Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):38-43
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000100007
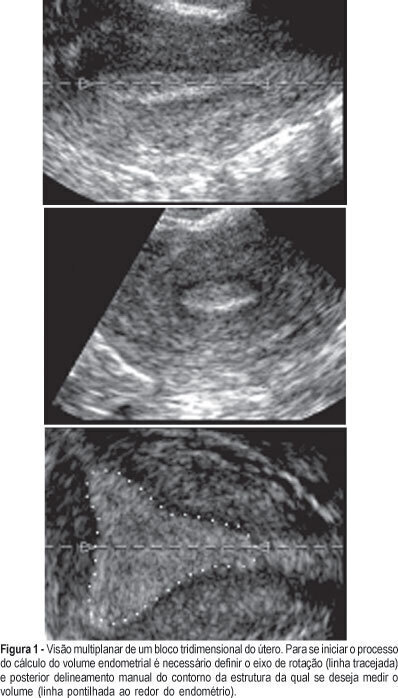
PURPOSE: to determine the intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility of endometrial volume measurements using the VOCAL®-imaging program (Virtual Organ Computer-aided AnaLysis). METHODS: one three-dimensional (3-D) ultrasound dataset of the endometrium was obtained from each of five infertile women with different endometrial volumes. For each 3-D dataset, the endometrial volume was calculated by two different observers using the manual mode in four different rotational steps (30º, 15º, 9º and 6º). Ten measurements were obtained with each method and observer from each 3-D dataset. We have used one-way ANOVA and the Tukey post-test to verify the differences among means and the intraclass correlation coefficient to test reliability. RESULTS: rotational methods employing a rotation step of 30º were associated with lower endometrial volume readings in 3 of the 5 patients. There were no significant differences between the means obtained by the 15º, 9º or 6º step rotation. No significant difference was found between the means obtained by the two different observers. The intraclass correlation coefficients were significantly lower with 30º (all under 0.984) than with the other step rotations (all above 0.996). CONCLUSIONS: the use of a rotational step of 15º or less provides reliable readings of endometrial volume: there were no significant differences between the means calculated by the two observers, associated with highintraclass correlation coefficient (>0.996). We recommend the 15º step rotation because it is quicker to be performed than 6º and 9º.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):380-387
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700002
PURPOSE: to evaluate all maternal deaths that occurred between 1927 and 2001, among 164,161 patients admitted to the Maternidade Therezinha de Jesus, the obstetrical service of the "Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora", Brazil. METHODS: a retrospective study of 144 maternal deaths that occurred in the maternity hospital in 75 years, with 131,048 live births in the same period of time, analyzing all patients's records regarding their clinical history and data from death certificates. Autopsies were not performed. Data obtained were age, parity, gestation length, complications, moment, and causes of death. The index of maternal mortality (IMM) period 100 thousand live births was utilized. For statistical analysis the chi2 test and the exponential smoothing technique were used (alpha=0.05). RESULTS: IMM decreased from 1544 in the period 1927-1941 to 314 (p<0.001) between 1942 and 1956 and from 1957 to 1971 it was reduced to 76.4 per 100 thousand live births (p<0.001). Nevertheless, since 1972 there was no further significant improvement (IMM=46 in the last 15 years, p=0.139). Maternal mortality was more frequent in the 15 to 39 years age group, in nulliparous patients with term pregnancies and mostly in the immediate postpartum period (53%). Direct obstetric causes occurred in 79.3% and indirect causes in 20.7% of the cases. Analyzing the evolution of the causes of death, it was found that in the first period of time the most frequent direct obstetric causes in descending order were puerperal infection, eclampsia and uterine rupture, while in the second period they were prepartum hemorrhage and eclampsia, and from 1977 to 2001 hemorrhage, abortion and preeclampsia. Analysis of the past 15 years showed the absence of maternal deaths by either preeclampsia or puerperal infection and the main causes were peripartum hemorrhage, abortion and indirect obstetrical causes. Relating maternal mortality to the type of delivery by the relative risk between cesarean section and vaginal delivery, it was found that when the indication of cesarean section is inevitable its risk is lower (relative risk = 0.6) than through vaginal delivery. CONCLUSIONS: despite the reduction along the 75 years of study, maternal mortality of 46 per 100,000 live births is still very high, and there was no significant decrease since 1972. Many deaths are avoidable. Hemorrhage is at present the most frequent cause of maternal death, the decision to intervene should be fast, and a proper indication for a cesarean section is a safe option. Maternal mortality caused by abortion is increasing alarmingly and family planning is essential.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):380-389
To analyze the consumption of minimally-processed and ultraprocessed foods in relation with sociodemographic variables, maternal habits, educational activity received during prenatal care and clinical history.
A cross-sectional, analytical and descriptive study with 1,035 pregnant women who lives in the municipalities of the metropolitan region of Grande Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil (RMGV-ES), and who were hospitalized in establishments of the Unified Health System (SUS) due to childbirth (April-September 2010). The food frequency questionnaire, pregnant woman’s card and information from the medical records of the health facility unit were analyzed. The Chi-square test and the binary logistic regression model were used to investigate the association between the independent variables and the consumption of ultraprocessed foods.
It was identified that pregnant women ≤ 19 years of agewere 2.9 timesmore likely to consume ultraprocessed foods (confidence interval [CI] 95% 1.683-5.168, p< 0.001), while those ≥ 35 years old were less likely to consume them (odds ratio [OR] 0.265, 95% CI 0.105-0.666, p= 0.005). Maternal smoking increased the odds of consumption of ultraprocessed foods by 2.2 times (95% CI 1.202-4.199, p= 0.011) and pregnant womenwho did not obtain information on healthy food during prenatal care presented 54.1% less chances of consuming minimally-processed foods (OR 0.459, 95% CI 0.307-0.687, p< 0.001).
Smoking during the gestational period and being a teenager are factors that influence the consumption of ultraprocessed foods of pregnant women. Race/ color, head of household, age group, receiving of information about feeding in the prenatal period and not having smoked in gestation determined the consumption of minimally-processed foods.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):380-384
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800002
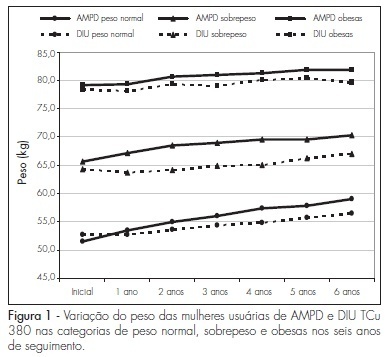
PURPOSE: to determine weight variation in women with different Body Mass Index (BMI) in use of trimestral injections of depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA), and compare it to women users of a non-hormonal method. METHODS: retrospective study with the chart review of 226 DMPA users and 603 controls, users of DIU TCu380A. Women were distributed in categories, according to their initial BMI, as having normal weight (<25 kg/m²), overweight (25 to 29,9 kg/m²) and being obese (>30 kg/m²), and were followed-up for six years, with yearly measurements of weight and BMI. The statistic test ANOVA was used to measure the weight variation among the groups in each BMI category every year. RESULTS: the average age at the onset of the method employed was higher in the study group than in the controls, in all the BMI categories: 31.6±SD 7.1 X 27.4±SD 5.5 in the normal weight category (p<0.0001); 37.3±SD 6.8 X 29.2±SD 6.0 in the overweight category (p<0.0001); and 35.3±SD 6.4 X 29.7±SD 5.8 among obese women (p<0.0001). DMPA users showed weight increase as compared to the controls in the overweight category (p=0.0082); and the weight increase along the observation period was also higher among the DMPA users than among the controls, for the normal weight (p<0.0001) and overweight (p=0.0008) categories. In the obese group, there was no BMI variation between the groups, nor along the period during which they were using the method. CONCLUSIONS: there was no change in weight gain among DMPA users from the obese category. Prospective studies should be done with metabolic tests to establish the determining factors of weight gain in normal and overweight women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(12):381-387
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001200002
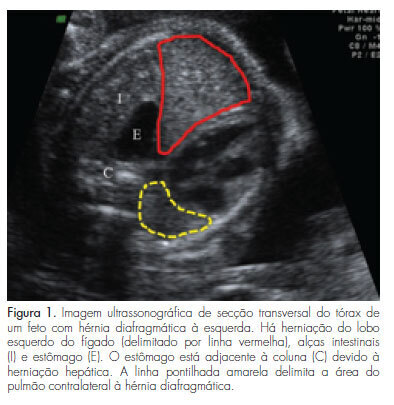
PURPOSE: To compare postnatal survival to hospital discharge of fetuses with severe isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia, who underwent tracheal occlusion, with that of nonrandomized contemporaneous controls. METHODS: Experimental nonrandomized controlled study, performed from April 2007 to September 2011. Fetuses with severe isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia with liver herniation into the chest and lung area-to-head circumference ratio <1.0, who underwent tracheal occlusion (study group) or expectant management (non-randomized contemporaneous controls), were compared in terms of lung area-to-head circumference ratio and observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio (observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio) at the time of diagnosis, gestational age at birth, and survival to hospital discharge. Modifications in lung area-to-head circumference ratio and o/e lung area-to-head circumference ratio after tracheal occlusion were also analyzed. Fisher's exact test, Mann-Whitney's or Wilcoxon's tests were used for the comparisons. RESULTS: There were no significant differences between the Study Group (TO=28) and Controls (n=13) in terms of the lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p=0.709) and the observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p=0.5) at the time of diagnosis and gestational age at birth (p=0.146). The survival to hospital discharge was higher (p=0.012) in the tracheal occlusion group (10/28=35.7%) than in controls (0/13=0.0%). There was a significant increase in lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p<0.001) and observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p<0.001) between the diagnosis of the congenital diaphragmatic hernia [lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 0.80 (0.40-0.94); observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 27.0 (15.3-45.0)], and the day before retrieval of the balloon [lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 1.2 (0.50-1.80); observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 40.0 (17.5-60.0)]. CONCLUSIONS: There was a significant improvement in the survival rate to hospital discharge of fetuses with severe isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia, who underwent tracheal occlusion in comparison to nonrandomized contemporaneous controls.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(8):381-385
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800004
PURPOSE: to examine the association between cytogenetic characteristics and clinical and epidemiological changes in patients with Turner syndrome (TS). METHODS: Forty-two patients were included. Data were collected using a standardized questionnaire in interviews conducted with the responsible person and, when possible, with the patient. A detailed physical examination was performed. The association between karyotype, stigmata and clinical disorders were examined using the χ2 test. RESULTS: Sixty-four percent of TS patients were 45,X; 26,2% 45,X/46,X;7% 45,X/46Xi(Xq), and 2,3% 45,X/46,X,Del(Xq). Regardless of the karyotype, all patients had short stature. Low hair implantation was more frequent in patients with 45,X (p=0.03). Cardiovascular abnormalities (45%), otitis (43%), thyroid dysfunction (33%) and hypertension (26.6%) were the most frequent clinical disorders, but without correlation with the karyotype. Anthropometric measurements revealed a positive linear correlation of waist and hip circumference with age (r=0.9, p=0.01). Thirty-one patients (74%) were using or had previously used growth hormone (43%), sex steroids (30%), thyroxine (11.9%) or oxandrolone (9.5%). Comparison between gestational age at birth and learning difficulties showed a prevalence ratio of 1.71 (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: Low hair implantation is the most prevalent stigma in patients with a 45,X karyotype and the most common clinical changes were cardiovascular problems, otitis, thyroid dysfunction and hypertension; however, they did not show any correlation with the karyotype.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):381-384
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700003
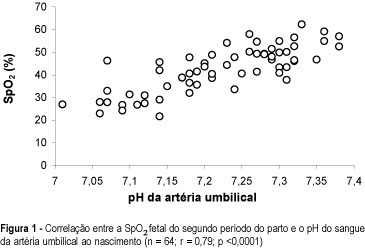
Purpose: to study the correlation between fetal oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry during second stage of labor and umbilical artery pH at birth. Patients and Methods: fetal oxygen saturation (FSpO2) was monitored by pulse oximetry during the second stage of labor in 64 singleton pregnancies at term, with vertex presentation. Umbilical blood was sampled immediately after delivery for subsequent measurement of venous and arterial blood gases and pH. All fetuses maintained FSpO2 > or = 30% through the first stage of labor, until the start of second stage. Results: the mean FSpO2 at the second stage of labor correlated significantly with umbilical artery pH at birth (n = 64, r = 0.79, p <0.001). There was no significant corre-lation between FSpO2 at the second stage of labor and umbilical artery oxygen saturation at birth. Conclusion: fetal oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry during second stage of labor has a good correlation with umbilical artery pH at birth.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):381-387
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700003
Objective: to evaluate the diagnosis, characteristics of pregnancy, maternal complications and perinatal outcome in cases of congenital hydrocephalus, and to associate them with pregnancy and delivery variables. Methods: 116 pregnancies with this diagnosis were evaluated before or after delivery, 112 of them occurring at the Maternity ward of CAISM/UNICAMP during the period between 1986 and 1995. For perinatal variables, complete data of 82 newborns were used. For data analysis, distributions and means were calculated and c² and Fisher exact tests were applied. Results: generally the diagnosis was made before delivery, confirmed by ultrasound and the delivery was through a cesarean section in cases. Cephalocentesis was performed in 11 cases and complications were more frequent in vaginal delivery than cesarean section. Low Apgar scores were more frequent among newborn babies delivered vaginally. Congenital hydrocephalus was also associated with important neonatal and perinatal morbidity and mortality, with other malformations, and a very low number of children without sequelae. Conclusions: the evaluation of these factors may be of great value for the obstetrician who is following pregnant women with this fetal malformation. This could better support the decisions that, although medical and ethical, should take into account the risk-benefit ratio of measures to be taken.