Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(7):349-352
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000700005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the ovarian reserve of infertile patients with severe ovarian endrometriosis, submitted to excisional surgery of endometriomas and attended from February to November, 2008. METHODS: prospective study, including 30 patients with endometriosis grades III and IV, with severe ovarian impairment, submitted to excisional surgery of the endometriomas, and 30 patients with endometriosis grades I and II, allocated as a Control Group. The ovarian reserve was indirectly assessed, through the basal (U/L) follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), between the third and fifth days of the cycle, 12 months after the surgery. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated according to Quetelet's formula [weight (kg)/height(cm²)]. The Mann-Whitney non-parametric U test was used to compare the variables "age", "BMI" and "basal SFH" between the groups. RESULTS: there was no significant difference between the groups about age and BMI. Concerning basal FSH, in the group of patients with severe endometriosis, the average value was 7.0 U/L, while in the Control Group, it was 5.6 U/L (p=0.3), what demonstrates that the difference between the two groups was not significant. CONCLUSIONS: the surgery did not affect the ovarian reserve of patients with severe ovarian endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):349-354
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700005
PURPOSE: to describe the prevalence and behavioral profile of genital infections in women attended at a Primary Health Unit in Vitoria, ES. METHODS: a transversal study including 14 to 49-year-old women attended by the Family Health Program (FHP). Exclusion criteria were: having been submitted to gynecological examination in less than one year before, and history of recent treatment (in the last three months) for genital infections. An interview including socio-demographic, clinical and behavioral data was applied. Genital specimens were collected for cytology, GRAM bacterioscopy and culture, and urine sample for molecular biological test for Chlamydia trachomatis. RESULTS: two hundred and ninety-nine women took part in the study. The median age was 30.0 (interquartile interval: 24;38) years old; the average age of the first intercourse was 17.3 (sd=3.6) years old. The first pregnancy average age was 19.2 (3.9) years old. About 70% reported up to 8 years of schooling; 5% reported previous Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD), and 8%, the use of illicit drugs. Only 23.7% reported consistent use of condoms. Clinical complaints were: genital ulcer (3%); dysuria (7.7%); vaginal discharge (46.6%): pruritus (20%) and pelvic pain (18%). Prevalence rates were: Chlamydia trachomatis 7.4%; gonorrhea 2%; trichomoniasis 2%; bacterial vaginosis 21.3%; candidiasis 9.3%; and cytological changes suggestive of HPV 3.3%. In the final logistic regression model, the factors independently associated to genital infections were: abnormal cervical mucus, OR=9.7 (CI95%=5.6-13.7), previous HIV testing, OR=6.5 (CI95%=4.0-8.9), having more than one partner during the previous year, OR=3.9 (CI95%=2.7-5.0), and having more than one partner in life, OR=4.7 (CI95%=2.4-6.8). CONCLUSIONS: results show a high rate of genital infections and the need of preventive measures, such as STD surveys and risk reduction programs for women that look for routine gynecological service.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):349-354
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500002
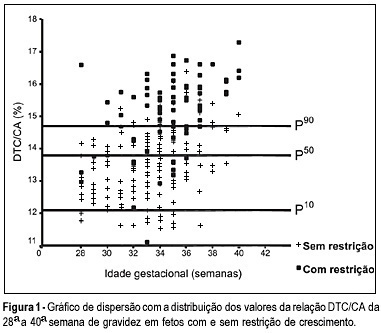
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the accuracy of both the transverse diameter of the cerebellum (TDC) and of the transverse diameter/abdominal circumference (TDC/AC) ratio in the detection of fetal growth restriction (FGR), in high-risk pregnancies. METHOD: a prospective cross-sectional study was carried out in 260 patients with gestational age between 28 and 40 weeks. The TDC and AC of fetuses were measured through ultrasound and the fetuses with TDC below the 10th percentile or TDC/AC ratio above the 90th percentile (>14.6) were classified as FGR suspects. After birth, the accuracy of the TDC and TDC/AC was evaluated using the neonatal diagnosis of FGR as the gold standard (birth weight <10th percentile). RESULTS: after birth, 79 newborns (30.4%) were classified as small for gestational age. The TDC was appropriate in 74 (93.7%) of these fetuses and small in only 5 (6.3%). The sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), positive (PPV) and negative (NPV) predictive values and accuracy of the TDC in the prediction of FGR were 6.3, 93.4, 29.4, 69.5, and 67%, respectively. The TDC/AC >14.6 correctly identified 59 of the 79 growth-restricted fetuses, with 27 false-positives and 20 false-negatives, SE of 74.5%, SP of 85.1%, PPV of 68.6%, NPV of 88.5% and 81.9% accuracy. CONCLUSION: the TDC is not a good screening parameter for the detection of FGR while the TDC/AC ratio above the 90th percentile is effective in this detection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(8):349-356
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000800003
PURPOSE: To characterize prenatal care and to evaluate the association of its adequacy with maternal, socioeconomic and environmental sanitation characteristics, as well as the influence of these factors on the birth weight of the children. METHODS: The eligible population for the study consisted of all women who had children during 2009 and lived in the city of Queimadas at the time of data collection. Information was collected with a questionnaire applied to the mothers in Family Health Basic Units or in their residence. The prenatal care adequacy index (outcome variable) was defined as adequate when the mother attended six or more prenatal visits and began monitoring during the first trimester of pregnancy (<20 weeks). Hierarchical logistic regression was performed to estimate the odds ratios for inadequate prenatal care and a multiple linear regression model was used to estimate the effect of adequacy of prenatal care and maternal, socioeconomic and environmental sanitation variables on birth weight. The statistical program used was Rv2.10.0, with the level of significance set at p <5%. RESULTS: Of a total of 199 women studied, 78.4% were classified as having received adequate prenatal care. After adjustment for other predictors, maternal age of 19 years or less remained as an explanatory variable of inadequate prenatal care (OR 4.27, 95%CI 1.10 - 15.89). Even after controlling for variables, child's birth weight was negatively associated with water supply from a well/spring and burnt/buried garbage, accounting for weight reductions of the order of 563.8, 262.0 and 951.9 g, respectively. CONCLUSION: Adequate prenatal care can alleviate the influence of socioeconomic disparities related to health care. Even in this situation, teenage mothers are more likely to receive inadequate prenatal care and low birth weight is favored by improper sanitation conditions (such as water supply and garbage disposal).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(6):349-354
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000600002
Purpose: to evaluate the histopathologic results of cone specimens of patients undergoing loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) and their relationship with the localization of the lesion. Methods: in a retrospective study, 134 clinical reports of patients with abnormal findings of cervical cytology and/or biopsy undergoing LEEP were reviewed. The colposcopic findings were divided into three groups according to the localization of the lesion. Group I (n = 36): patients with ectocervical lesions and fully visible squamocolumnar junction; Group II (n = 50): patients with lesions at the ectocervix and endocervix, and Group III (n = 48): patients with unsatisfactory colposcopy. Results: the mean age in Group I was 33 years and there were 8.3% positive margins. In Group II the mean age was 39 years, with 36% positive margins. Group III had a mean age of 48 years and presented 29.2% positive margins. The percentage of residual disease was 4.2% in Group I, 31.6% in Group II and 35.5% in Group III. Conclusion: patients with lesions at the endocervical canal showed a higher rate of positive margins. Patients with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia at the endocervical canal and older than 40 years have a greater chance of showing positive margins and residual disease, therefore requiring stricter cytologic and colposcopic follow-up.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):349-355
The new coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2, SARSCoV- 2) is a virus that causes a potentially serious respiratory disease that has spread in several countries, reaching humans in all age groups, including pregnant women. The purpose of this protocol is to provide technical and scientific support to Brazilian obstetricians regarding childbirth, postpartum and abortion care during the pandemic.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):349-349
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000500011
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):349-349