You searched for:"Paula Andrea de Albuquerque Salles Navarro"
We found (14) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):413-420
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900006
PURPOSE: To characterize and compare clinical, anthropometric and biochemical-metabolic variables in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), stratified according to body mass index (BMI). METHODS: A cross-sectional study conducted on 78 women aged 18 to 45 years with a clinical diagnosis of PCOS by the Rotterdam criteria. Patients were stratified according to BMI. The variables analyzed were: age, marital status, physical inactivity, menstrual irregularity, blood pressure (BP), anthropometric measurements, lipid profile, fasting glucose, and hormone measurements. To compare the variables between the different BMI values we used analysis of variance and the Kruskal-Wallis test. The level of significance was set at 5% for all tests. RESULTS: The patients had a mean age of 26.3 years, 79.5% of them were sedentary and 68% had hyperandrogenism. Waist circumference, waist/hip ratio, waist/height ratio and percentage of body fat were higher in the obese group. The markers of cardiovascular risk (CVR - fasting glucose, systolic and diastolic BP and LDL-cholesterol) were directly proportional to BMI, whereas HDL-cholesterol and SHBG were inversely related to BMI. CONCLUSION: The presence of markers of CVR factors increased proportionally to BMI, indicating that the metabolic profile of obese women with PCOS is more unfavorable than that of non-obese patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):413-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800007
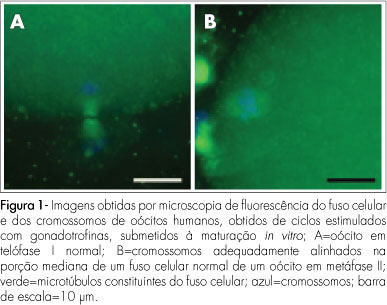
PURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro mature oocytes from stimulated cycles of infertile women with endometriosis, and with male and/or tubal infertility factors (Control Group), comparing the rates of in vitro maturation (IVM) between the two groups evaluated. METHODS: fourteen patients with endometriosis and eight with male and/or tubal infertility factors, submitted to ovarian stimulation for intracytoplasmatic sperm injection have been prospectively and consecutively selected, and formed a Study and Control Group, respectively. Immature oocytes (46 and 22, respectively, from the Endometriosis and Control Groups) were submitted to IVM. Oocytes presenting extrusion of the first polar corpuscle were fixed and stained for microtubules and chromatin evaluation through immunofluorescence technique. Statistical analysis has been done by the Fisher's exact test, with statistical significance at p<0.05. RESULTS: there was no significant difference in the IVM rates between the two groups evaluated (45.6 and 54.5% for the Endometriosis and Control Groups, respectively). The chromosome and meiotic spindle organization was observed in 18 and 11 oocytes from the Endometriosis and Control Groups, respectively. In the Endometriosis Group, eight oocytes (44.4%) presented themselves as normal metaphase II (MII), three (16.7%) as abnormal MII, five (27.8%) were in telophase stage I and two (11.1%) underwent parthenogenetic activation. In the Control Group, five oocytes (45.4%) presented themselves as normal MII, three (27.3%) as abnormal MII, one (9.1%) was in telophase stage I and two (18.2%) underwent parthenogenetic activation. There was no significant difference in meiotic anomaly rate between the oocytes in MII from both groups. CONCLUSIONS: the present study data did not show significant differences in the IVM or in the meiotic anomalies rate between the IVM oocytes from stimulated cycles of patients with endometriosis, as compared with controls. Nevertheless, they have suggested a delay in the outcome of oocyte meiosis I from patients with endometriosis, shown by the higher proportion of oocytes in telophase I observed in this group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(8):541-541
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000800010
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):575-581
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200008
PURPOSE: To compare serum anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) levels on the seventh day of ovarian stimulation between normal and poor responders. METHODS: Nineteen women aged ≥35, presenting with regular menses, submitted to ovarian stimulation for assisted reproduction were included. Women with endometriosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome or those who were previously submitted to ovarian surgery were excluded. On the basal and seventh day of ovarian stimulation, a peripheral blood sample was drawn for the determination of AMH, FSH and estradiol levels. AMH levels were assessed by ELISA and FSH, and estradiol by immunochemiluminescence. At the end of the stimulation cycle patients were classified as normal responders (if four or more oocytes were obtained during oocyte retrieval) or poor responders (if less than four oocytes were obtained during oocyte retrieval or if the cycle was cancelled due to failure of ovulation induction) and comparatively analyzed by the t-test for hormonal levels, length of ovarian stimulation, number of follicles retrieved, and number of produced and transferred embryos. The association between AMH and these parameters was also analyzed by the Spearman correlation test. RESULTS: There was no significant difference between groups for basal or the seventh day as to AMH, FSH and estradiol levels. There was a significant correlation between seventh day AMH levels and the total amount of exogenous FSH used (p=0.02). CONCLUSIONS: AMH levels on the seventh day of the ovarian stimulation cycle do not seem to predict the pattern of ovarian response and their determination is not recommended for this purpose.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):612-623
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000008
Despite a wide heterogeneity of clinical manifestations related to endometriosis, a high prevalence of the disease is observed in infertile women and in those with chronic pelvic pain. This enigmatic condition has a high socioeconomic impact, and the described data regarding efficacy of the therapeutic approaches are quite conflicting. Thus, the purpose of the present study was to describe the available scientific evidence about the applicable therapeutic modalities and to provide recommendations for the treatment of infertility and the chronic pelvic pain related to endometriosis. Although suppression of ovarian function in patients with minimal or mild endometriosis is not effective in improving fertility, ablation of the lesions associated with adhesiolysis seems to be more effective than exclusive diagnostic laparoscopy. There is no sufficient evidence to determine whether surgical excision in cases of moderate or severe disease would improve the pregnancy rates. In vitro fertilization seems to be an adequate approach, especially in cases of coexistence of infertility factors and/or failure of other treatments. The possibility of using GnRH for 3 to 6 months before in vitro fertilization should be considered. Regarding pain relief, suppression of ovarian function for 3 to 6 months in patients with laparoscopically-confirmed disease reduces the pain associated with endometriosis. All studied medication seem to have similar efficacy, differing only in terms of adverse effects and costs. Ablation of endometriotic lesion reduces the pain associated with endometriosis, being less effective in cases of minimal disease. Exeresis of endometriomas with diameter > 4 cm seems to improve the rate of natural fecundity and the rate for ??? obtained after assisted reproduction procedures, in addition to reducing both pain and recurrence risk. Finally, it is important to emphasize that this subject is much controversial and the recommendations herein described should be revised as randomized controlled clinical trials with adequate casuistic generate more concrete and reliable evidence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):715-720
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001200005
PURPOSE: to investigate the effects of previous bilateral tubal sterilization on the outcome of in vitro fertilization. METHODS: retrospective study of 98 consecutive in vitro fertilization cycles. Fifty-five women with previous tubal sterilization without any other infertility factor (TL group) were compared with 43 women with infertility due only to mild male factor (MI group. Age, cancellation rate per induction cycle, response to ovulation induction (number of days of ovulation induction, total amount of gonadotrophin units used, number of follicles and oocytes retrieved), fertilization and cleavage rates, number of transferred embryos and clinical pregnancy per transfer cycle were the variables considered. RESULTS: the cycle discontinuation rate due to poor response, results of ovulation induction, fertilization and cleavage rates, number of transferred embryos and the occurrence of clinical pregnancy were similar in both groups. Considering solely the variable age in TL group, we observed that patients older than 35 years required higher gonadotrophin doses during ovulation induction (2445 versus 2122 IU), presented lower response with fewer follicular growth (11.3 versus 15.8) and less oocytes retrieved (6.1 versus 8.5) compared to younger women (34 years old or less). CONCLUSIONS: tubal sterilization did not interfere with in vitro fertilization outcomes. We observed a worse response to ovulation induction in women older than 35 years, who had previous tubal sterilization.