Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):329-335
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400011
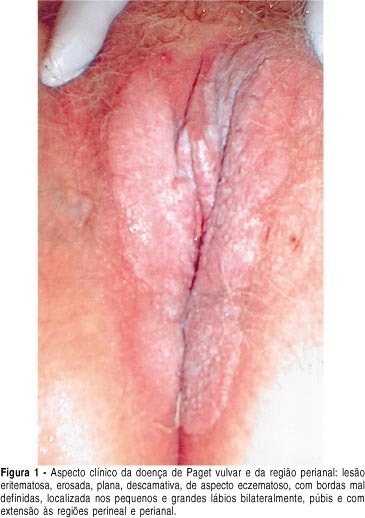
Extramammary Paget's disease (EPD) is an uncommon neoplasic condition observed mostly in areas with numerous apocrine and or eccrine glands. In the woman it is most commonly seen on the vulva, although it can occur in other locations. Vulvar Paget's disease (VPD) can be classified into primary, of cutaneous origin, and secondary, of extracutaneous origin, with significant clinical e prognostic implications. Clinically VPD begins insidiously with pruritus and burning sensation. The lesion appears as a solitary patch with an eczematous, erythematous and squamous surface. This is a report of a case of a 72-year-old patient with an erythematous slightly thickened patch lesion with spots of erosion involving both the right and the left majus and minus labia, the clitoris, the pubic region, and the perineal and perianal regions. The operation performed included radical vulvectomy and bilateral inguinal lymphadenectomy. The histopathology revealed invasive Paget's disease. Immunohistochemical methods showed positive Paget cells for CEA, EMA, and cytokeratin pan. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of EPD is discussed, with differential diagnosis and reference to immunohistochemical methods. Recurrence rate is 30%, even with margin control. Experience with EPD is limited and long-term follow-up is required to exclude recurrence of the disease and development of an associated cancer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):33-38
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100007
PURPOSE: To create longitudinal reference intervals for pulsatility index (PI) of the umbilical (UA), middle cerebral (MCA), uterine (UtA) arteries and ductus venosus (DV) in a Brazilian cohort. METHODS: A longitudinal observational study performed from February 2010 to May 2012. Low risk pregnancies were scanned fortnightly from 18 to 40 weeks for the measurements of PI of the UA, MCA, DV and UtA. Linear mixed models were used for the elaboration of longitudinal reference intervals (5th, 50th and 95th percentiles) of these measurements. PI obtained for the placental and abdominal portions of the umbilical artery were compared by the t-test for independent samples. Two-sided p values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS: A total of 164 patients underwent 1,242 scans. There was significant decrease in PI values of all vessels studied with gestational age (GA). From the 18th to the 40th week of pregnancy, the median PI values of UA (abdominal and placental ends of the cord), MCA, DV and the mean PI of the UtA ranged from 1.19 to 0.74, 1.33 to 0.78, 1.56 to 1.39, 0.58 to 0.41, and 0.98 to 0.66, respectively. The following equations were obtained for the prediction of the medians: PI-UA=1.5602786 - (0.020623 x GA); Logarithm of the PI-MCA=0.8149111 - (0.004168 x GA) - [0.02543 x (GA - 28.7756)²]; Logarithm of the PI-DV=-0.26691- (0.015414 x GA); PI-UtA = 1.2362403 - (0.014392 x GA). There was a significant difference between the PI-UA obtained at the abdominal and placental ends of the umbilical cord (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: Longitudinal reference intervals for the main gestational Doppler parameters were obtained in a Brazilian cohort. These intervals could be more adequate for the follow-up of maternal-fetal hemodynamic modifications in normal and abnormal pregnancies, a fact that still requires further validation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(1):33-37
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000100006
Purpose: to evaluate the agreement between the urodynamic and ultrasonography diagnoses of urinary incontinence, as well as to correlate the variables of both examinations. Methodology: three hundred eighty-one patients with urine loss were selected, from the Sectior of Urogynecology and Vaginal Surgery of the Division of Gynecology, Escola Paulista de Medicina - Federal University of São Paulo. All of them were submitted to urodynamic study, according to the standardization of the International Society of Continence, and to ultrasonography of the bladder neck, with a 6 MHz trasvaginal transducer. We analyzed the maximum closing urethral pressure (MCUP) and the etiological diagnosis of the urine loss. In the ultrasonography, the position of the bladder neck was evaluated in relation to the inferior border of the pubic symphysis, and its mobility as well as the diameter of the urethra and bladder neck. The women were categoriaed according to the urodynamic study in to stress urinary incontinence, detrusor instability and mixed urinary incontinence. Results: 1) the bladder neck, at rest was most frequently above the inferior border of the pubic symphysis and, during effort, below or at the height of the bony reference, in the three groups; 2) the mobility of the bladder neck was similar in the groups; 3) there was no significant correlation between MCUP and the diameter of the urethra and of the bladder neck. Conclusion: we deem that ultrasonography of the bladder neck is always a complement to the clinical evaluation and the urodymanic study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(1):33-36
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000100006
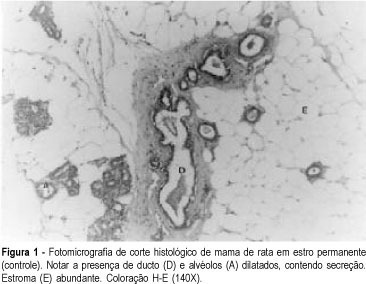
Purpose: to evaluate the morphologic and morphometric alterations produced by tamoxifen and conjugated estrogens in the mammary epithelium of rats in persistent estrus. Methods: thirty-three adult female rats in persistent estrus induced with 1.25 mg testosterone propionate were divided at random into three groups: GI -- which received only water, control group (n = 12); GII -- treated with 500 mug tamoxifen daily (n = 10); GIII -- treated with 30 mug conjugated estrogens per day (n = 11). The first inguinal-abdominal pair of mammary glands of the animals was extirpated and processed for morphologic and morphometric study. Data were analyzed statistically by the Kruskal-Wallis rank analysis of variance (p < 0.05). Results: the morphologic study revealed signs of epithelial atrophy and the morphometric study showed a statistically significant reduction in the mean number of ducts and alveoli in groups II (10.1 and 1.9, respectively) and III (11.1 and 3.5, respectively) compared to group I (25.0 and 6.6, respectively). There was no significant difference between groups II and III. Conclusions: the results of this study indicate that tamoxifen as well as conjugated estrogens at the tested doses produced mammary epithelial atrophy in rats in persistent estrus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):33-35
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100006
We have analyzed 93 pregnant women with Papanicolaou smears suggesting human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (Schneider et al's criteria) with the purpose of studying the effect of maternal age, stage of pregnancy and number of pregnancies on the incidence of this infection. The control group consisted of 93pregnant women with Papanicolaou smears not suggestive of HPV infection. The results demonstrated that HPV infection is associated with pregnant women under 20 years of age, but no differences were found regarding stage and number of pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):330-336
To assess the impact of pre-pregnancy obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) on the gestational and perinatal outcomes.
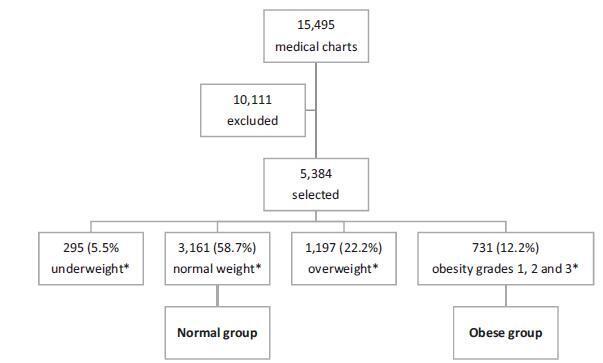
Retrospective cohort study of 731 pregnant women with a BMI ≥30 kg/m2 at the first prenatal care visit, comparing them with 3,161 women with a BMI between 18.5 kg/m2 and 24.9 kg/m2. Maternal and neonatal variables were assessed. Statistical analyses reporting the demographic features of the pregnant women (obese and normal) were performed with descriptive statistics followed by two-sided independent Student’s t tests for the continuous variables, and the chi-squared (χ2) test, or Fisher’s exact test, for the categorical variables. We performed a multiple linear regression analysis of newborn body weight based on the mother’s BMI, adjusted by maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertensive disorders, and cesarean deliveries to analyze the relationships among these variables. All analyses were performed with the R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) for Windows software, version 3.1.0. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Obesity was associated with older age [OR 9.8 (7.8-12.2); p < 0.01], hyperglycemic disorders [OR 6.5 (4.8-8.9); p < 0.01], hypertensive disorders [OR 7.6 (6.1-9.5); p < 0.01], caesarean deliveries [OR 2.5 (2.1-3.0); p < 0.01], fetal macrosomia [OR 2.9 (2.3-3.6); p < 0.01] and umbilical cord pH [OR 2.1 (1.4-2.9); p < 0.01). Conversely, no association was observed with the duration of labor, bleeding during labor, Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes after birth, gestational age, stillbirth and early neonatal mortality, congenital malformations, and maternal and fetal injury.
We observed that pre-pregnancy obesity was associated with maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertension syndrome, cesarean deliveries, fetal macrosomia, and fetal acidosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):331-339
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the epidemiologic data and signs of trophoblastic hyperplasia in patients with complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) and to estimate the risk associated with the persistence of the disease. METHODS:: we evaluated 214 patients with CHM submitted to uterine evacuation between 1980 and 2001. The patients were included prospectively. All patients were followed until negative bHCG with weekly clinical evaluation and bHCG quantification. We considered persistence when the patient needed another treatment after uterine evacuation. The risk factors for persistence were evaluated through univariate and multivariate analysis, and the odds ratio (OR) was calculated for each one. RESULTS: among the epidemiologic factors, only negative Rh was significant (OR=2.28). All signs of trophoblastic hyperplasia, represented by uterine size larger than expected, sonographic uterine volume, tecaluteinic cysts, and betaHCG higher than 10(5) were associated with risk for the presistence of the disease. The presence of at least one sign of trophoblastic hyperplasia showed sensitivity of 82% and predictive positive value of 35.1% (OR=4.8). The logistic regression identified larger uterine size than expected and bHCG higher than 10(5) as risk factors for persistence of the gestational trophoblastic disease (OR=4.1 and 5.5, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: the signs of trophoblastic hyperplasia showed good sensitivity to predict persistence of the disease; however, the low predictive positive value does not allow using these criteria to change treatment. It is very important to reinforce the importance of serial betaHCG quantification in these high-risk patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):331-335
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500005
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether there is an association between recurrent spontaneous abortion and atopy. METHODS: this was a case-control study with 230 women: 71 with a history of recurrent spontaneous abortion (group A) and 159 with a history of successful pregnancy (group B). The evaluation included a questionnaire in order to investigate the personal history of atopy, considering symptoms of atopic dermatitis, urticaria, rhinitis, asthma, conjunctivitis and gastric or intestinal symptoms. The presence of specific IgE in response to a pool of inhalants, Phadiatop, detected by an enzymatic fluorescence reaction in blood was also investigated. The data were analyzed by Fisher's exact test and a p value < 0.05 was set as level of significance. RESULTS: a positive history of atopy was observed in 57.7% of group A patients and in 55.3% of group B patients. The incidence of positive IgE against Phadiatop was 38% and 33.9% in groups A and B, respectively. Association of allergy disease with positive Phadiatop (presence of specific IgE) was detected in 28.2% of group A and in 22% of group B patients. There was no significant difference between the groups. CONCLUSIONS: we did not observe any association between recurrent spontaneous abortion and atopy.