You searched for:"Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral"
We found (23) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(5):299-303
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000500005
Purpose: to evaluate the intrauterine treatment of anemic fetuses that underwent intrauterine transfusions due to rhesus isoimmunization. Methods: the authors studied sixty-one fetuses undergoing intrauterine transfusions by the intravascular, intraperitoneal or both routes. The hydropic fetuses (19.7%) received only intravascular intrauterine transfusions. There was an overall number of 163 intrauterine transfusions with a mean of 2.7 procedures for each case. The indications for intrauterine transfusions were high values of bilirubin in amniotic fluid analyses by the Liley method or a hemoglobin concentration of cord blood below 10.0 g/mL. Results: the overall perinatal survival rate was 46% for hydropic fetuses and 84% for the nonhydropic ones. There were no maternal side effects related to the procedures. Half of the intrauterine transfusions were performed by the intravascular route. The mean gestational age at the delivery was 34.8 weeks. Conclusions: despite better perinatal results with intrauterine transfusions guided by ultrasound, especially using intravascular procedures, rhesus isoimmunization remains as an important cause of high rates of perinatal morbidity and mortality.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(5):323-328
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500004
PURPOSE: to determine whether an elective cesarean section at the 38th week of gestation for HIV positive patients, in spite of decreasing vertical transmission, increases the risk of maternal death. METHODS: fifty-eight HIV-infected patients were studied and submitted to the complete ACTG 076 protocol (oral administration of zidovudine in the prenatal period associated with the intravenous form at delivery) followed by an elective cesarean section at the 38th week of gestation. The control group consisted of 226 noninfected women (the first four patients submitted to an elective cesarian section after each cesarian section in infected patient). The analyzed variables were: uterine atonia, puerperal fever, abdominal wall infection, urinary infection, endometritis, average blood loss, surgery time, and hospitalization time. Data were analyzed by the c² test (the Fisher test was used when there were less than 5 cases). The relative risk was calculated with the Epi-Info 6.0 program. RESULTS: results show that the elective cesarean section performed on HIV-positive patients, when compared to the control group, did not present a higher incidence of uterine atonia, puerperal fever, abdominal wall infection, urinary infection or endometritis. However, a greater average blood loss (2.26 relative risk) was recorded as well as an extended surgery time (3.32 relative risk). The HIV-infected patients remained less time in hospital than the noninfected control group (0.33 relative risk). CONCLUSION: we conclude that there was no increase in maternal morbidity after cesarean section as a means of interrupting gestation in the HIV-infected patients.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(7):341-348
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700004
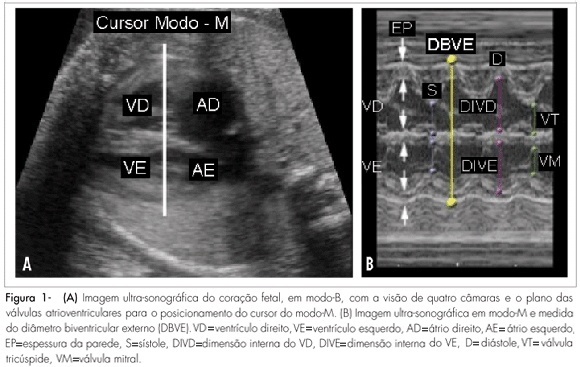
PURPOSE: to verify the correlation between ultrasonography heart measures and hemoglobin deficit in fetuses of alloimmunized pregnant women. METHODS: a transversal study, including 60 fetuses, with 21 to 35 weeks of gestational age, from 56 isoimmunized pregnant women. A number of 139 procedures were performed. Before cordocentesis for the collection of fetal blood, cardiac measures and femur length (FL) were assessed by ultrasonography. The external biventricular diameter (EBVD) was obtained by measuring the distance between the epicardic external parts at the end of the diastole, with the M-mode cursor perpendicular to the interventricular septum, in the atrioventricular valves. The measure of the atrioventricular diameter (AVD) was obtained by positioning the same cursor along the interventricular septum, evaluating the distance between the heart basis and apex. The FL was determined from the trochanter major to the distal metaphysis. The cardiac circumference (CC) was also calculated. To adjust the cardiac measure to the gestational age, each of these measures were divided by the FL measure. Hemoglobin concentration has been determined by spectrophotometry with the Hemocue® system. Hemoglobin deficit calculation was based in the Nicolaides's normality curve. RESULTS: direct and significant correlations were observed between the cardiac measures evaluated and the hemoglobin deficit. To predict moderate and severe anemia, the sensitivity and specificity found were 71.7 and 66.3% for EBVD and FL, 65.8 and 62.4% for AVD and FL, and 73.7 and 60.4% for CC and FL, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: ultrasonography cardiac measures assessed from fetuses of isoimmunized pregnant women correlate directly with hemoglobin deficit.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(6):365-371
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000600007
Purpose: to evaluate the accuracy of prenatal ultrasound in the diagnosis of nephrouropathies. Methods: the authors followed-up 127 pregnancies referred to the Fetal Medicine Center of UFMG with suspicion of these anomalies. Fetal biometry, growth, vitality, and associated malformations were evaluated. Finally, a detailed description of the renal system was made to define the prenatal morphologic diagnosis of the malformations to be compared with the postnatal diagnosis. Results: based on the kappa index (statistical method that measures the concordance between different measurements, methods or measurement instruments: below 0.40, poor agreement; between 0.40 and 0.75, good agreement; above 0.75, excellent ageement), the authors found an excellent concordance (kappa index 0.95). Among the 127 cases, there were only 9 misdiagnoses, all of them of obstructive uropathies: 6 cases showed different obstruction levels after delivery and in three cases there were confounding diagnosis with multicystic kidney. Conclusions: the detailed ultrasonographic description of the renal system is a good method for prenatal diagnosis of the fetal nephropathies, allowing some options to modify the outcome of these fetuses, like to send them to specialized centers, to anticipate delivery and even to apply intrauterine therapy, in order to preserve the renal function. Serial echography and amnioinfusion can be used to improve the precision of prenatal diagnosis.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(6):413-418
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600005
PURPOSE: to determine the existence of association between blood pressure rise and plasma ANP and BNP levels in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, considering the existence of a hypertensive state before pregnancy and supportive drug influence on these hormones. METHODS: in a case-control transversal study, 86 pregnant women were assessed regarding arterial pressure level and plasma ANP and BNP levels. Clinical and laboratory tests were carried out to diagnose preeclampsia and the use of hypotensive drugs and magnesium sulfate was considered. Hormone determinations were obtained through radioimmunoassay, after extraction in C18 Sep-pak columns. Correlation was investigated by means and regression analysis in the whole group of pregnant women and in specific groups, considering prior hypertension. RESULTS: plasma ANP values were 41.5±7.3, 78.4±13.1 and 89.2±13.4pg/mL (p<0.00001) and plasma BNP values were 79.5±15.8, 176.7±42.2 and 208.3±63.5 pg/mL (p=0.005), respectively, for mean blood pressure =107 mmHg, 107-139 mmHg and =140 mmHg. It was verified that the positive correlation between plasma ANP concentrations and pressure levels in preeclampsia did not depend on the existence of a hypertensive state before pregnancy (p<0.0001: preeclampsia and p<0.01: preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension), whereas BNP dosages were not associated with the arterial pressure in the group with arterial hypertension prior to pregnancy (p=0.004: preeclampsia and p=0.18: preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension). CONCLUSION: aggravation of hypertension in preeclampsia correlates with serum ANP and BNP concentrations, although BNP values may be influenced by the existence of a prior hypertensive state.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(7):431-438
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000700004
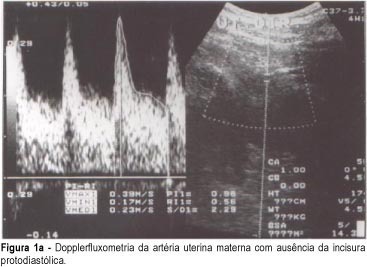
Purpose: to evaluate the association between the presence of diastolic notch in the maternal uterine arteries, and the histopathological changes of the uteroplacental vessels. Methods: transversal study of 144 women with single pregnancy interrupted by cesarean section between 27 and 41 weeks. In this sample, 84 had pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia and the other 60 were normal. In this group, Doppler study of both uterine arteries and placental bed biopsy was performed. Results: of the total of 144 patients, 88 patients (61%) had a biopsy fragment that was considered representative of the placental bed. The diastolic notch was present in 40 patients (70%) of the total of cases with inadequate physiologic alterations and absent in 28 patients (90%) of the total of cases with physiologic alterations (p=0.0000). The Doppler study showed 70% sensitivity, 90% specificity, 44% positive predictive value and 97% negative predictive value. The association between bilateral diastolic notch of uterine arteries and acute atherosis in the placental bed was also significant (24 out of 25 cases -- p=0.000). The Doppler study showed 96% sensitivity, 70% specificity, 26% positive predictive value and 99% negative predictive value, while for arteriolosclerosis its results were 80% sensitivity, 55% specificity, 17% positive predictive value and 96% negative predictive value. Conclusions: the diastolic notch in the maternal uterine is a safe indicator of pathological vessel alteration in the placental bed. The adequate trophoblast migration into the myometrium, revealed by physiologic changes, results in the absence of bilateral diastolic notch of the maternal uterine arteries.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
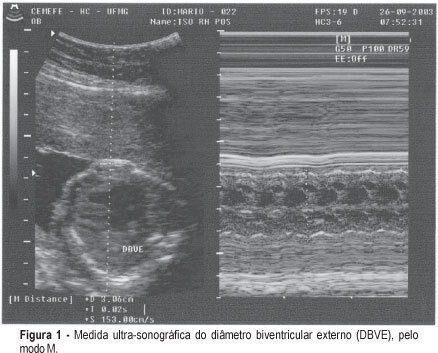
PURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(8):577-583
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800006
PURPOSE: to determine the relationship between the Doppler indices of inferior vena cava and ductus venosus and the fetal hemoglobin concentration. METHODS: a cross-sectional prospective study was performed at the "Centro de Medicina Fetal HC UFMG" from January 1998 to July 2001. Thirty-one pregnant women with isoimmunization, detected by an indirect Coombs test >1:8, underwent a protocol for the identification of fetal hemolysis. When intrauterine transfusions were indicated, the umbilical cord hemoglobin concentration was measured at the begining of the procedure. In the other cases, it was measured at delivery. Every single intrauterine transfusion preceded by Doppler flow velocity waveforms from inferior vena cava and ductus venosus was defined as one case. Hemocue® (B-Hemoglobin Photometer Hemocue AB; Angelholm, Sweden) was used to measure the fetal hemoglobin concentration. In all cases, inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler examinations were performed before the collection of fetal blood samples. For the inferior vena cava Doppler, the studied indices were pulsatility index for veins (PVI), peak velocity index for veins (PVIV) and atrial/systole ratio (CA/SV ratio or preload index); for ductus venosus, PVI, PVIV and systole/atrial ratio (SV/CA ratio). The relationship between inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler indices and cord blood hemoglobin concentration was obtained by simple linear regression analysis. Moreover, an association between those indices and the finding of fetal hemoglobin <10 g/dL was shown by the c² test, significant at p<0.05. RESULTS: seventy-four procedures were studied. In twenty-three cases fetal hemoglobin was below 7 g/dL. A significant negative correlation between all studied Doppler indices and fetal concentration of hemoglobin was observed (p<0.05). The highest Doppler index values were observed in severe anemic fetuses. Fetuses with cord blood hemoglobin below 10 g/dL presented inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler indices over the 95 percentile for gestational age. CONCLUSIONS: Doppler flow velocity waveforms from inferior vena cava and ductus venosus may be used as a noninvasive marker of severe fetal anemia.