You searched for:"Paulo César Giraldo"
We found (10) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2013;35(10):453-457
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001000005
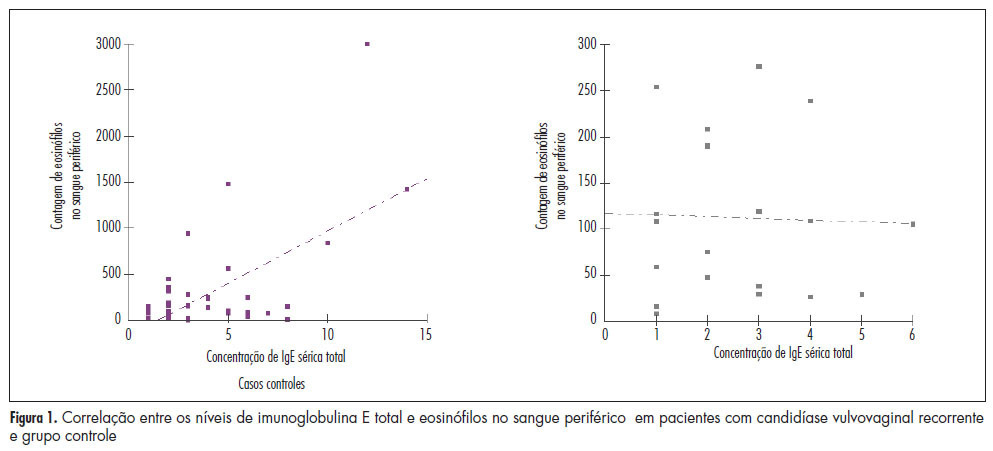
PURPOSE: To quantify the number of defense cells and immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels in peripheral blood sampled from women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. METHODS: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 60 women, 40 with vulvovaginal candidiasis and 20 controls. The defense cells were identified using an impedance system combined with flow cytometry and total and specific IgE was measured by chemiluminescence. The Mann-Whitney test was used for nominal variables and the Spearman test was used to determine the correlation of IgE concentration and eosinophils in peripheral blood. RESULTS: The number of eosinophils in peripheral blood from patients with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, 302.60 (±253.07), was significantly higher compared to control, 175.75 (±109.24) (p=0.037). Serum levels of total and specific IgE were similar in the groups of women with and without recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (p=0.361). However, there was a moderate positive correlation between eosinophils and total serum IgE in the candidiasis group (r=0.25). CONCLUSION: Women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis are more likely to have eosinophils in peripheral blood.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(10):634-641
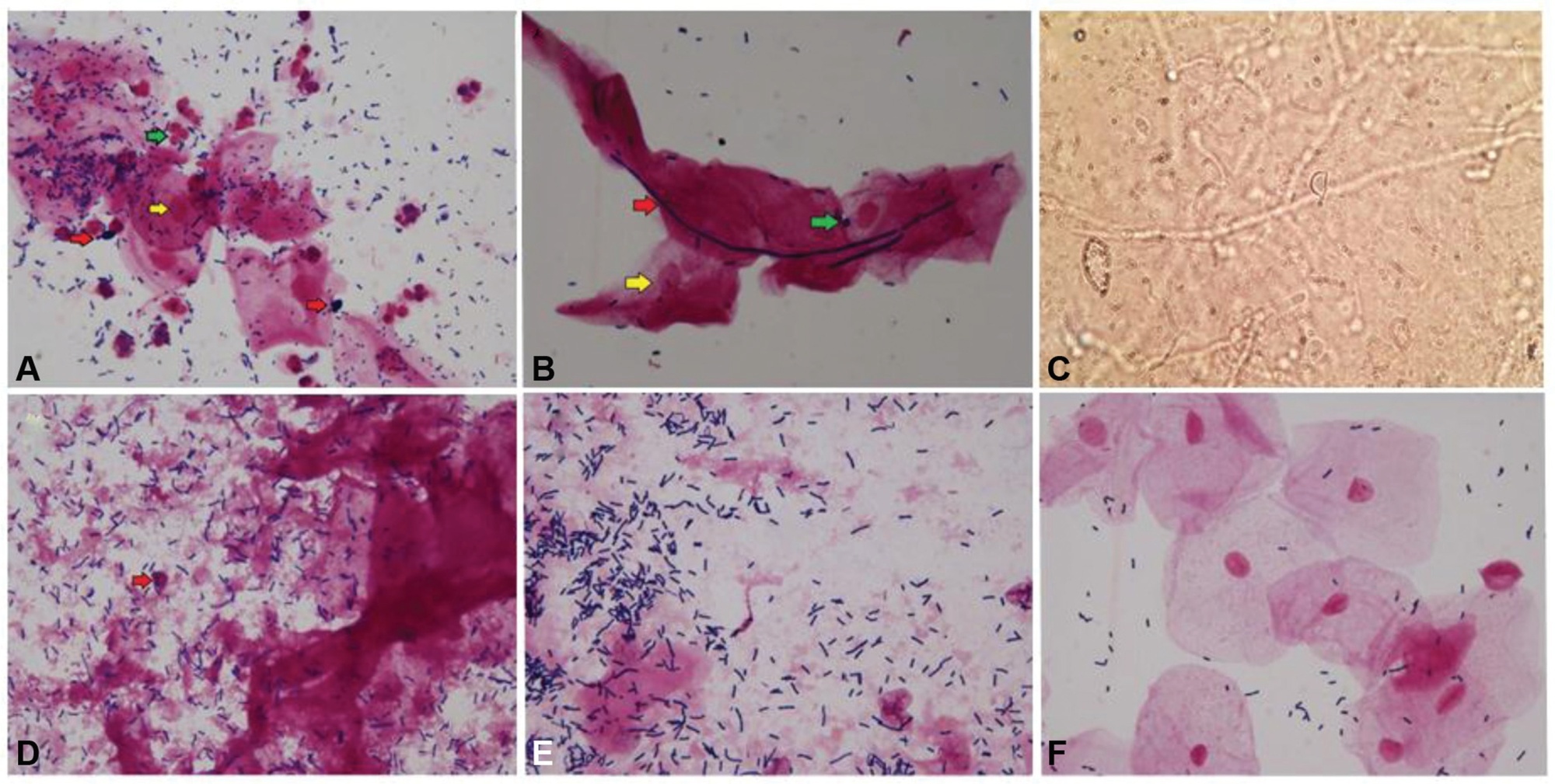
To identify clinical, microscopic, and biochemical characteristics that differentiate cytolytic vaginosis (CV) from vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).
The present cross-sectional study analyzed the vaginal contents of 24 non-pregnant women aged 18 to 42 years who were attended at the Genital Infections Clinic at Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher da Universidade Estadual de Campinas (CAISM-UNICAMP). They were diagnosed either with (CV = 8, VVC = 8) or without vulvovaginitis or vaginal dysbiosis (controls). The socio-demographic, clinical, and gynecological data were obtained from a detailed patient interview. Samples of the vaginal contents were collected for analysis of vaginal pH, gram stain, and specific fungal culture. The Kruskal-Wallis and Fisher exact tests were used to compare the differences between the groups. Odds ratios were used to compare the categorical variables. The significance level was considered at p < 0.05.
Both women with CV and VVC had a lumpy vaginal discharge (p = 0,002) and vaginal hyperemia (p = 0.001), compared with controls. The inflammatory process was more intense in the VVC group (p = 0.001). In the CV group, there was statistical significance for the lactobacillus amount (p = 0.006), vaginal epithelium lysis (p = 0.001), and vaginal pH (p = 0.0002).
Cytolytic vaginosis and VVC diagnoses rarely differ on clinical characteristics but have different laboratorial findings. The present study highlights the importance of conducting an accurate investigation through laboratory tests rather than clinical criteria to avoid misdiagnosis.