Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):310-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700004
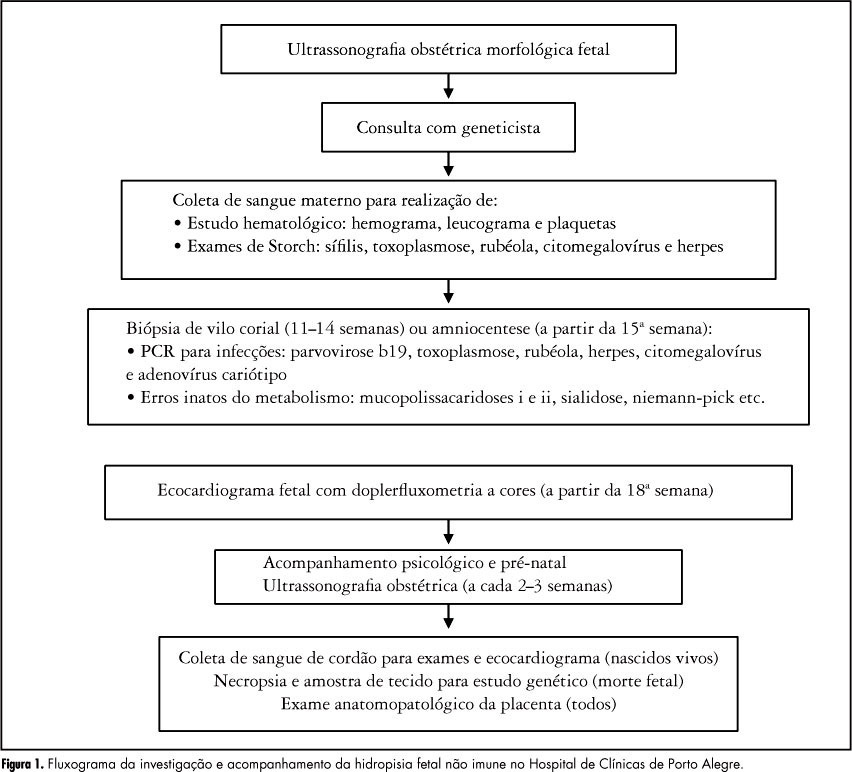
PURPOSE: To identify the etiology of nonimmune hydrops fetalis cases in pregnant women diagnosed and referred for prenatal care. METHODS: Retrospective analysis of cases with nonimmune hydrops fetalis that were monitored between March 1992 and December 2011. Diagnosis was confirmed by the presence of fetal subcutaneous edema (≥5 mm) with effusion in at least one serous cavity using obstetric ultrasound, and etiological investigation was conducted with cytogenetic (karyotype), infectious (syphilis, parvovirus B19, toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, adenovirus and herpes simplex), hematologic and metabolic (inborn errors) analysis and fetal echocardiography. Twin pregnancies were excluded. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ² test for adhesion (software R 2.11.1). RESULTS: We included 116 patients with nonimmune hydrops fetalis; the etiology was elucidated in 91 cases (78.5%), while 25 cases (21.5%) were classified as idiopathic. Most cases had a chromosomal etiology, for a total of 26 cases (22.4%), followed by lymphatic etiology with 15 cases (12.9% with 11 cases of cystic hygroma), and cardiovascular and infectious etiology with 14 cases each (12.1%). In the remaining cases, the etiology was thoracic in 6.9% (eight cases), malformation syndromes in 4.3% (five cases), extrathoracic tumors in 3.4% (four cases), metabolic in 1.7% (two cases), and hematologic, gastrointestinal and genitourinary in 0.9% (one case each). During the postnatal period, 104 cases were followed up until the 40th day of life, and 12 cases had intrauterine fetal death. The survival rate of these 104 newborns was 23.1% (24 survived). CONCLUSION: An attempt should be made to clarify the etiology of hydrops diagnosed during pregnancy since the condition is associated with a wide spectrum of diseases. It is especially important to determine whether a potentially treatable condition is present and to identify disease at risk for recurrence in future pregnancies for adequate pre-conception counseling.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(6):310-316
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000600008
PURPOSE: To compare the metabolic characteristics of obese and non-obese young women with polycystic ovary syndrome (POS) from the Brazilian Southeast. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study conducted on 218 women of reproductive age with a diagnosis of POS - 90 non-obese women (BMI between 18.5 and 29.9 kg/m²), and 128 obese patients (BMI >30 kg/m²) selected at the time of diagnosis. The frequency of insulin resistance (IR), glucose intolerance (GI), metabolic syndrome (MetS) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) and mean values of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL), were compared between obese and non-obese patients with POS. The two groups were also compared in terms of clinical and hormonal characteristics (follicle stimulating hormone, prolactin, thyroid stimulating hormone, total testosterone, dihydroepiandrostenedione sulfate, and 17-hydroxyprogesterone). Statistical analysis was performed using the SAS 9.0 software. Quantitative variables were compared by the Student´s t-test (data with normal distribution) or by the Mann-Whitney test (non-parametric distribution). Qualitative variables were compared by the Fisher test. The level of significance was set at 5% (p<0.05) in all analyses. RESULTS: The frequency of IR, GI and MetS was significantly higher in obese than non-obese patients with POS (66.7, 29.9, and 63% versus 24.7, 12.2, and 16.4%, respectively). Obese patients had higher TC and TG levels (189.8±35.8 mg/dL and 145.4±71.1 mg/dL, respectively) than non-obese patients (172.1±38.4 mg/dL and 99.3±54 mg/dL, respectively). Both groups had mean HDL levels below 50 mg/dL. CONCLUSIONS: Young obese women with POS have a higher frequency of IR, GI and MS than non-obese. However, the occurrence of metabolic disorders is elevated also in the non-obese patients, suggesting that the presence of the syndrome may favor the development of metabolic comorbidities with potential medium- and long-term repercussions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):310-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500008
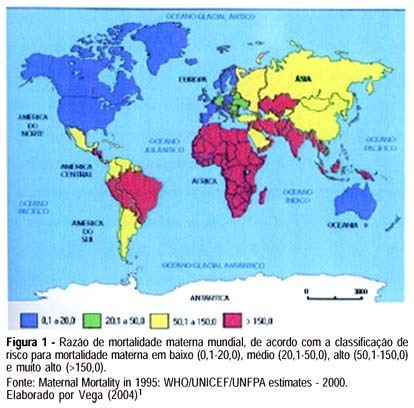
Maternal mortality rate (MM) is a health quality indicator that is directly influenced by the economic, cultural and technological level of a country. Official data of MM in Brazil, although underestimated, point to the lack of quality in pregnancy, childbirth and puerperium care services. This characteristic is common in developing countries, where poorer pregnant women as well as those facing greater difficulty to quality care access are found. Prenatal care cannot prevent major childbirth complications, which are important causes of MM; however, some interventions during the prenatal period can favor maternal prognosis and prevent MM. In this setting, this study brings a scientifically based update concerning effective interventions for maternal mortality prevention during the prenatal period. The most important strategies consist of a tripod with specific interventions related to maternal health promotion, risk prevention and assurance of nutritional support during gestation, in addition to criteria to investigate gestational risk and inclusion of the pregnant woman in the basic component of the prenatal care model. It ends with the definition of priorities in the prevention of MM related to eclampsia/preeclampsia and reinforces the importance of normalization of reference systems for obstetric emergency cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):311-311
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500010
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):311-311
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500011
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):311-316
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400008
OBJECTIVE: to assess the concordance of different urodynamic parameters with simplified cystometry, thus improving the cost-benefit relationship for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) diagnosis in woman. METHODS: we evaluated retrospectively the medical records of thirty patients treated, from January 2000 to March 2001. All patients had been submitted to physical and gynecological examinations. A conventional urodynamic study had been made using a Dynograph R-611 recorder. Simplified cystometry had used a saline tube with "Y" connector, connected to a Foley 14 Fr catheter, which allowed measurement of intra-vesical pressure at the same time as physiological saline infusion. The following parameters were analyzed: residual volume, bladder capacity, complacency, involuntary detrusor contractions, and abdominal leak-point pressure. The Pearson test of agreement and the Wilcoxon signed rank test were used to verify the concordance between related samples, with p < 0,05. RESULTS: the average age was 50 years old (28-70). Concordance between studies for stress urinary losses was 67%, and for detrusor involuntary contractions, 90%. The average residual volume was significantly different: by simplified cystometry it was 16.8 ml versus 2 ml by conventional urodynamics (p < 0.01). The average maximum vesical capacity by urodynamic study was 440.5 ml, and by simplified cystometry, 387 ml (p < 0.05). Vesical complacency was on average, significantly larger in simplified cystometry (43.0 ml/cmH2O) than in the urodynamic study (31.5 ml/cmH2O), with p < 0.01. CONCLUSION: preliminary evaluations suggest that the urogynecologic propedeutic associated with cystometry is an option to be considered in the clinical and preoperative assessment of patients with SUI instead of conventional urodynamics, particularly when the latter is not available. Simplified cystometry is an accessible exam that grants comparable results for the detection of involuntary detrusor contractions and for the identification of urinary loss, providing the examiner with trustworthy data on vesical behavior.
Summary
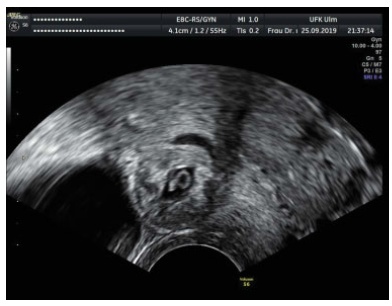
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):311-316
A cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) is a scary and life-threatening complication of cesarean section (CS). Nevertheless, the incidence of CS is constantly growing. The CSP incidence is 0,15% of pregnancies after CS which represents 6,1% of all ectopic pregnancies in women with condition after CS. Therefore, it should be more present in the clinical daily routine. From mild nonspecific symptoms to hypovolemic shock, diagnosis and therapy must be performed quickly. With the progressive growth of the scar pregnancy, a uterine rupture involves the risk of severe bleeding, and an emergency hysterectomy could be necessary. Prolongation of pregnancy has been successful only in a few cases.We report 11 cases from our hospital in the past 10 years. In the discussion, treatment options of this complication with an increasing incidence, which is associated with serious morbidity and mortality, are presented based on the current literature. Treatment options include drug therapy, but also surgical or combined procedures with radiological intervention.