Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):283-290
Cesarean section (CS) delivery, especially without previous labor, is associated with worse neonatal respiratory outcomes. Some studies comparing neonatal outcomes between term infants exposed and not exposed to antenatal corticosteroids (ACS) before elective CS revealed that ACS appears to decrease the risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), transient tachypnea of the neonate (TTN), admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and the length of stay in the NICU.
The present retrospective cohort study aimed to compare neonatal outcomes in infants born trough term elective CS exposed and not exposed to ACS. Outcomes included neonatal morbidity at birth, neonatal respiratory morbidity, and general neonatal morbidity. Maternal demographic characteristics and obstetric data were analyzed as possible confounders.
A total of 334 newborns met the inclusion criteria. One third of the population study (n=129; 38.6%) received ACS. The present study found that the likelihood for RDS (odds ratio [OR]=1.250; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.454-3.442), transient TTN (OR=1.,623; 95%CI: 0.556-4.739), and NIUC admission (OR=2.155; 95%CI: 0.474-9.788) was higher in the ACS exposed group, although with no statistical significance. When adjusting for gestational age and arterial hypertension, the likelihood for RDS (OR=0,732; 95%CI: 0.240-2.232), TTN (OR=0.959; 95%CI: 0.297--3.091), and NIUC admission (OR=0,852; 95%CI: 0.161-4.520) become lower in the ACS exposed group.
Our findings highlight the known association between CS-related respiratory morbidity and gestational age, supporting recent guidelines that advocate postponing elective CSs until 39 weeks of gestational age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):283-290
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005292
To determine the basic expression of ABC transporters in an epithelial ovarian cancer cell line, and to investigate whether low concentrations of acetaminophen and ibuprofen inhibited the growth of this cell line in vitro.
TOV-21 G cells were exposed to different concentrations of acetaminophen (1.5 to 15 μg/mL) and ibuprofen (2.0 to 20 μg/mL) for 24 to 48 hours. The cellular growth was assessed using a cell viability assay. Cellular morphology was determined by fluorescence microscopy. The gene expression profile of ABC transporters was determined by assessing a panel including 42 genes of the ABC transporter superfamily.
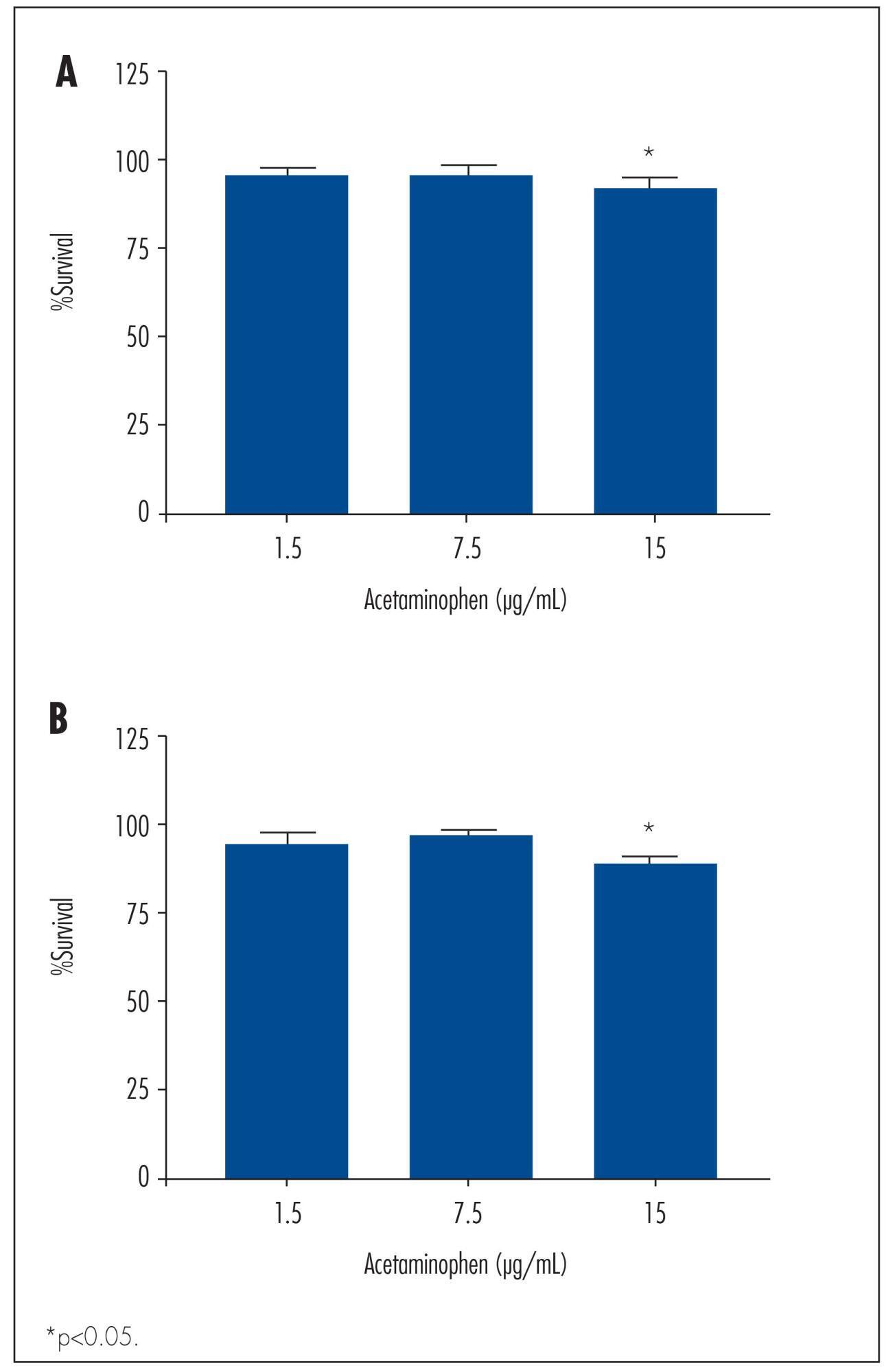
We observed a significant decrease in TOV-21 G cell growth after exposure to 15 μg/mL of acetaminophen for 24 (p=0.02) and 48 hours (p=0.01), or to 20 μg/mL of ibuprofen for 48 hours (p=0.04). Assessing the morphology of TOV-21 G cells did not reveal evidence of extensive apoptosis. TOV-21 G cells had a reduced expression of the genes ABCA1, ABCC3, ABCC4, ABCD3, ABCD4 and ABCE1 within the ABC transporter superfamily.
This study provides in vitro evidence of inhibitory effects of growth in therapeutic concentrations of acetaminophen and ibuprofen on TOV-21 G cells. Additionally, TOV-21 G cells presented a reduced expression of the ABCA1, ABCC3, ABCC4, ABCD3, ABCD4 and ABCE1 transporters.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):283-289
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):283-288
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000500009
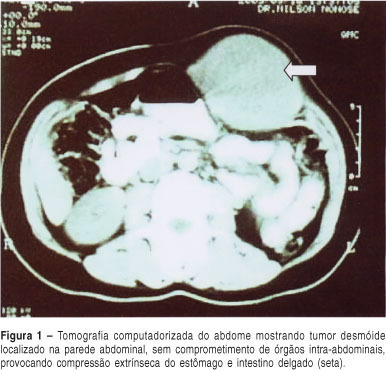
Desmoid tumors are neoplasms of the conjunctive tissue that are characterized by exclusive locoregional growth, frequent recurrence and minimal metastatic potential. They mainly affect individuals with familial adenomatous polyposis of the colon, and rarely occur isolated. The single form of this neoplasm most frequently appears in women of reproductive age, and during pregnancy. A case of a desmoid tumor of large proportions located in the abdominal wall is described. It appeared at the 17th week of pregnancy in a woman without any history of familial adenomatous polyposis. The neoplasm was totally extirpated, with the use of a polypropylene prosthesis for reconstitution of the abdominal wall. One year after the surgery, the patient continues to be well, while using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of relapses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(4):283-288
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000400010
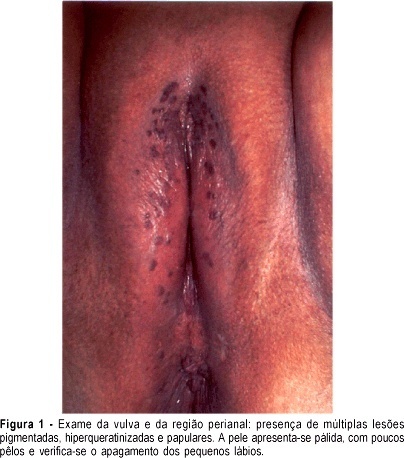
High-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN III) is a visible lesion; therefore, it is accessible to biopsy and thus, to a histological diagnosis. There are two forms of vulvar cancer precursors: VIN caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and VIN associated with untreated lichen simplex chronicus, squamous cell hyperplasia, and lichen sclerosus. There may be overlap of the two forms. The term bowenoid papulosis, although discouraged, identifics a clinical form of VIN III. Such lesion appears as pigmented, wart-like growths or papules. VIN III is associated with HPV in more than 80% of the cases, and there is perianal involvement in 40% of the times. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia is difficult to cure and relapses can occur at any time for many years. Although there is no defined standard treatment, studies point to surgery, respecting a free margin, as the most adequate one.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(6):285-292
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000600004
PURPOSE: to investigate the main factors associated with fetal death in the city of Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil. METHODS: an observational, case-control study, including cases attended from June 1st 2004 to 31st March 2005. A number of 116 stillbirth cases and 472 live birth controls, with deliveries assisted at the service, were included. The cases were identified in the record book from the delivery room. The puerperium women were identified by the name and register number at a puerperium infirmary. The controls were selected, using the puerperium infirmary neighborhood criterion, identifying the beds with numbers immediately lower (two patients) and higher (two patients) than the patient's, as far as they had delivered live babies. In case they did not agree to participate in the research, the next beds with numbers consecutively lower or higher were approached. The χ2 association and Fisher's exact tests were used when necessary to test the association between the independent (predictive) and dependent (stillborn) variables, considering 5% as the significance level. To determine the association strength, the estimate of relative risk for case-control cases, Odds Ratio (OR) was used, with 95% as the confidence interval (CI). Logistic regression analysis according to the hierarchy model was done to control confounding factors. RESULTS: the fetal mortality rate corresponded to 24.4 by 1,000 births. After the multivariate analysis, the variables which kept significantly associated with fetal death were: malformation (OR=7.5; CI=3.2-17.4), number of pre-natal appointments lower than six (OR=4.4; CI=2.5-7.5), hemorrhagic syndromes (OR=2.9; CI=1.4-5.7), attendance in another hospital unit along the 24 hours which preceded the patient's admission in the institution (OR=2.9; CI=1.8-4.6), mothers' age over or equal to 35 years old (OR=2.2; CI=1.0-4.9) and schooling lower than eight years (OR=1.6; CI=1.02-2.6). CONCLUSIONS: it was found a high fetal mortality coefficient, the main factors associated with death were: malformation, number of pre-natal appointments lower than six, hemorrhagic syndromes, history of attendance previous to the hospital admission, mothers' age over or equal to 35 and schooling lower than eight years.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):285-289
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000600008
Extrauterine leiomyomas are rare, benign, and may arise in any anatomic sites. Their unusual growth pattern may even mimic malignancy and can result in a clinical dilemma. Occasionally, uterine leiomyomas become adherent to surrounding structures. They also develop an auxiliary blood supply, and lose their original attachment to the uterus, thus becoming 'parasitic'. Parasitic myomas may also be iatrogenically created after uterine fibroid surgery, particularly if morcellation is used. This report presented two cases of parasitic myomas with sepsis, both requiring right hemicolectomy. It reviewed the pertinent literature.
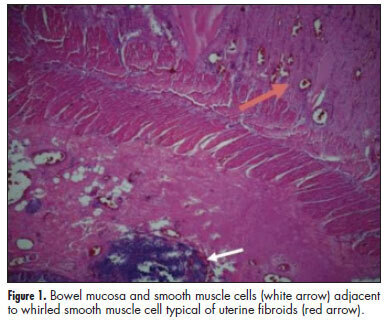
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):285-291
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500004
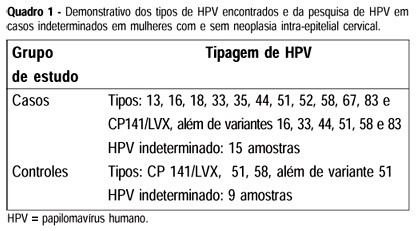
PURPOSE: to identify risk factors for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and human papillomavirus (HPV) types among women with CIN, and to compare with HPV types among patients with normal cervix. METHODS: a total of 228 patients were studied, of whom 132 with CIN (cases) and 96 with normal cervix (controls). In the two groups consisting of women selected among outpatients attended in the same hospital, living near the place of the research, mean ages were similar (34.0±8.3 years) and there was a predominance of married women. Possible risk factors for CIN were investigated with the application of a questionnaire surveying age, marital status, level of schooling, age at first coitus, number of pregnancies, number of sexual partners, method of used contraception, reference of previously sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and smoking habits, with a comparison between the studied groups. Samples were collected for oncologic colpocytology and HPV search through polymerase chain reaction (PCR), using MY09/MY11 primers; then colposcopic and histopathological examinations were performed. For statistical analysis of the association between risk factors and CIN, odds ratio with 95% confidence interval and chi2 and Fisher tests were used at a significance level of 0.05. The logistic regression method with the significance expressed by the p value with maximum likelihood was also applied. RESULTS: the following variables remained in the logistic regression model: HPV infection of high oncogenic risk (OR=12.32; CI 95%: 3.79-40.08), reference of previous STDs (OR=8.23; CI 95%: 2.82-24.04), early age at first coitus (OR=4.00; CI 95%: 1.70-9.39) and smoking habit (OR=3.94; CI 95%: 1.73-8.98). PCR was positive in 48.5 and 14.6% in the case and control groups, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: the main risk factor for CIN was oncogenic HPV infection, with types 16, 18, 33, 35, 51, 52, 58, and 83. Among patients with a high-degree lesion, there was a predominance of HPV-16 or type 16 variant. In patients with normal cervix oncogenic, HPV types 51, 58, and 51 variant were also identified.