You searched for:"Mauro Abi Haidar"
We found (10) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):667-672
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900008
PURPOSE: to compare the results of hysterosonography with those of hysteroscopy and the histopathologic study in postmenopausal women. METHODS: hysterosonography, hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy were performed in 59 women who had an endometrial echo over 4 mm, age above 40 years and amenorrhea over one year, and whose follicle-stimulating hormone levels were over 35 mIU/mL. Patients using hormones were excluded, as well those in whom it was impossible to perform histerosonography, histeroscopy or endometrial biopsy. The statistical analysis was performed using the nonparametric "G"-Cochran and McNemar tests. In addition, sensitivity and specificity, as well as positive and negative predictive values were determined. The value of 0.05 or 5% for rejection level of the null hypothesis was applied. RESULTS: the agreement rates of hysterosonographic results compared to hysteroscopy and histopatology were 94.8 ande 77.6%, respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of hysterosonographic evaluation of the abnormal endometrial cavity were 98 and 75%, respectively, when compared to hysteroscopy. In addittion, positive and negative predictive values of hysterosonography were 96 and 86%, respectively. When the histopathologic study was used as the gold standard, sensitivity and specificity were 98 and 33%, with positive predictive value of 76% and negative predictive value of 86%, for the detection of the endometrial cavitary changes. One great concern were the histopathologic results of two patients with uterine synechia who showed endometrial hyperplasia. Also, one patient was diagnosed as normal using histerosonography and the histopatological result showed simple hyperplasia. CONCLUSIONS: our data suggest that hysterosonography presented good sensitivity as compared with hysteroscopy. However, uterine synechia is the great limitation of this method as compared with histopathology.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(12):731-736
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200005
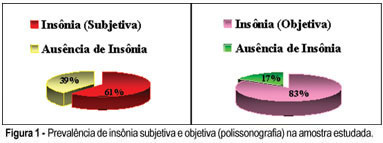
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of reported sleep disturbances through polysomnographic recording (PSG) in a sample of postmenopausal women. METHODS: thirty-three postmenopausal women with a mean age of 56 years, a mean body mass index (BMI) of 27 kg/m², with 7.7 years of recognized postmenopausal period, and a mean Kupperman index of 17, were selected. The inclusion criteria were: age range from 50 to 65 years, at least one year of amenorrhea and an FSH which equaled or exceeded 30 mU/ml; they should not be undergoing hormone therapy, and should display normal laboratory test results. The patients with severe clinical diseases and/or decompensated were excluded; also the ones with suspicion of carcinoma of endometrium and/or breast cancer, a BMI over 30 kg/m² and those who ingested hypnotic drugs. The patients followed a routine climacteric check-up, answered a questionnaire about sleep and underwent an all-night PSG recording. Frequencies in percentage of emerging sleep complaints based on the questionnaire and those pertaining to PSG diagnosis were then calculated separately. RESULTS: the subjective prevalence of insomnia was 61% against 83% in the PSG recordings. The prevalence of apnea reported was 23% against 27% in the PSG. The subjective restless legs syndrome prevalence was 45%, and the objective, 27%. CONCLUSION: there was a high prevalence of sleep disturbances in postmenopausal patients, specially insomnia, apnea and restless legs.