You searched for:"Roberto Eduardo Bittar"
We found (20) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(10):433-435
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):455-459
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005271
To analyze the obstetrical and neonatal outcomes of pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses after 35 weeks based on umbilical cord nucleated red blood cells count (NRBC).
NRBC per 100 white blood cells were analyzed in 61 pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses and normal Doppler findings for the umbilical artery. The pregnancies were assigned to 2 groups: NRBC≥10 (study group, n=18) and NRBC<10 (control group, n=43). Obstetrical and neonatal outcomes were compared between these groups. The χ2 test or Student's t-test was applied for statistical analysis. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The mean±standard deviation for NRBC per 100 white blood cells was 25.0±13.5 for the study group and 3.9±2.2 for the control group. The NRBC≥10 group and NRBC<10 group were not significantly different in relation to maternal age (24.0 versus 26.0), primiparity (55.8 versus 50%), comorbidities (39.5 versus55.6%) and gestational age at birth (37.4 versus 37.0 weeks). The NRBC≥10 group showed higher rate of caesarean delivery (83.3 versus 48.8%, p=0.02), fetal distress (60 versus 0%, p<0.001) and pH<7.20 (42.9 versus 11.8%, p<0.001). The birth weight and percentile of birth weight for gestational age were significantly lower on NRBC≥10 group (2,013 versus 2,309 g; p<0.001 and 3.8 versus 5.1; p=0.004; respectively). There was no case described of 5th minute Apgar score below 7.
An NRBC higher than 10 per 100 white blood cells in umbilical cord was able to identify higher risk for caesarean delivery, fetal distress and acidosis on birth in small for gestational age fetuses with normal Doppler findings.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(7):463-468
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000700006
Purpose: to evaluate, in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, the correlation between cervical length and spontaneous preterm delivery. Methods: cervical length was evaluated in 641 pregnant women between 11-16 weeks' and 23-24 weeks' gestation. Cervical assessment was performed by a transvaginal scan with the patient with empty bladder in a gynecological position. Cervical length was measured from the internal to the external os. The gestational age at delivery was correlated with the length of the cervix. To compare the means in groups of pregnant women who had a term or preterm delivery, we used Student's t test. Sensitivity, specificity, false-positive and false-negative rates, and accuracy were calculated for cervical length of 20 mm or less, 25 mm or less and 30 mm or less in the prediction of preterm delivery. Results: the measurement of cervical length, between 11 and 16 weeks of pregnancy, did not show any statistically significant difference on comparing women who had preterm and term delivery (40.6 mm and 42.7 mm, respectively, p=0.2459). However, the difference between the two groups at 23 to 24 weeks was significant (37.3 mm in the group who delivered prematurely and 26.7 mm in the term group, p=0.0001, Student's t test). Conclusion: there was no significant difference in cervical length, at 11 to 16 weeks, between pregnant women who had a preterm and term delivery. However, at 23 to 24 weeks, cervical length was significantly different between the two groups, and this measurement might be used as a predictor for prematurity.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):509-515
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900003
Purpose: to evaluate the relationship between uterine contractions and premature delivery. Methods: between February 1996 and July 1998, 73 high risk pregnant women for preterm delivery, between the 24th and 34th weeks of gestation, were submitted to uterine contraction monitoring with tokodynamometers for 1 hour twice a week. The positive test was the presence of 4 contractions/h before the 30th week of gestation, and after this time, 6 contractions/h. Result: of 73 women, 17 patients (23.28%) were excluded from the final analysis because they presented obstetric problems or unfavorable development for the final result. The rate of preterm delivery was 21.23% (13/56). The mean frequency of uterine contractions was greater in women with preterm delivery than in those with term delivery. The test presented sensitivity of 69.23%, specificity of 86.04%, positive predictive value of 60% and negative predictive value of 90.24%. Conclusion: negative tests are associated with a low risk of preterm birth. When the test is positive, association with other premature delivery markers is necessary to improve our ability to efficiently identify patients at risk for preterm delivery.
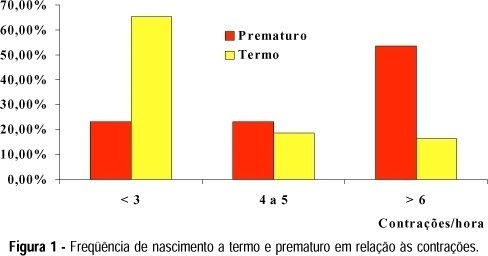
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):509-510
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):517-524
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900005
Purpose: to determine the behavior of doppler velocimetry during the course of risk pregnancies and to compare the perinatal results obtained for concepti with retarded intrauterine growth (RIUG) with those for concepti considered adequate for gestational age (AGA). Methods: a prospective study of the evolution of doppler ultrasound was made in 38 pregnant women with of idiopathic intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) in previous pregnancy. A relationship was established between this antecedent and the new pregnancy. The pregnant women studied were divided into two groups in agreement with their neonates birthweight. Group 1 was associated with IUGR and group 2 with adequate birth weight. IUGR was confirmed in 23.7% of the cases. Umbilical and uterine artery doppler velocimetry was performed from 20 to 40 weeks of gestation. Middle cerebral artery doppler velocimetry was analyzed after 28 weeks of gestation, twice a month, being the last valued examination before birth. Results: the uterine and umbilical artery ratio at 24 and 28 weeks of gestation, respectively, correlated with the presence of IUGR. There was no difference between the two groups regarding the presence or absence of a small notch in the uterine artery wave form and middle cerebral artery doppler velocimetry ratio, at the last examination before birth. There was a relationship between neonatal stay in hospital for more than three days and the presence of IUGR. Conclusions: doppler ultrasound should be used in the follow-up of cases with a high risk of IUGR. It allows the detection of the fetuses at high risk of hypoxia and, by interrupting the pregnancy, fetal distress-related complications may be avoided.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(8):529-533
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000800008
Purpose: to evaluate the relationship between bacterial vaginosis (BV) and spontaneous preterm delivery. Method: a total of 611 pregnant women from the general antenatal clinic of the "Clínica Obstétrica do Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade de São Paulo" were enrolled in this study. All pregnancies were dated by an early scan. Iatrogenic preterm deliveries were excluded. The presence of bacterial vaginosis was evaluated between 23 and 24 weeks of pregnancy by a Gram stain of the vaginal smear collected from the posterior vaginal wall using a sterile swab. Vaginal pH was also assessed from the lateral vaginal wall by a Universal 0-14 pH strip produced by Merck. Result: a complete follow-up was obtained in 551 patients and bacterial vaginosis was diagnosed in 103 (19%) cases. Among the patients with BV in the vaginal smear, 9.7% delivered before 37 weeks against only 3.2% in the group with normal vaginal smear (p=0.008). The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and false-positive rate for preterm delivery in the presence of bacterial vaginosis on Gram stain of the vaginal smear were 41.7, 82, 80.2 and 18%, respectively, with a relative risk of 1.8 for preterm delivery. The mean vaginal pH in the group of positive BV was 4.9 and in the group with normal smear it was 4.3 (p=0.0001). Conclusion: bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy increases the risk for spontaneous preterm delivery, with a relative risk of 1.8.
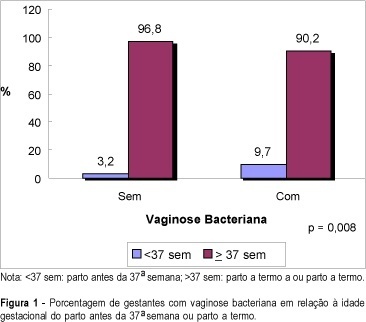
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):561-566
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900010
Preterm delivery is the most common cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. About 75% of preterm births follow preterm labor. The pathogenesis of spontaneous preterm birth is complex and its clinical management is based on a careful assessment of the risks for mother and infant and on continuing the pregnancy versus delivery. The goal of the present article is to review the diagnosis of preterm labor, the tocolytic treatment, glucocorticoid therapy, antimicrobial treatment, and management of progressive preterm labor.