You searched for:"Maria Regina Torloni"
We found (13) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):501-502
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):524-534
To assess the knowledge, attitude, and practice of Brazilian physicians about immediate postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion.
Cross-sectional online survey involving physicians on duty in public Brazilian hospitals. Participants answered an anonymous questionnaire with close-ended questions to assess their knowledge, attitude, and experience on the immediate postpartum and postabortion insertion of copper intrauterine devices.
One hundred twenty-seven physicians working in 23 hospitals in the 5 geographic regions of Brazil completed the questionnaire. Most were female (68.5%) and worked in teaching hospitals (95.3%). The mean (standard deviation) knowledge score (0–10 scale) was 5.3 (1.3); only 27.6% of the participants had overall scores ≥7.0. Most physicians (73.2%) would insert a postpartum intrauterine device in themselves/family members. About 42% of respondents stated that they had not received any training on postpartum or postabortion intrauterine device insertion. In the past 12 months, 19.7%, 22.8%, and 53.5% of respondents stated they had not inserted any intrauterine device during a cesarean section, immediately after a vaginal delivery, or after an abortion, respectively.
Most study participants have a positive attitude toward the insertion of intrauterine devices in the immediate postpartum period, but they have limited knowledge about the use of this contraceptive method. A large percentage of respondents did not have previous training on postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion and had not performed any such insertions in the last 12 months. Strategies are needed to improve the knowledge, training, and experience of Brazilian physicians on immediate postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):554-560
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900009
PURPOSE: to evaluate the performance of cytogenetic analysis, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the study of numerical chromosomal anomalies and in fetal sex determination of spontaneous abortion material. METHODS: cytogenetic analysis was performed on 219 spontaneous abortion specimens. Forty of these cases were also submitted to fetal sex determination using nested-PCR. Thirty-two of these cases were selected due to failed cytogenetic culture and the other eight were selected randomly. Twenty samples were submitted to the FISH technique, using probes for chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y. Thirteen of these samples were selected due to failed cytogenetic culture and the other seven were randomly selected. The success rates of each technique were compared using the chi2 test and an established p<0.05 level of significance. The results of samples submitted to more than one test were evaluated for accuracy, using the cytogenetic result as the gold standard. RESULTS: cytogenetic analysis was successful in 84.9% of the samples and in 51.1% of them the results were abnormal: 65.2% trisomy, 17.9% triploidy, 9.4% tetraploidy, 4.2% chromosome X monosomy, and 1.1% each for double trisomy, tetrasomy and structural abnormality. The most frequent trisomy was that of chromosome 16 (39%). The success rate of FISH and PCR techniques (90%) did nod differ significantly from the cytogenetic analysis. In all cases submitted to more than one test, the results were identical to those obtained through cytogenetic analysis. Samples that failed to grow on cytogenetic test and that were submitted to other techniques of molecular biology had a success rate of 87.5 and 84.6% for PCR and FISH, respectively. CONCLUSION: cytogenetic analysis of spontaneous abortions had a high success rate and chromosomal anomalies were identified in over half of the cases. Molecular biology techniques (PCR and FISH) complemented the cytogenetic study and proved to be reliable in the detection of numerical chromosomal anomalies and in fetal sex determination.
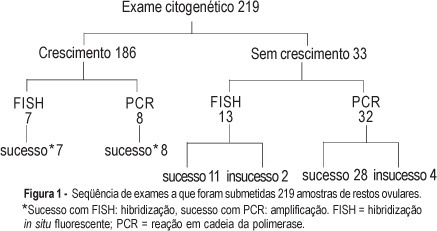
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):641-647
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800008
OBJECTIVE: to investigate whether it is possible to predict acidemia at birth in pregnancies with placental insufficiency using venous-arterial indices: pulsatility index for vein (PIV) of the ductus venosus (DV) over PI of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) and PIV of the DV over PI of the umbilical artery, and establish cut-off values for this prediction. PATIENTS AND METHODS: this was a prospective cross-sectional study involving forty-seven patients with placental insufficiency (umbilical artery resistance and pulsatility indices above the 95th percentile for gestational age) who were submitted to Dopplervelocimetry in the last 24 hours before delivery. All pregnancies were singleton, over 26 weeks of age and without structural or chromosome anomalies. Arterial cord blood was obtained for gasometry immediately after birth. Acidemia was defined as umbilical arterial pH < 7.20 in the absence of uterine contractions and pH < 7.15 in the presence of contractions. Metabolic or mixed acidemia at birth were considered pathological. A ROC curve was calculated for the venous-arterial indices: PIV DV/PI umbilical artery (UA) and PIV DV/PI MCA. A cut-off value was established and sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values and positive and negative likelihood ratios were calculated. RESULTS: The DV/UA PI index was not a good predictor of acidemia at birth. The DV/MCA PI index was related to acidemia at birth (area under the curve 0,785, p = 0,004). The cut-off value was: 0,582, sensitivity 66,7%, specificity 77,1 and accuracy 74,5%. CONCLUSION: the PIV DV/PI MCA ratio is adequate for predicting acidemia at birth in pregnancies with placental insufficiency. The cut-off value was: 0,582.
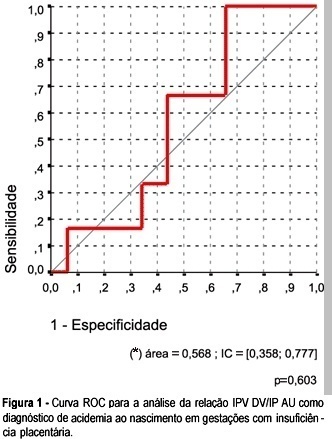
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):670-675
To describe the experience of a distance education course on sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth for residents.
This prospective educational intervention study was conducted by investigators from the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil, between April and September 2014. The participants were 219 physicians (residents from the 1st to the 6th years). The duration of the course was of 24 hours (10 video lectures and online chats). At baseline, the participants answered questions about their training, attitude and experience regarding sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth; before and after the course, they answered questions to assess their knowledge about the topic; at the end of the course, they answered questions on the quality of the course. The Student t-test was used to compare the before and after scores of the knowledge tests; values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A total of 143 residents concluded the course; most were in their 1st (27.2%) or 3rd (29.4%) years of residency. There was a significant increase in themean scores of the questionnaires that assessed the knowledge of the topic: 4.4 (1.6) versus 6.0 (1.3; maximum score: 10), before and after the course respectively (p < 0.0001). Most of the participants (74.1%) declared that the quality of the course as a whole reached their expectations, and 81.1% would recommend the course to a friend.
The online Sexology course for Obstetrics and Gynecology residents increased their knowledge about the sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth, and fulfilled the participants’ expectations. The experience described heremay serve as a model for other sexuality courses targeting similar audiences.