You searched for:"ALESSANDRA CRISTINA MARCOLIN"
We found (21) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(5):317-321
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500003
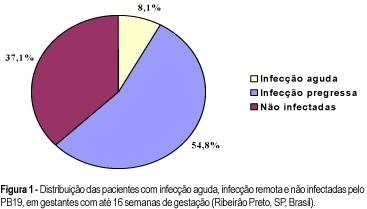
PURPOSE: to evaluate the rate of seropositivity for parvovirus B19 (PB19) among pregnant women and the rate of seroconversion against this infection during pregnancy. METHODS: prospective study carried out in the Hospital of the Medical School of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. In the first stage of the present study, we evaluated 245 pregnant women with gestational age less than 16 weeks to determine the seroprevalence of PB19 infection by ELISA. According to the serological results we determined if the PB19 infection was an acute infection (IgM positive and IgG negative or positive), or a former infection (IgM negative and IgG positive). In the second stage of this study, 73 previously seronegative pregnant women were tested again when they came to the hospital for delivery (IgM and IgG), to detect the seroconversion rate during pregnancy. RESULTS: the seroprevalence of the PB19 infection until 16 weeks of gestation was 62.9% (95% IC: 56.8-68.9), divided into acute infection (8.1%), or former infection (54.8%). Of the 73 patients, seronegative in the first stage of this investigation, seven (9.6%) showed seroconversion during pregnancy (95% IC: 2.8-16.3), two (2.7%) showed acute serological infection and five (6.9%) presented markers of past infection. The final seroprevalence of PB19 infection during pregnancy was 72.5%. CONCLUSIONS: considering that only the acute PB19 infection is associated with risk for vertical transmission, the high seroprevalence of this infection observed in this study would be protecting these fetuses against this form of infection. Despite the relatively high rate of seroconversion against PB19 infection during the pregnancy period, we did not observe any symptomatic neonate in this group.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2016;38(7):348-355
To identify the epidemiological risk factors for congenital anomalies (CAs) and the impact of these fetal malformations on the perinatal outcomes.
This prospective cohort study comprised 275 women whose fetuses had CAs. Maternal variables to establish potential risk factors for each group of CA and perinatal outcomes were evaluated. The primary outcome was CA. Secondary outcomes included: fetal growth restriction (FGR); fetal distress (FD); premature rupture of membranes (PROM); oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios; preterm delivery (PTD); stillbirth; cesarean section; low birth weight; Apgar score < 7 at the 1st and 5th minutes; need for assisted ventilation at birth; neonatal infection; need for surgical treatment; early neonatal death; and hospitalization time. Chi-square (x2) test and multilevel regression analysis were applied to compare the groups and determine the effects of maternal characteristics on the incidence of CAs.
The general prevalence of CAs was of 2.4%. Several maternal characteristics were associated to CAs, such as: age; skin color; level of education; parity; folic acid supplementation; tobacco use; and history of previous miscarriage. There were no significant differences among the CA groups in relation to FGR, FD, PROM, 1-minute Apgar score > 7, and need for assisted ventilation at birth. On the other hand, the prevalence of the other considered outcomes varied significantly among groups. Preterm delivery was significantly more frequent in gastrointestinal tract/abdominal wall defects. The stillbirth rate was increased in all CAs, mainly in isolated fetal hydrops (odds ratio [OR]: 27.13; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 2.90-253.47). Hospitalization time was higher for the urinary tract and congenital heart disease groups (p < 0.01). Neonatal death was significantly less frequent in the central nervous system anomalies group.
It was possible to identify several risk factors for CAs. Adverse perinatal outcomes were presented in all CA groups, and may differ according to the type of CA considered.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(6):349-355
The new coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2, SARSCoV- 2) is a virus that causes a potentially serious respiratory disease that has spread in several countries, reaching humans in all age groups, including pregnant women. The purpose of this protocol is to provide technical and scientific support to Brazilian obstetricians regarding childbirth, postpartum and abortion care during the pandemic.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2014;36(9):387-392
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005053
To evaluate the cases of uterine rupture and dehiscence of the uterine scar at a low-risk maternity and to point out possibilities for an improved approach to these complications.
A descriptive study was conducted at a 30-bed low-risk maternity hospital that provides care to users of the public health system. The investigation was carried out by searching for cases in the delivery room registry book and later reading the medical records in order to obtain the data. The information was inserted on a form previously elaborated for this study. Cases of uterine rupure and dehiscence of the uterine scar diagnosed from 1998 to 2012 were included, with the determination of incidence, aspects related to risk factors and diagnosis, association with the use of misoprostol and oxytocin, and the outcomes observed.
A total of 39,206 deliveries were performed in this maternity during the study period, with 12 cases of uterine rupture and 16 cases of dehiscence of uterine scar being observed. The most relevant results were a high perinatal mortality associated with uterine rupture and the unsuccessful diagnosis of this complications. It was not possible to demonstrate an association with the use of misoprostol or oxytocin.
The adverse outcomes of uterine rupture could be minimized if efforts were directed at improving the diagnostic performance of the assisting teams.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2015;37(10):441-445
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(7):471-477
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000700007
Purpose: to assess the diagnostic and therapeutic aspects and the complications of symptomatic urinary tract infections (UTI) during pregnancy of patients who were hospitalized. Methods: a total of 136 pregnant women with a clinical diagnosis of pyelonephritis were studied. The studied parameters were: age and parity of patients, gestational age of diagnosis, epidemiologic aspects, laboratory evaluation for UTI, treatment and clinic evolution, prophylaxis and complications. Results: pyelonephritis was diagnosed at the same proportions at all gestational ages. The incidence of UTI was higher among primigravidae. Only 29.3% of the pregnant women had a previous history of UTI; 57.0% were anemic and 93.0% had altered urinalysis. Escherichia coli was the most prevalent uropathogen (75.8% of cases), with low percentages of sensitivity to ampicillin (60.6%) and high percentages of sensitivity to cefuroxime (95,5%). The highest rate of clinical improvement was obtained for the pregnant women treated with cefuroxime (95.7%). Prophylaxis was needed in 11.0% of the patients. Preterm labor occurred in 33.3% of the pregnant women who delivered in our service and preterm delivery occurred in 18.9%. Conclusions: the present results support the need for an early diagnosis and effective treatment of UTI in pregnant women in order to prevent the frequent occurrence of perinatal complications such as premature labor and delivery. We emphasize the need of a periodical evaluation of the pattern of sensitivity of the etiologic agents to the antimicrobials allowed for use during pregnancy, with cefuroxime being adopted as the antibiotic of choice for the treatment of UTI during pregnancy.