Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):397-402
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900002
PURPOSES: To analyze the sociodemographic and behavioral profile of sex partners, the proportion of those inadequately treated as well as to verify how many of them were inadequately treated and why some were not treated. METHODS: Quantitative study with data collected from May to October, 2008 at five public maternities in Fortaleza, Ceará. A survey was carried out with parturients who were hospitalized with syphilis and had a stable sex partner. We analyzed sociodemographic variables and those related to communication, diagnosis and treatment of sex partners. The data were entered into the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences and were analyzed using frequency distributions, measures of central tendency and dispersion. RESULTS: The study included 56 pregnant women. Most sexual partners were young adults aged on average 29 years, 50% of them had studied for less than seven years, 82.1 worked and 46.4% had a family income of less than a minimum wage. Of all the partners, 92.9% were the child's father and 69.6% lived with the women. Fifty percent and 12% were alcohol and drug users, respectively. Most partners (75.0%) were told about the diagnosis by the women, and in 78.6% of cases they were aware of the VDRL result before or during the prenatal period. However, 25.0% of the women did not communicate the result to their partners for the following reasons: not knowing the importance of the partner's treatment (50.0%), not being together after the diagnosis (42.9%) and having a quarrel (7.1%). Of the partners who were informed about the result before or during the prenatal period, 56.0% were treated and six (42.8%) were considered to have been properly treated. Among the ones who did not receive treatment, 63.6% refused it because they did not feel sick, because they did not believe in the treatment and because they were afraid of injections. CONCLUSIONS: Partners are told about the syphilis diagnosis of the pregnant women; however, only a few are properly treated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(9):398-403
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004996
To evaluate the impact of continued education provided by an external quality control laboratory on the indicators of internal quality control of cytopathology exams.
The internal quality assurance indicators for cytopathology exams from 12 laboratories monitored by the External Quality Control Laboratory were evaluated. Overall, 185,194 exams were included, 98,133 of which referred to the period preceding implementation of a continued education program, while 87,061 referred to the period following this intervention. Data were obtained from the Cervical Cancer Database of the Brazilian National Health Service.
Following implementation of the continued education program, the positivity index (PI) remained within recommended limits in four laboratories. In another four laboratories, the PI progressed from below the limits to within the recommended standards. In one laboratory, the PI remained low, in two laboratories, it remained very low, and in one, it increased from very low to low. The percentage of exams compatible with a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) remained within the recommended limits in five laboratories, while in three laboratories it progressed from below the recommended levels to >0.4% of the total number of satisfactory exams, and in four laboratories it remained below the standard limit. Both the percentage of atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) in relation to abnormal exams, and the ratio between ASC-US and intraepithelial lesions remained within recommended levels in all the laboratories investigated.
An improvement was found in the indicators represented by the positivity index and the percentage of exams compatible with a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, showing that the role played by the external quality control laboratory in providing continued education contributed towards improving laboratory staff skills in detecting cervical cancer precursor lesions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):398-408
The present study aimed to evaluate the antenatal care adequacy for women who gave birth at the University Hospital of Santa Catarina in Florianopolis (Brazil) during the COVID-19 pandemic, and to evaluate the association of adequacy with sociodemographic, clinical, and access characteristics.
Data were collected between October and December 2020, including 254 patients who delivered in the University Hospital from Federal University of Santa Catarina and answered our questionnaires. Additional data were obtained from patients’ antenatal booklets. Antenatal care was classified as adequate, intermediate, or inadequate according to the number of appointments, gestational age at the beginning of follow-up, and tests results. We carried out a descriptive statistical analysis and a bivariate/with odds ratio analysis onmaternal sociodemographic, clinical and health access variables that were compared with antenatal adequacy.
Antenatal care was considered adequate in 35.8% of cases, intermediate in 46.8%, and inadequate in 17.4%. The followingmaternal variables were associated with inadequate prenatal care (intermediate or inadequate prenatal care): having black or brown skin colour, having two or more children, being of foreign nationality, not being fluent in Portuguese, and using illicit drugs during pregnancy; the clinical variables were more than 6 weeks between appointments, and not attending high-risk antenatal care; as for access, the variables were difficulties in attending or scheduling appointments, and attending virtual appointments only.
In a sample of pregnant women from a teaching hospital in Florianópolis during the COVID-19 pandemic, antenatal care was considered adequate in 35.8%, intermediate in 46.8%, and inadequate in 17.4% of cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(8):398-404
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the characteristics regarding care of Bolivian pregnant women and their outcomes in Hospital Municipal Vereador José Storopolli. METHODS: a cross-sectional retrospective case-control study comparing two groups of pregnant women from 2003 to 2007. The Study Group included 312 Bolivian pregnant women and the Control Group, 314 Brazilian women. The groups were compared with respect to demographic variables, the presence of maternal complications and perinatal outcomes. Statistical analysis was performed by χ2 test and, when necessary, by applying Yates' correction. RESULTS: compared to Brazilian mothers, a smaller number of Bolivian women received prenatal care (16.4 versus 5.1%, p<0.001) and among those that did, the percentage of those who had less than five visits was higher (50 versus 19.3%, p<0.001). Compared to the Brazilian group, the Bolivian group had fewer unwed mothers (12.1 versus 25.4%, p<0.001) and a lower number of nulliparous women (34.1 versus 43.6%, p=0.017). Congenital syphilis had a higher incidence in the Bolivian group (2.9 versus 0.5%, p<0.05), as well as a higher number of newborns classified as large for gestational age (14.6 versus 5.8%, p <0.001). CONCLUSIONS: the failure to attend prenatal care or its completion with an inadequate number of consultations, and the higher number of cases of congenital syphilis observed among the Bolivian women show the great vulnerability of this ethnic minority group to health problems. Consequently, it is necessary a strategic planning of the sectors responsible for coordinating assistance in our country, in order to reduce this disparity, either through socio-economic improvements or by the implementation of health care tailored to the needs of this group.
Summary
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):399-404
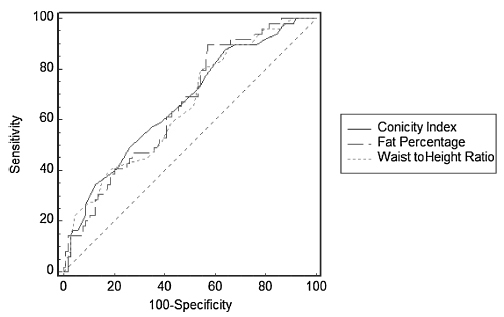
To determine the diagnostic accuracy and the cutoff point of the variables conicity index, waist to height ratio and fat percentage to detect urinary incontinence in physically active older women.
A total of 152 women were analyzed. The instruments used were the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ [Area 4]) to check the level of physical activity, and the Diagnostic Form to obtain sociodemographic data and presence of urinary incontinence. To calculate the conicity index, waist to height ratio and fat percentage, body mass, height and waist circumference were measured. Descriptive and inferential statistics were used. Cutoff points, sensitivity (S) and specificity (SP) were determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. A 5% significance level was adopted.
The prevalence of urinary incontinence was of 32.2%. The cutoff point with better sensitivity and specificity for the conicity index was 1.23 (S =87.8; SP =35.9); for the waist to height ratio, it was 0.57 (S =79.6; SP =45.6); and for the fat percentage, it was 39.71 (S =89.8; SP =42.7). The area under the ROC curve was 0.666 for the conicity index, 0.653 for the waist to height ratio, and 0.660 for the fat percentage.
The cutoff points for the anthropometric measurements conicity index, waist to height ratio and fat percentage indicate that these measures can be used to predict urinary incontinence in physically active older women. Furthermore, fat percentage seemed to be the best measure for this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):399-404
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500009
OBJECTIVE: to observe if there is any alteration in the Dopplervelocimetry of the uterine arteries of nursing and not nursing women after the insertion of the copper T 380 intrauterine device (IUD). METHODS: prospective, analytical, self-paired clinical assay, with 100 patients in whom we evaluated the color doppler flow: resistance index (RI), pulsative index (PI) and systole/diastole (SD) ratio. Nursing and not nursing women were assessed before IUD insertion as well as 30 days (one cycle) and 90 days (three cycles) after the insertion. RESULTS: the values obtained in the uterine arteries before insertion were: RI: 0.9, PI: 2.4, and SD ratio: 10.0. The values 30 days after insertion were: RI: 0.9, PI: 2.5 and SD ratio: 10.7. After three cycles we found a value of 0.9 for RI, 2.5 for PI and 10.7 for SD ratio. The comparison of the results before and after the IUD insertion showed a p value of 0.51 for RI, of 0.37 for PI and of 0.51 for SD ratio, demonstrating that after the insertion of the IUD, there were no significant changes in Dopplervelocimetry. Also, there were not significant differences between nursing and not nursing women, concerning these parameters. CONCLUSIONS: the use of copper T 380 IUD has no effect on the Doppler indices of the uterine arteries of both nursing and not nursing women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(1):4-10
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000100002
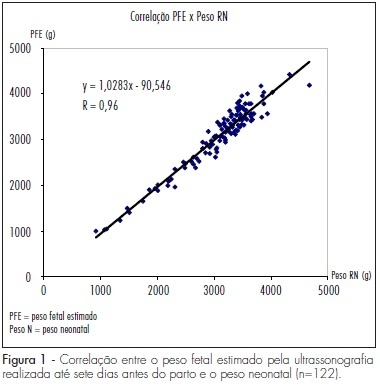
PURPOSE: to evaluate the correlation between the estimated fetal weight (EFW) by ultrasonography and the neonatal weight (NW), as well as the EFW's capacity to predict changes in NW among pregnant women in João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. METHODS: a diagnostic validation study, including 122 pregnant women who have had the EFW calculated by ultrasonography up to seven days before delivery and the NW established immediately after birth, with a specific newborn's scale. The correlation between EFW and NW measurements was assessed by Pearson's correlation coefficient and by the mean difference between them. EFW and NW were classified as: low for the gestational age (LGA), adequate for the gestational age (AGA) and high for the gestational age (HGA), according to the percentiles 10 and 90 of the respective reference curves. The diagnosis of EFW deviation has been validated using the values of the Alexander's NW reference curve as gold-standard, by estimating the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values. RESULTS: there has been a high linear correlation between the EFW and NW (R=0.96), and the difference between them has varied from -474 g to +480 g, with an average of +3 g. Most of the highest percent weight estimate variations were between 10 and 15%. EFW has had 85.7% of sensitivity and 100% of specificity for the detection of LGA, and 100 and 77.2%, respectively, for the detection of HGA. CONCLUSIONS: EFW is able to predict NW adequately, and the reference EFW tested has had a good performance in the screening of fetal growth deviation, in the population studied.