48.7% of cases, while 16.2% remained unknown. When analyzing both together with the ReCoDe system, only 9.9% of stillbirths remained as "unclassified." CONCLUSIONS: The proportion of diagnoses in the cause of death among the pathological and clinical evaluation showed no significant difference. When comparing the results of the cause of death suggested by the clinic/pathology with the use of the ReCoDe system, it appears that this tool has helped to clarify the cause by reducing the amount of those that remained without a possible etiology.