You searched for:"Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto"
We found (27) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2014;36(6):251-258
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004976
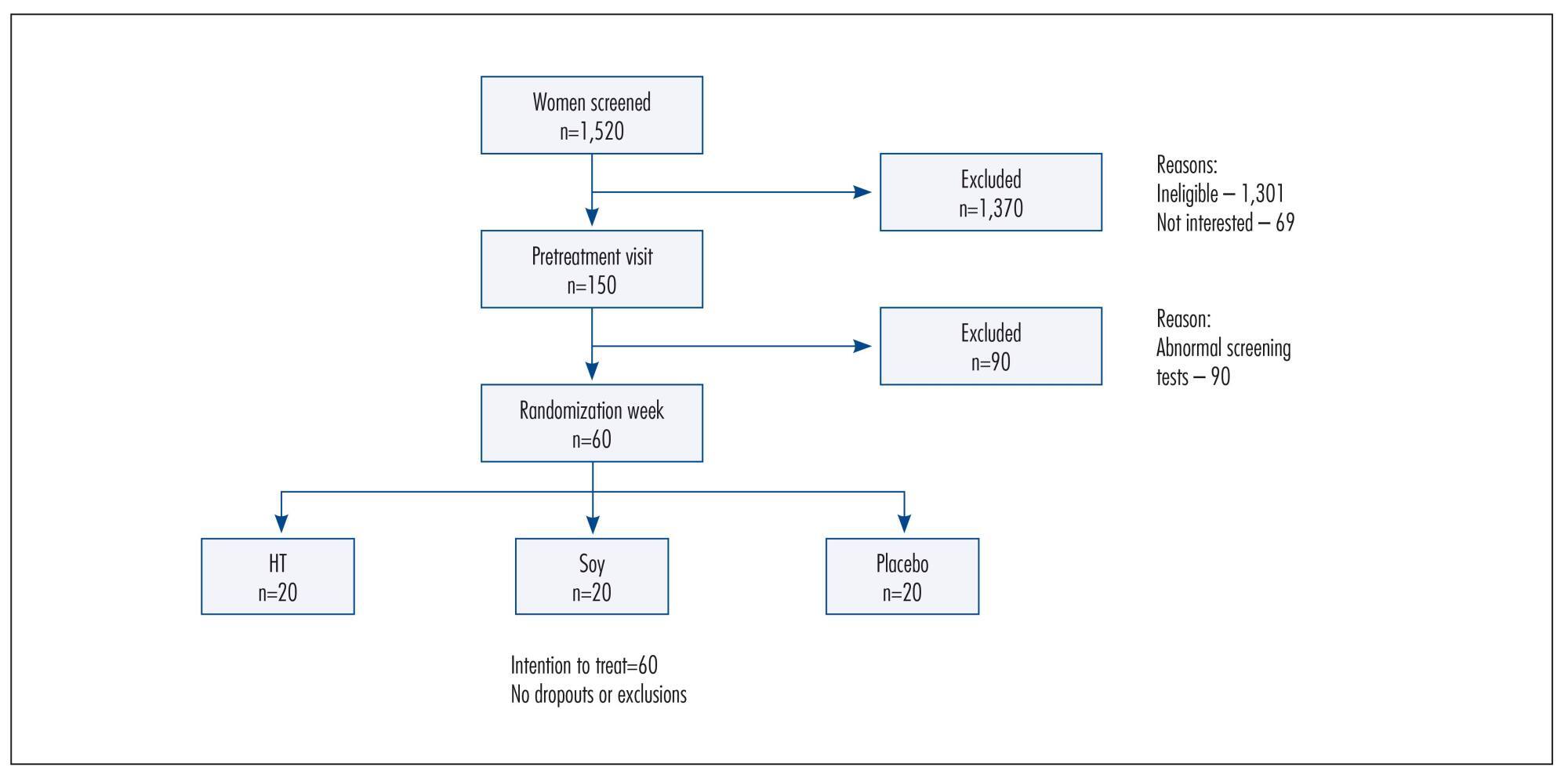
To assess the effects of a soy dietary supplement on the main biomarkers of cardiovascular health in postmenopausal women compared with the effects of low-dose hormone therapy (HT) and placebo.
Double-blind, randomized and controlled intention-to-treat trial. Sixty healthy postmenopausal women, aged 40-60 years, 4.1 years mean time since menopause were recruited and randomly assigned to 3 groups: a soy dietary supplement group (isoflavone 90mg), a low-dose HT group (estradiol 1 mg plus noretisterone 0.5 mg) and a placebo group. Lipid profile, glucose level, body mass index, blood pressure and abdominal/hip ratio were evaluated in all the participants at baseline and after 16 weeks. Statistical analyses were performed using the χ2 test, Fisher's exact test, Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), paired Student's t-test and Wilcoxon test.
After a 16-week intervention period, total cholesterol decreased 11.3% and LDL-cholesterol decreased 18.6% in the HT group, but both did not change in the soy dietary supplement and placebo groups. Values for triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, glucose level, body mass index, blood pressure and abdominal/hip ratio did not change over time in any of the three groups.
The use of dietary soy supplement did not show any significant favorable effect on cardiovascular health biomarkers compared with HT. Clinical Trial Registry: The trial is registered at the Brazilian Clinical Trials Registry (Registro Brasileiro de Ensaios Clínicos - ReBEC), number RBR-76mm75.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1998;20(5):267-271
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500006
Objective:To analyze the levels of endogenous sexual steroids and gonadotrophin in women with and without endometrial cancer. Methodology:We developed a clinical comparative study on 20 postmenopausal women with endometrial cancer and 20 postmenopausal women without endometrial cancer. The age, the postmenopausal time and the index of body mass were used as matching variables. The plasma levels of the endogenous sexual steroids were measured using radioimmunoassay and immunoenzymatic methods. For the statistic analysis we used the Student's t test. Results: The levels of androstenedione (A), total testosterone (t) and free testosterone (TL) were higher in the women with endometrial cancer, and those of the luteinic hormone (LH) were significantly lower values in these women. We also observed that the ratio (E1/A) showed significantly lower in the group of women with cancer, while the ratio (E2/E1) did not present any differences between groups. Conclusions: We emphasize the potentiality of sexual steroids and gonadotrophins in the genesis of endometrial adenocarcinoma in postmenopausal women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(5):287-292
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500006
Purpose: to evaluate the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on the systolic and diastolic blood pressure of postmenopausal women. Methods: a total of 166 users and 136 non-users of hormone replacement were evaluated retrospectively during a period of three years. All women were assisted at the Menopause Outpatient Clinic of CAISM -- Unicamp, where the variations of these parameters were evaluated at the end of each year in relation to the initial parameters. The data analysis was performed through Student's t test, Mann-Whitney test, and the Wilcoxon nonparametric test. Results: we observed that the systolic blood pressure of HRT users was statistically lower at the end of the third year of use, compared to the initial values (p = 0.01). There was no significant difference in the diastolic blood pressure between users and non-users. Conclusion: hormone replacement therapy did not produce changes in the parameters studied in women properly assisted during the use of HRT.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2013;35(7):295-300
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000700003
PURPOSE: To evaluate the prevalence of women aged 50 years or more who are sexually active and their self-perception with respect to their sexual lives. Associated factors were also assessed. METHODS: A cross-sectional, population-based, self-reported household survey involving 622 Brazilian women aged 50 years or more. Sociodemographic, clinical, and behavioral factors were evaluated. The sexual life self-perception was classified as very good, good, fair, poor, or very poor. Data were analyzed using the χ² test, Fisher's exact test, and Poisson multiple regression analysis. Prevalence ratios and their 95% confidence intervals were also calculated. RESULTS: Of the women in this sample, 228 (36.7%) reported having a sexual life and, of these, 53.5% classified it as very good or good, while 46.5% considered it fair, poor, or very poor. The bivariate analysis indicated that being postmenopausal (p=0.025) and using natural remedies to treat the menopause (p=0.035) were factors associated with the woman classifying their sexual lives as fair, poor, or very poor. Multiple regression analysis showed that more women who had used or were currently using natural remedies for the menopause scored their sexual lives as fair, poor, or very poor. CONCLUSIONS: More than half the women aged 50 years or more in this study were not sexually active. A poorer sexual life self-perception was associated with the use of natural remedies to treat menopausal symptoms. This may indicate a need to improve the way in which these women are evaluated and treated. Women's assessment of their own sexual lives may prove a useful tool in clinical practice.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1998;20(6):303-308
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600002
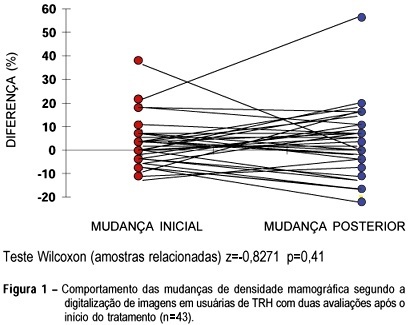
Objective: to compare mammographic density changes, case by case, according to image digitization in three consecutive evaluations of users or nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy (HRT). Methods: 59 postmenopausal women were evaluated, 43 being users of cyclic or continuous estro-progestin hormonal replacement therapy, and 16 nonusers. The criteria of inclusion were: amenorrhea for at least 12 months, a normal mammographic examination at the beginning of the HRT (users) or the clinical follow-up without HRT (nonusers), at two incidences (mediolateral and craniocaudal). The following variables were used for the evaluation of mammary density: initial change - the difference between the first mammography after HRT performed in 12 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT-and final change - the difference between the second mammography after HRT performed in 24 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT. Wilcoxon and c² tests were used in order to evaluate the differences in mammographic density changes. Results: more than half (56.3%) of the women, HRT users with initial increase in mammographic density remained with the increase after the final evaluation. This finding was not significant (p=0.617). In the same group, the initial nonincrease was significantly associated with the final nonincrease (p=0.017). Among the nonusers, all breasts that were not totally fat at the initial evaluation presented a mammographic density decrease at the final evaluation. Conclusions: the majority of HRT users presenting mammographic density increase at the first evaluation, after approximately one year of use, remained with the increase at a second evaluation. After some time, the nonusers tended to present a significant mammographic density decrease (p=0.003).
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2012;34(7):335-342
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700008
PURPOSE: To evaluate whether climacteric women undergoing liver transplantation had higher prevalence of decreased bone mass than those without any liver disease. METHODS: A cross-sectional study with 48 women receiving follow-up care at a university hospital in Southeastern Brazil, from February 4th 2009 to January 5th 2011, was conducted. Of these women, 24 were 35 years or older and had undergone liver transplantation at least one year before study entry. The remaining 24 women had no liver disease and their ages and menstrual patterns were similar to those of transplanted patients. Laboratorial tests (follicle-stimulating hormone and estradiol) and bone density measurements of the lumbar spine and femur (equipment Hologic, Discovery WI) were performed. Statistical analysis was carried out by Fisher's exact test, simple Odds Ratio (OR), and multiple logistic regression. RESULTS: Mean age of the women included in the study was 52.8 (±10.7) years-old, 27.1% were premenopausal and 72.9% were peri/postmenopausal. Approximately 14.6% of these women exhibited osteoporosis and 35.4% had low bone mass. The following items were associated with decreased bone mass: being postmenopausal (OR=71.4; 95%CI 3.8 - 1,339.7; p<0.0001), current age over 49 years-old (OR=11.4; 95%CI 2.9 - 44.0; p=0.0002), and serum estradiol levels lower than 44.5 pg/mL (OR=18.3; 95%CI 3.4 - 97.0; p<0.0001). Having a history of liver transplantation was not associated with decreased bone mass (OR=1.4; 95%CI 0.4 - 4.3; p=0.56). CONCLUSION: Liver transplantation was not associated with decreased bone mass in this group of climacteric women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(9):433-440
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the level of physical activity, quality of life and associated factors in women aged 60 or older. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted on 271 women who go to a Leisure Center and women attended at a menopause ambulatory in Campinas (SP). The women were invited to take part in the research, carried out through interviews. The instruments used were the version 8 of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) modified for the elderly population in order to evaluate their physical activity, and the World Health Organization Questionnaire of Quality of Life specific for this group (WHOQOL-OLD) to evaluate their quality of life. IPAQ results were assessed using tertiles. The association between the WHOQOL-OLD and the IPAQ results and subject characteristics was assessed by the Student's t test, Mann-Whitney test and multiple analyses. RESULTS: the average age of women was 67.4±5.3 years. Among these women, 33% were classified as being less active. Analysis of each physical activity domain showed that 60.8% of the time was spent in sitting activities (1,701.6±986.1 minutes/week). Multiple analyses indicated that attending a leisure center in Campinas (SP) and being 70 years old or older increased the chances of engaging in moderate-intensity or vigorous-intensity physical activity by 11.4 and 2.8 times, respectively. The average quality of life score was 66.9±11.7. The highest value was observed in the domain related to sensory abilities (72.0±18.8) and the lowest value was related to autonomy (60.3±16.2). Linear regression showed that a good self-perception of health increased the quality of life score by 7.3 points, the use of a bigger amount of medication decreased it by 4.4 points and the performance of moderate or vigorous physical exercise increased the score by 4.8 points. CONCLUSION: women spend prolonged periods of time in sitting activities. The importance of engaging in moderate/vigorous-intensity physical activity is evident for obtaining a good quality of life.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(7):435-441
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700006
Purpose: to describe sociodemographic characteristics of a group of climacteric women in order to discover the frequency and the variables associated with obesity and android profile of body fat distribution. Methods: an observational study was carried out in 518 patients aged 45 to 65 years, in a climacterium outpatient clinic. Age, color, menopausal status, duration of menopause, physical activity, smoking status, diet, alcohol intake, personal and family antecedents of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia and obesity were considered. Body mass index and the waist/hip ratio were the dependent variables. For the statistical analysis Wilcoxon test, Pearson's correlation coefficient, with a 5% level of significance, and multivariate analysis using regression model were used. Results: more than two thirds of the participants were nonobese with an android profile and postmenopausal. One fourth had physical activity and were smokers; half reported an inadequate diet and one fifth were alcoholics. Patients with an android profile presented higher mean age than women with gynecoid pattern. Personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes and family history of diabetes were related to obesity and android pattern. Postmenopausal status was significantly associated with the android profile. Conclusions: the majority of the participants were nonobese with an android profile, white, postmenopausal, sedentary, neither smokers nor alcoholics. The main factors related to obesity and android pattern were personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes, family history of diabetes and particularly, postmenopausal status with android profile.