You searched for:"Henrique Vítor Leite"
We found (18) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(7):341-348
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700004
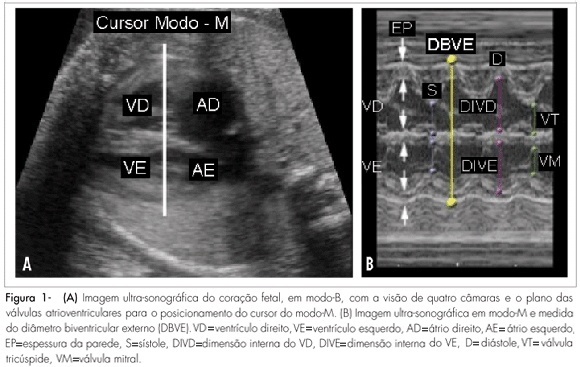
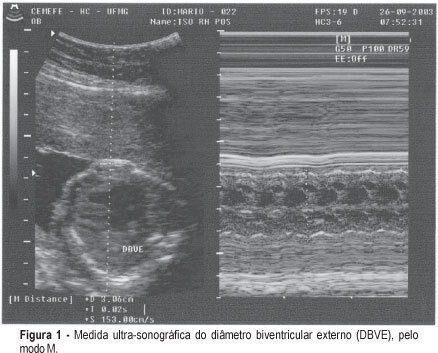
PURPOSE: to verify the correlation between ultrasonography heart measures and hemoglobin deficit in fetuses of alloimmunized pregnant women. METHODS: a transversal study, including 60 fetuses, with 21 to 35 weeks of gestational age, from 56 isoimmunized pregnant women. A number of 139 procedures were performed. Before cordocentesis for the collection of fetal blood, cardiac measures and femur length (FL) were assessed by ultrasonography. The external biventricular diameter (EBVD) was obtained by measuring the distance between the epicardic external parts at the end of the diastole, with the M-mode cursor perpendicular to the interventricular septum, in the atrioventricular valves. The measure of the atrioventricular diameter (AVD) was obtained by positioning the same cursor along the interventricular septum, evaluating the distance between the heart basis and apex. The FL was determined from the trochanter major to the distal metaphysis. The cardiac circumference (CC) was also calculated. To adjust the cardiac measure to the gestational age, each of these measures were divided by the FL measure. Hemoglobin concentration has been determined by spectrophotometry with the Hemocue® system. Hemoglobin deficit calculation was based in the Nicolaides's normality curve. RESULTS: direct and significant correlations were observed between the cardiac measures evaluated and the hemoglobin deficit. To predict moderate and severe anemia, the sensitivity and specificity found were 71.7 and 66.3% for EBVD and FL, 65.8 and 62.4% for AVD and FL, and 73.7 and 60.4% for CC and FL, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: ultrasonography cardiac measures assessed from fetuses of isoimmunized pregnant women correlate directly with hemoglobin deficit.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(6):365-371
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000600007
Purpose: to evaluate the accuracy of prenatal ultrasound in the diagnosis of nephrouropathies. Methods: the authors followed-up 127 pregnancies referred to the Fetal Medicine Center of UFMG with suspicion of these anomalies. Fetal biometry, growth, vitality, and associated malformations were evaluated. Finally, a detailed description of the renal system was made to define the prenatal morphologic diagnosis of the malformations to be compared with the postnatal diagnosis. Results: based on the kappa index (statistical method that measures the concordance between different measurements, methods or measurement instruments: below 0.40, poor agreement; between 0.40 and 0.75, good agreement; above 0.75, excellent ageement), the authors found an excellent concordance (kappa index 0.95). Among the 127 cases, there were only 9 misdiagnoses, all of them of obstructive uropathies: 6 cases showed different obstruction levels after delivery and in three cases there were confounding diagnosis with multicystic kidney. Conclusions: the detailed ultrasonographic description of the renal system is a good method for prenatal diagnosis of the fetal nephropathies, allowing some options to modify the outcome of these fetuses, like to send them to specialized centers, to anticipate delivery and even to apply intrauterine therapy, in order to preserve the renal function. Serial echography and amnioinfusion can be used to improve the precision of prenatal diagnosis.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(6):413-418
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600005
PURPOSE: to determine the existence of association between blood pressure rise and plasma ANP and BNP levels in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, considering the existence of a hypertensive state before pregnancy and supportive drug influence on these hormones. METHODS: in a case-control transversal study, 86 pregnant women were assessed regarding arterial pressure level and plasma ANP and BNP levels. Clinical and laboratory tests were carried out to diagnose preeclampsia and the use of hypotensive drugs and magnesium sulfate was considered. Hormone determinations were obtained through radioimmunoassay, after extraction in C18 Sep-pak columns. Correlation was investigated by means and regression analysis in the whole group of pregnant women and in specific groups, considering prior hypertension. RESULTS: plasma ANP values were 41.5±7.3, 78.4±13.1 and 89.2±13.4pg/mL (p<0.00001) and plasma BNP values were 79.5±15.8, 176.7±42.2 and 208.3±63.5 pg/mL (p=0.005), respectively, for mean blood pressure =107 mmHg, 107-139 mmHg and =140 mmHg. It was verified that the positive correlation between plasma ANP concentrations and pressure levels in preeclampsia did not depend on the existence of a hypertensive state before pregnancy (p<0.0001: preeclampsia and p<0.01: preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension), whereas BNP dosages were not associated with the arterial pressure in the group with arterial hypertension prior to pregnancy (p=0.004: preeclampsia and p=0.18: preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension). CONCLUSION: aggravation of hypertension in preeclampsia correlates with serum ANP and BNP concentrations, although BNP values may be influenced by the existence of a prior hypertensive state.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
PURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(8):577-583
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800006
PURPOSE: to determine the relationship between the Doppler indices of inferior vena cava and ductus venosus and the fetal hemoglobin concentration. METHODS: a cross-sectional prospective study was performed at the "Centro de Medicina Fetal HC UFMG" from January 1998 to July 2001. Thirty-one pregnant women with isoimmunization, detected by an indirect Coombs test >1:8, underwent a protocol for the identification of fetal hemolysis. When intrauterine transfusions were indicated, the umbilical cord hemoglobin concentration was measured at the begining of the procedure. In the other cases, it was measured at delivery. Every single intrauterine transfusion preceded by Doppler flow velocity waveforms from inferior vena cava and ductus venosus was defined as one case. Hemocue® (B-Hemoglobin Photometer Hemocue AB; Angelholm, Sweden) was used to measure the fetal hemoglobin concentration. In all cases, inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler examinations were performed before the collection of fetal blood samples. For the inferior vena cava Doppler, the studied indices were pulsatility index for veins (PVI), peak velocity index for veins (PVIV) and atrial/systole ratio (CA/SV ratio or preload index); for ductus venosus, PVI, PVIV and systole/atrial ratio (SV/CA ratio). The relationship between inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler indices and cord blood hemoglobin concentration was obtained by simple linear regression analysis. Moreover, an association between those indices and the finding of fetal hemoglobin <10 g/dL was shown by the c² test, significant at p<0.05. RESULTS: seventy-four procedures were studied. In twenty-three cases fetal hemoglobin was below 7 g/dL. A significant negative correlation between all studied Doppler indices and fetal concentration of hemoglobin was observed (p<0.05). The highest Doppler index values were observed in severe anemic fetuses. Fetuses with cord blood hemoglobin below 10 g/dL presented inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler indices over the 95 percentile for gestational age. CONCLUSIONS: Doppler flow velocity waveforms from inferior vena cava and ductus venosus may be used as a noninvasive marker of severe fetal anemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(8):649-653
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800009
PURPOSE: to assess the correlation between middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity and umbilical cord blood hemoglobin concentration and to determine its diagnostic value. PATIENTS AND METHODS: a cross-sectional prospective study was performed from January 2000 to May 2003. Forty-four isoimmunized pregnant women underwent a protocol for the identification of fetal hemolysis. When intrauterine transfusions were indicated, the umbilical cord blood hemoglobin concentration was measured at the beginning of the procedure. Each intrauterine transfusion preceded by Doppler velocimetry of the middle cerebral artery was regarded as one case, summing up eighty-three procedures. In all cases, the middle cerebral artery Doppler examinations were performed within the three hours preceding fetal blood sample collection. The systolic velocity peak was recorded and considered abnormal when its value was above 1.5 times the median for the corresponding gestational age. Hemocue® (B-Hemoglobin Photometer Hemocue AB; Angelholm, Sweden) was the device used to measure fetal hemoglobin concentration. The relationship between middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity and cord blood hemoglobin was obtained by the chi2 test, considered significant at p<0.05. RESULTS: in thirty-three cases the cord blood hemoglobin concentration was below 10.0 g/dL. There was a strong correlation between the two measured variables (p<0.001). The middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity with values above 1.5 times the median was associated with cord blood hemoglobin concentration below 10 g/mL (p<0,001). The sensitivity of an increased middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity was 75.8% for the detection of a cord blood hemoglobin level of 10 g/dL or lower. CONCLUSION: the middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity can be used as a noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(10):653-657
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001001000007
Purpose: to verify if there is an association between the mean blood velocity in the descending thoracic aorta and fetal anemia diagnosis. Methods: this is a prospective, cross-sectional study in which the mean blood velocities in the fetal aorta, in 66 fetuses at risk for severe anemia due to severe Rh immunization, and cord blood hemoglobin levels were analyzed comparatively. The hemoglobin level was obtained by cordocentesis if an intravascular transfusion was performed for severe anemia, however, if the fetus received an intrauterine transfusion by the intraperitoneal route or if the fetus did not receive a transfusion at all, hemoglobin level was measured at the time of pregnancy termination by umbilical cord puncture. The authors made a statistical association between the mean blood velocity in fetal descending thoracic aorta and the diagnosis of fetal anemia. The c² test was used for statistical analysis and a p value <0,05 was used to indicate significance. Results: there was a significant and indirect association between the mean blood velocity in the descending thoracic aorta and the detection of fetal anemia. The mean blood velocity in fetal thoracic aorta had a sensitivity of 47.4% for the diagnosis of moderate fetal anemia (Hg<10.0 g/dL), with a p value <0.01 by the Fisher exact test, and a sensitivity of 54.5% for severe Rh isoimmunization (Hg<7.0 g/dL), with a p value =0.01. Conclusion: this study revealed a significant indirect correlation between mean blood velocity in the descending thoracic aorta and the detection of fetal anemia due to Rh isoimmunization.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(10):663-668
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of intravascular transfusion on ductus venosus and inferior vena cava Doppler ultrasound indexes (SV/CA) and to relate it to hemoglobin levels before transfusion. METHODS: this is a transversal prospective study. A total of 62 intravascular transfusions were performed in 27 fetuses from pregnancies with red blood cell isoimmunization. The 62 cases were divided into two groups: (1) fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion £10 g/dL and (2) fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion >10 g/dL. The SV/CA and CA/SV indexes were measured using color Doppler ultrasound 6 h before and 12 h after intravascular transfusion. The index values before and after transfusion in all 62 cases were compared. Thereafter we compared these indexes before and after transfusion regarding each group. The Wilcoxon test was used and the results were considered statiscally significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: when we studied the whole group (62 cases) no significant difference was observed between the CA/SV index before and after transfusion (p=0.775). On the other hand, a significant increase in the SV/CA index was observed after transfusion (p=0.004). No significant differences were observed in both the SV/CA and CA/SV indexes before and after transfusion in the group of fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion £10 g/dL (p=0.061 and p=0.345, respectively). There was a significant increase in the CA/SV index after transfusion in fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion >10 g/dL (p=0.049), but the SV/CA index did not change in this group (p=0.086). CONCLUSION: venous Doppler study may be useful to understand fetal hemodynamic adjustment after intravascular transfusion. An increase in SV/CA without change in CA/SV after transfusion in anemic fetuses may be an important compensatory mechanism to increase intravascular volume. The increase in CA/SV index in fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion <10 g/dL suggests a state of fetal hypervolemia.