You searched for:"Manuel de Jesus Simões"
We found (18) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):281-284
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500006
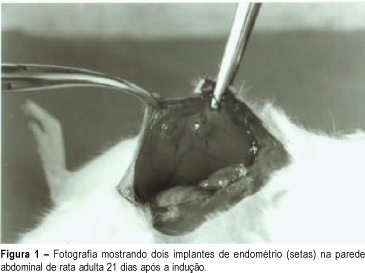
Purpose: to demonstrate the experimental endometriosis induction in animals. Method: we used adult female Wistar rats weighing 200 - 250 g anesthetized with ethyl ether to open the abdominal cavity. After identifying the uterine horns, we removed an approximately 4 cm fragment from the right uterine horn. This fragment was placed in physiological saline and, with the aid of a stereoscopic magnifying glass, the endometrium was separated from the myometrium and cut into rectangles of approximately 4 x 5 mm. These rectangles were fastened to the lateral abdominal wall near great blood vessels, taking care that the free portion of the endometrium was directed towards the lumen of the abdominal cavity. After 21 days the animals were again operated to observe the size of the implants and to remove the ectopic endometrium for microscopic analysis. Results: we macroscopically observed a significant growth of the endometrial implants. Microscopic examination showed presence of glandular epithelium and stroma similar to topic epithelium. Conclusion: this model reproduces endometriosis in the female rat allowing a better study of this pathology, mainly the action of drugs on these implants.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):328-334
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700002
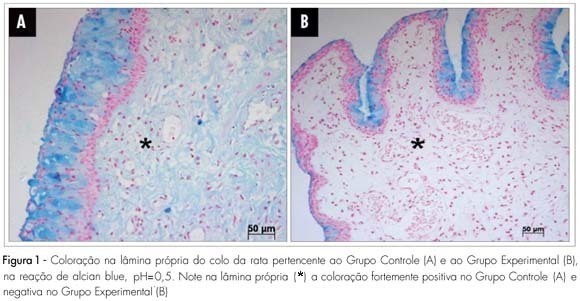
PURPOSE: to study the histochemical changes related to the uterine cervix glycosaminoglycan of the albino female rat, after local ministration of hyaluronidases at the end of pregnancy. METHODS: ten female rats with positive pregnancy tests were randomly distributed in two numerically equal groups. The control group (Cg) was built up with rats that received a single dose of 1 mL of distilled water in the uterine cervix, under anesthesia, at the 18th pregnancy day. In the experimental group (Exg), the rats received 0.02 mL of hyaluronidase, diluted in 0.98 mL of distilled water (1 mL as a total), under the same conditions as the Cg. At the 20th pregnancy day, the rats were anesthetized once again and submitted to dissection, and the cervix prepared for histochemical study with alcian blue dye and its blockades (pH=0.5, pH=2.5, methylation and saponification). RESULTS: strongly positive reaction in the lamina propria (+3) has been seen in the Cg, and negative reaction in the Exg, with pH=0.5 alcian blue staining. With pH=2.5, staining has also been strongly positive (+4) in the Cg, and weakly positive (+1) in the Exg slide. After methylation, both groups have shown negative reaction, with pH=2.5 alcian blue staining. The lamina propria staining became negative after methylation in both groups, followed by saponification and enzymatic digestion on slide. CONCLUSIONS: there is clear predominance of sulphated glycosaminoglycans in the Cg as compared to the Exg and a small amount of identified carboxylated glycosaminoglycans in the Exg. The changes evidenced in the extracellular matrix have suggested that the hyaluronidase injected in the uterine cervix has promoted biochemical changes compatible with cervix maturation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(1):33-36
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000100006
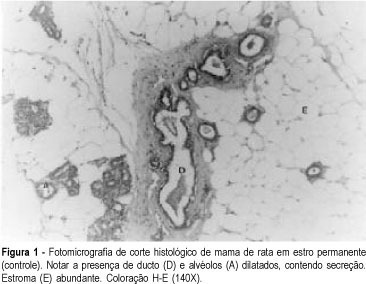
Purpose: to evaluate the morphologic and morphometric alterations produced by tamoxifen and conjugated estrogens in the mammary epithelium of rats in persistent estrus. Methods: thirty-three adult female rats in persistent estrus induced with 1.25 mg testosterone propionate were divided at random into three groups: GI -- which received only water, control group (n = 12); GII -- treated with 500 mug tamoxifen daily (n = 10); GIII -- treated with 30 mug conjugated estrogens per day (n = 11). The first inguinal-abdominal pair of mammary glands of the animals was extirpated and processed for morphologic and morphometric study. Data were analyzed statistically by the Kruskal-Wallis rank analysis of variance (p < 0.05). Results: the morphologic study revealed signs of epithelial atrophy and the morphometric study showed a statistically significant reduction in the mean number of ducts and alveoli in groups II (10.1 and 1.9, respectively) and III (11.1 and 3.5, respectively) compared to group I (25.0 and 6.6, respectively). There was no significant difference between groups II and III. Conclusions: the results of this study indicate that tamoxifen as well as conjugated estrogens at the tested doses produced mammary epithelial atrophy in rats in persistent estrus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):489-493
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800004
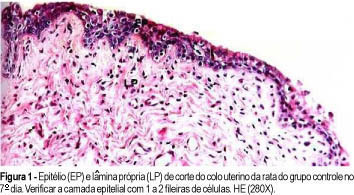
Purpose: to study the effect of copaíba oil on the uterine cervix of oophorectomized rats. Method: 120 female adults were used, divided into four groups: control, water, corn oil and copaíba oil. All animals were submitted to bilateral oophorectomy, and kept in cages for twenty days before applying the substances. These substances were applied by vaginal route at a dose of 0.3 ml, once a day until the predetermined day of sacrifice (7, 14 e 21 days). Results: the animals from the copaíba oil group showed on all days of the study exuberant, keratinous stratified squamous epithelium with about 10 epithelial cell layers and the chorion with conjunctive tissue, fibroblasts, collagen fibers, blood vessels and some leukocytes. Conclusions: The copaíba oil used in this experimental model promoted a thickening of the epithelium, which was keratinous stratified squamous, and epithelium increase was progressive along the study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):524-528
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900004
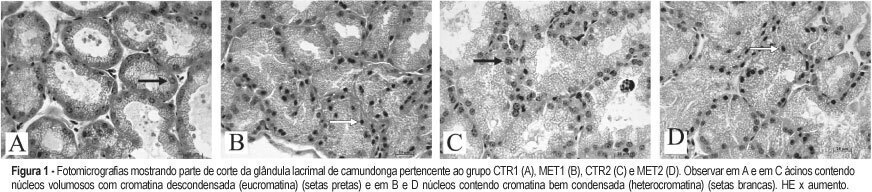
PURPOSE: to evaluate the morphological changes in murine lacrimal glands by metoclopramide-induced hyperprolactinemia during the proestrus phase or pregnancy. METHODS: forty adult mice were divided into two groups: CTR1 (control) and MET1 (treated with metoclopramide). After fifty days, half of the mice were sacrificed. The remaining animals were mated, and then labeled as pregnant controls (CTR2). Part of these animals were treated with metoclopramide and constituted the metoclopramide-treated pregnant (MET2) group. The CTR2 and MET2 groups were sacrificed on the 6th day of pregnancy. The blood was collected for determination of the hormonal levels of estradiol and progesterone by a chemoluminescent method. The lacrimal glands were then removed, fixed in 10% formaldehyde and stained with HE. The morphometric analysis was performed using the Axion Vision program (Carl Zeiss) to measure acinar nuclear and cellular volumes. RESULTS: the nuclear and cellular volumes of the lacrimal glands in the MET1-(152.2±8.7; 6.3±1.6 µm³) and MET2-(278.3±7.9; 27.5±0.9 µm³) treated groups were lower than those in CTR1 (204.2±7.4; 21.9±1.3 µm³) and CTR2 (329.4±2.2; 35.5±2.0 µm³), respectively. There was a significant hormonal level reduction in the animals that received metoclopramide compared to controls (CTR1: estradiol = 156.6±42.2 pg/ml; progesterone = 39.4±5.1 ng/ml; MET1: estradiol = 108.0±33.1 pg/ml; progesterone = 28.0±6.4 ng/ml; CTR2: estradiol = 354.0±56.0 pg/ml; progesterone = 251.0±56.0 ng/ml; MET2: estradiol = 293.0±43.0 pg/ml, progesterone = 184.0±33.0 ng/ml). CONCLUSION: metoclopramide-induced hyperprolactinemia produced morphological signs of reduction of cellular activity in lacrimal glands during the proestrus phase and pregnancy. It is hypothesized that this effect might be related to the hyperprolactinemia-induced decrease in the hormonal production of estrogen and progesterone.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):595-602
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800002
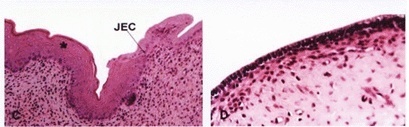
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of estradiol benzoate associated with dexamethasone on the squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) of rats in permanent estrus (PE) and then ovariectomized (Ovx). METHODS: thirty female rats were divided into six groups of five animals each: PhEG rats in physiological estrus (PhE) treated with propylene glycol (vehicle); OVXG rats in PhE, Ovx and treated with vehicle; PEG - rats in PE treated with vehicle; PEOVXG rats in PE, Ovx and treated with vehicle; ESTRG rats in PE, Ovx and treated with 10 mg per day benzoate of estradiol, and DEXAG in PE, Ovx and treated with 10 mg per day estradiol benzoate associated with 0.8 mg dexamethasone. PE induction was performed with 1.25 mg testosterone propionate per animal per day after birth. After 90 days, rats in the OVXG, EPOVXG, ESTRG, and DEXAG groups were ovariectomized. After 21 days of castration, all animals received the corresponding treatment for five days. At the end of the experiment, all animals were sacrificed and the uteri removed for histological routine. RESULTS: the borders of the SCJ in the PEG were irregular and not clearly delineated, with many buds towards the direction of the lamina propria as well as a reduction in the leukocyte number compared to the PhEG. The SCJ of the OVXG and PEOVXG was not very visible, with cubical epithelium on the endometrial side and with reduction in the layers of squamous epithelium due to stromal atrophy. The SCJ in the ESTRG was more developed than in the OVXG and PEOVXG, but it was similar to that of the PEG, having unclear borders. In contrast, the SCJ of the DEXAG was well-delineated and similar to the PhEG. CONCLUSION: our data suggest that estrogen associated with dexamethasone may be important for remodeling SCJ morphology in female rats with previously induced permanent estrus and subsequent ovariectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(12):598-603
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001200004
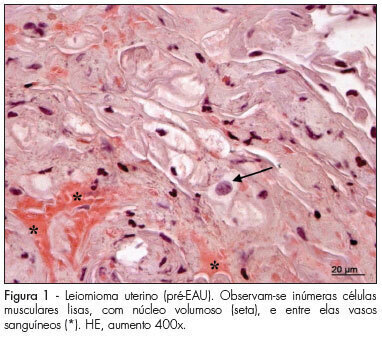
PURPOSE: to analyze histomorphometric consequences of the uterine arteries embolization (UAE) in the uterine tissue, especially by collagen tissue quantification through uterine biopsy, before and after treatment of uterine leiomyoma. METHODS: 15 patients with symptomatic leyomioma and/or infertility, submitted to UAE, participated in the study according to the study exclusion criteria, after having signed an informed consent. Uterine biopsy was performed in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle, before and three months after the procedure, to evaluate the collagen. After the histological processing of the material, 3 µ slices were prepared, some of them dyed with hematoxiline-eosin (HE) and others with the specific dye for collagen fibers (Picrosirius red). Then, the slides were examined and interpreted, and the collagen quantified. The amount was calculated as the percent of the area composed by collagen, and the result expressed in mean±standard deviation (SD). Data has then been submitted to statistical analysis by Student's paired t test (p<0.05). RESULTS: the presence of smooth muscle cells was observed in the biopsies performed before the treatment, surrounded by a rich network of collagen fibers, which are part of the tumor, blood vessels and fibroblast nuclei. On the slides of biopsies performed after the treatment, it was observed the presence of widespread coagulation necrosis, vascular thrombosis, calcification and lymphoplasmocitary infiltration areas and clear reduction of the collagen component. The percentage of collagen fibers was higher in the pre-UAE group (84.07±1.41), than in the post-UAE (81.05±1.50) group, with p<0.0001, and 95% confidence interval (CI95%) from 2.080 to 3.827. CONCLUSION: the quantitative and qualitative collagen reduction clearly shows that the proposed treatment is efficient in reducing the tumoral mass, composed mainly by collagen fibers intermingled with neoplasic smooth muscle cells. Nevertheless, complementary studies are needed to investigate the functional and biological consequences of these histological changes.