You searched for:"Carolina Sales Vieira"
We found (14) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(9):470-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000900008
Adequate postpartum contraception is recommended in order to prevent mother and infant morbidity. The mother-infant benefits of lactation are well recognized, and exclusive, regular and frequent breastfeeding is an effective contraceptive method for amenorrheic patients. However, the resumption of fertility varies among women and access to health services is not guaranteed in many regions of the world. We searched the articles in Medline (PubMed) related to the subject published between 1971 to April 2008 and selected the most relevant articles in the literature about postpartum contraception. Short interpregnancy intervals increase maternal and fetal complications and therefore effective postpartum contraception is imperative. The ideal method prescribed should be effective and safe, id est, should not interfere with lactation or alter the hemostatic system. During the postpartum period, ideally non-hormonal methods should be used because they do not alter lactation or hemostasis. However, in populations with difficult access to health or with an early start of calorie supplementation to the newborn, the option should be for progestogens-only contraceptives, ideally initiated after six weeks or earlier in special situations.
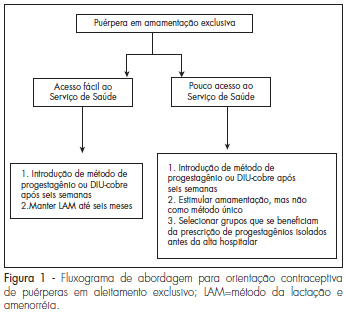
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(10):538-547
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000008
Exogenous female hormones used for contraception or postmenopausal hormonal replacement therapy are associated with an increase of venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk, mainly because they cause a hypercoagulable state. The risk is highest during the first year of use and it is not cumulative. The dose of estrogen, the type of estrogen and progestogen, the route of administration of female sex steroid hormones, and the hereditary risk factors for VTE of each patient can interfere on the final risk for VTE. The knowledge of their effect on hemostasis is essential for a correct prescription.
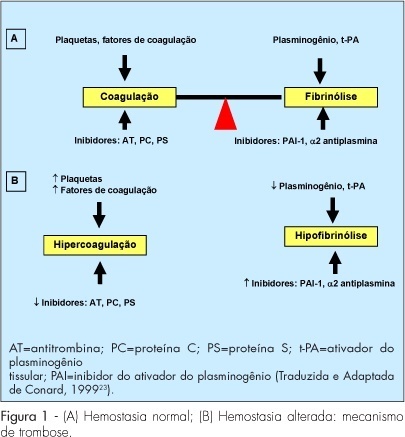
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):585-585
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):692-696
To evaluate the effects of nutritional counseling on the dietary habits and anthropometric parameters of overweight and obese adolescentswith polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
This was a prospective, longitudinal and auto-controlled study. Thirty adolescents aged 13-19 years-old, diagnosed with PCOS received nutritional counseling and were followed-up for 6 months. After the follow-up period, the results were evaluated through body weight, body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC).
Sixty-percent of the adolescents adhered to the nutritional counseling and, of these, 50% lost weight. Adolescents who lost weight changed their dietary habits by adopting hypocaloric diets and eating more meals per day, as per nutritional counseling. The waist circumference (WC) decreased significantly, although the body weight decreased non-significantly after adoption of a hypocaloric diet.
Although there was no significant weight loss, there was a considerable reduction in theWCassociated with hypocaloric diets and with eating a greater number of meals per day.