Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):391-398
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500008
OBJECTIVE: to analyze the maternal blood pressure and heart rate variation of primigravid women during labor and early puerperium. METHODS: sixty primigravid women were included in the study, and submitted to ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) with SpaceLabs 90207 monitor during labor and the first 12 h of puerperium. The records of blood pressure and heart rate were done every 15 min during labor and every 30 min during the first 12 h of puerperium. Three periods during labor (until cervix dilated 7 cm, cervix dilated between 8 cm and total dilatation, and delivery period) and two during puerperium (first and twelfth hours), were analyzed. First of all the results were analyzed without considering the kind of analgesia used and then the patients were divided into three groups, according to the anesthetic technique: local, lumbar extradural or subarachnoid. Results were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and paired Student's t-test for blood pressure and heart rate in each group during labor and puerperium. The nonpaired Student's t-test was used to compare different groups. A p value < 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. RESULTS: when the results were analyzed without considering the analgesic procedure, the values of systolic blood pressure during labor were significantly higher than in early puerperium. During labor, systolic blood pressure values were higher in the periods of later cervical dilatation and delivery than during early cervical dilatation. In the 12th h of puerperium the systolic blood pressure was lower than in the first hour. Diastolic blood pressure did not change during labor and was higher than in early puerperium. Heart rate increased during labor and decreased during puerperium. The systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate were the same both in local or lumbar extradural anesthesia groups; however, in the subarachnoid group the systolic and diastolic blood pressure did not change during labor. CONCLUSIONS: labor increased systolic blood pressure and heart rate. During labor, systolic and diastolic blood pressure were higher than in early puerperium. Both blood pressure and heart rate significantly fell from the first to the 12th hour of puerperium. The different anesthetic techniques did not affect blood pressure or heart rate, as compared with the primigravid group when the anesthetic technique was not taken into consideration.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):391-398
This study was conducted to determine the seroprevalence of HIV among pregnant women in Brazil and to describe HIV testing coverage and the uptake of antenatal care (ANC).
Between October 2010 and January 2012, a probability sample survey of parturient women aged 15-49 years who visited public hospital delivery services in Brazil was conducted. Data were collected from prenatal reports and hospital records. Dried blood spot (DNS) samples were collected and tested for HIV.We describe the agespecific prevalence of HIV infection and ANC uptake with respect to sociodemographic factors.
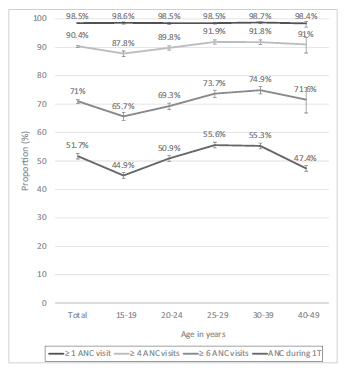
Of the 36,713 included women, 35,444 (96.6%) were tested for HIV during delivery admission. The overall HIV prevalence was of 0.38% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.31-0.48), and it was highest in: the 30 to 39 year-old age group (0.60% [0.40- 0.88]), in the Southern region of Brazil (0.79% [0.59-1.04]), among women who had not completed primary (0.63% [0.30-1.31]) or secondary (0.67% [0.49-0.97]) school education, and among women who self-reported as Asian (0.94% [0.28-3.10]). The HIV testing coverage during prenatal care was of 86.6% for one test and of 38.2% for two tests. Overall, 98.5% of women attended at least 1 ANC visit, 90.4% attended at least 4 visits, 71% attended at least 6 visits, and 51.7% received ANC during the 1st trimester. HIV testing coverage and ANC uptake indicators increased with increasing age and education level of education, and were highest in the Southern region.
Brazil presents an HIV prevalence of less than 1% and almost universal coverage of ANC. However, gaps in HIV testing and ANC during the first trimester challenge the prevention of the vertical transmission of HIV. More efforts are needed to address regional and social disparities.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(9):393-397
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005066
To evaluate the obstetric and perinatal outcomes evolution of triplet pregnancies.
A prospective observational study was conducted in triplet pregnancies delivered over 16 years in a tertiary obstetric center with differentiated perinatal support. Evaluation of demographic factors, obstetric complications, gestational age at delivery, mode of delivery, birth weight and immediate newborn outcome were done over a 16 years period. A global characterization of the sample was performed considering the listed parameters. Variables were categorized in three groups according to year of occurrence: 1996-2000, 2001-2006, 2007-2011, and all parameters were compared.
Of the 33 triplets included, 72.7% resulted from induced pregnancies. All except one patient received prenatal corticosteroids and five received tocolytics. All women delivered prenatally and no significant differences were seen in the mean gestational age at delivery or birth weight towards time. There were three intrauterine fetal deaths. Neonatal immediate outcomes were not significantly different over the years.
Despite remarkable progresses in perinatal and neonatal cares, no noticeable impact in triplet gestations' outcomes was seen, sustaining that triplets should be avoided due to their great risk of prematurity and neonatal morbidities, either by limiting the numbers of embryos transferred or by fetal reduction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):393-399
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800004
PURPOSE: to study cervical colonization in women with preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. METHODS: two hundred and twelve pregnant women with preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes were studied. Two cervical samples from each woman were collected and bacterioscopy and culture were performed. Association of cervical microorganisms and urinary tract infection, chorioamnionitis, fetal stress, antibiotic use, prematurity, neonatal infection, and neonatal death were evaluated. RESULTS: the prevalence of endocervical colonization was 14.2% (CI95%=9.5-18.9%), with similar results in preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. Group B streptococcus was the most prevalent organism (9.4%). Other organisms isolated were Candida sp, Streptococcus sp, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus sp. The most common findings of bacterioscopy were a reduced number of lactobacilli and a great number of leukocytes. Endocervical colonization was associated with a higher occurrence of urinary tract infection (23.8 versus 5.4%; p<0.01), early-onset neonatal infection (25.0 versus 7.3%; p<0.01) and neonatal mortality (two cases in colonized women; p<0.02) when compared with a negative culture of endocervical mucus. CONCLUSIONS: this study showed high prevalence of endocervical colonization despite the use of a nonselective culture media. The main microorganism isolated was group B streptococcus, but other organisms were present in one third of the studied population. More studies are needed to evaluate the influence of endocervical colonization on obstetrical outcome and on neonatal infection and mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):393-400
Endometriosis causes a decrease in oocyte quality. However, this mechanism is not fully understood. The present study aimed to analyze the effect of endometriosis on cumulus cell adenosine triphosphate ATP level, the number of mitochondria, and the oocyte maturity level.
A true experimental study with a post-test only control group design on experimental animals. Thirty-two mice were divided into control and endometriosis groups. Cumulus oocyte complex (COC) was obtained from all groups. Adenosine triphosphate level on cumulus cells was examined using the Elisa technique, the number of mitochondria was evaluated with a confocal laser scanning microscope and the oocyte maturity level was evaluated with an inverted microscope.
The ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondria in the endometriosis group increased significantly (p < 0.05; p < 0.05) while the oocyte maturity level was significantly lower (p < 0.05). There was a significant relationship between ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondrial oocyte (p < 0.01). There was no significant relationship between cumulus cell ATP level and the number of mitochondrial oocytes with oocyte maturity level (p > 0.01; p > 0.01). The ROC curve showed that the number of mitochondrial oocytes (AUC = 0.672) tended to be more accurate than cumulus cell ATP level (AUC = 0.656) in determining the oocyte maturity level.
In endometriosis model mice, the ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondrial oocytes increased while the oocyte maturity level decreased. There was a correlation between the increase in ATP level of cumulus cells and an increase in the number of mitochondrial oocytes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):393-400
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700005
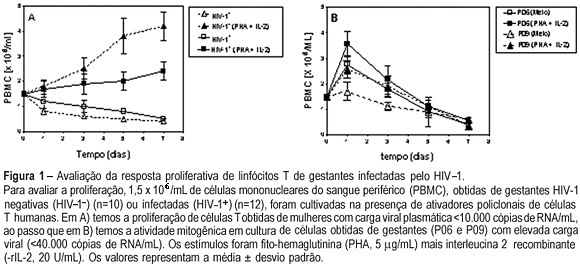
PURPOSE: to evaluate T cell proliferation and cytokine production in HIV-1-infected pregnant women and their impact on in vitro virus replication. METHODS: peripheral blood from 12 HIV-1-infected pregnant women and from their neonates was collected. As control, 10 samples from non-infected pregnants were also colleted. The CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts were assayed by flow cytometry. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and plasma were obtained by centrifugation with and without Ficoll-Hypaque gradient, respectively. The freshly purified PBMC were kept in cultures for seven days with PHA plus r-IL-2, and the lymphoproliferative response was assayed by Trypan blue dye exclusion. In some experiments we added anti-IL-10 monoclonal antibody. The plasma samples and supernatants from cell cultures were stored to determine both peripheral cytokine levels, by ELISA sandwich, and viral load, by RT-PCR. RESULTS: the results showed that the lymphoproliferative response was smaller in cultures obtained from HIV-1-infected women than in control cultures [4.2±0.37 vs 2.4±0.56 (x 10(6) cell/mL), p<0.005]. In both control and infected pregnant women who had low plasma viral load, the level of IL-10 was higher than in those with high viral replication (9.790±3.224 vs 1.256±350 pg/mL, p=0.002). The elevated TNF-alpha production detected in serum (7.200±2.440 pg/mL) and supernatants (21.350±15.230 pg/mL) was associated with higher plasma viral loads and vertical infection. The IL-10 blockade by anti-IL-10 antibodies augmented viral replication in the cell cultures. CONCLUSION: these results indicate that IL-10 production exerts a negative influence on virus replication, diminishing the probability of intrauterine HIV-1 infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(8):393-397
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800006
PURPOSE: to describe hysteroscopy findings in infertile patients. METHODS: this was a retrospective series of 953 patients with diagnosis of infertility evaluated by hysteroscopy. A total of 957 patients investigated for infertility were subjected to hysteroscopy, preferentially during the first phase of the menstrual cycle. When necessary, directed biopsies (under direct visualization during the exam) or guided biopsies were obtained using a Novak curette after defining the site to be biopsied during the hysteroscopic examination. Outcome frequencies were determined as percentages, and the χ2 test was used for the correlations. The statistical software EpiInfo 2000 (CDC) was used for data analysis. RESULTS: a normal uterine cavity was detected in 436 cases (45.8%). This was the most frequent diagnosis for women with primary infertility and for women with one or no abortion (p<0.05). Abnormal findings were obtained in 517 of 953 cases (54.2%), including intrauterine synechiae in 185 patients (19.4%), endometrial polyps in 115 (12.1%), endocervical polyps in 66 (6.0%), submucosal myomas in 47 (4.9%), endometrial hyperplasia in 39 (4.1%), adenomyosis in five (0.5%), endometritis (with histopathological confirmation) in four (0.4%), endometrial bone metaplasia in two (0.4%), and cancer of the endometrium in one case (0.1%). Morphological and functional changes of the uterus were detected in 5.6% of the cases, including uterine malformations in 32 (3.4%) and isthmus-cervical incompetence in 21 (2.2%). CONCLUSIONS: intrauterine synechiae were the most frequent abnormal findings in patients evaluated for infertility. Patients with a history of abortion and infertility should be submitted to hysteroscopy in order to rule out intrauterine synechiae as a possible cause of infertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):393-397
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700005
Purpose: to evaluate a possible relationship between fetal malformations (FM) and the use of sulfonylureas (SF) by diabetic pregnant women. Methods: we retrospectively studied 35 type 2 diabetic pregnant women followed at the Pathological Prenatal Care Outpatient Clinic of the University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, from 1993 to 1995. Twenty-two of these women had been inadvertently using sulfonylureas during the 1st trimester of gestation (SF group). We determined their prevalence of FM and compared it to that observed for pregnant diabetic women who were only on diet or insulin therapy (group C). We also analyzed other variables such as time of disease, age, metabolic control, and prenatal care. Results: there was no significant difference between groups in terms of age range, duration of diabetes, glycemic control, or early start of prenatal care, with the prevalence of FM being similar for the two groups (8.3% in group C and 13.6% in group SF). The malformations observed in group SF were: renal agenesis, pulmonary hypoplasia and ribbon gonads (patient 1); short limbs and abnormally implanted toes (patient 2); cleft palate, low implanted ears, neck webbing and saddle nose (patient 3), and micrognathia, dysplastic ears, imperforate anus, hypospadia, polydactily, ventricular septal defect and atrial septal defect (patient 4) in group C. Conclusions: these data do not allow us to attribute the malformations detected in group SF to the use of sulfonylureas, although not usually described alterations in diabetic embryopathy occurred in this group.