Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):245-249
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500003
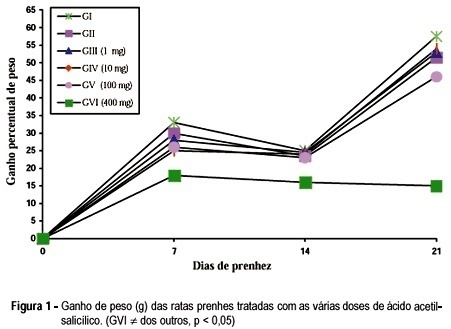
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effects of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) on the pregnancy of female albino rats. We used 60 pregnant female rats which were divided into six groups of ten cache. All the animals received daily by gavage, from the 5th (day zero) until the 20th day of pregnancy, 1 ml of the following: Group I - only distilled water (control); Group II - 0.2% aqueous solution of carboxymethylcellulose (vehicle); Groups III, IV, V and VI - 1, 10, 100 and 400 mg/kg body weight respectively, of ASA diluted in 0.2% carboxymethylcellulose solution. The animals were weighed on days 0, 7, 14 and 20 of pregnancy. Our results showed that the animals treated with 100 mg of ASA presented a reduction in the number of live newborns. The animals treated with 400 mg/kg/day presented not only a reduction in the number of live newborns but also decrease in maternal, newborn and placental weight.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):245-250
The aim of the present retrospective study was to investigate the effectiveness of single-dose gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist administration, the day after human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) triggering for final oocyte maturation, on the prevention of premature luteinization in patients with diminished ovarian reserve in in-vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles. The secondary objective of the study was to search the effect of this protocol on pregnancy outcomes.
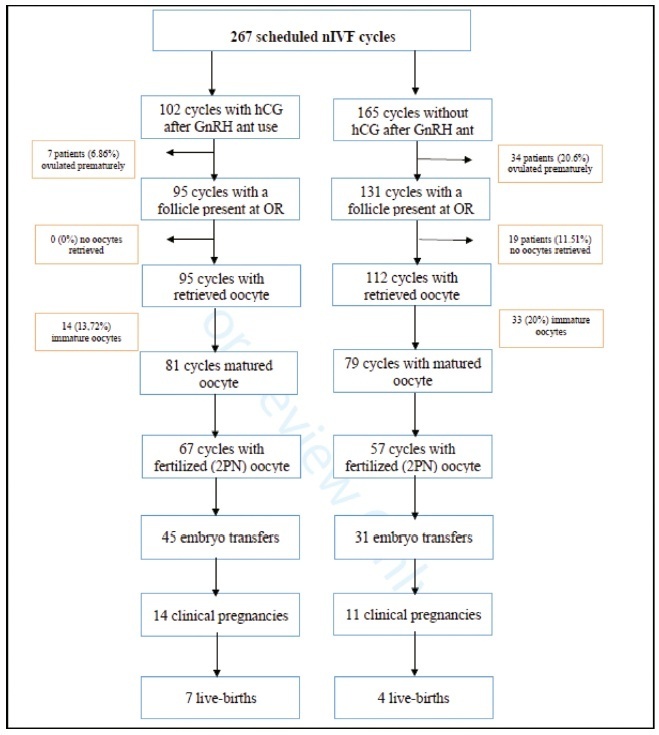
This is a retrospective study including 267 infertile patients who have single antral follicle seen with ultrasonography on the 2nd or 3rd day of the menstrual cycle before starting IVF treatment. We randomized patients into two groups. The case group comprised patients who had single-dose GnRH antagonist injection the day after hCG triggering formed, and the patients who had the standard treatment regime formed the control group. In both groups, the oocytes were collected 36 hours after hCG injection.
The premature ovulation rate was significantly low in the case group compared with the control group (6.86 versus 20.6% per scheduled cycle) (p=0.022). Also, the oocyte retrieval rate (93.14 versus 67.87% per scheduled cycle) (p=0.013), the oocyte maturity rate (79.42 versus 47.87%) (p=0.041), the fertilization rate (65.68 versus 34.54%) (p=0.018), and the embryo transfer rate per scheduled cycle (44.11 versus 18.78%) (p=0.003) were higher in the GnRH antagonist group than in the control group.
The administration of GnRH antagonist the day after hCG trigger in IVF treatments of patients with diminished ovarian reserve enabled a significant decrease in the rate of premature ovulation but had no effect on live birth rate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):245-247
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):245-245
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400015
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):245-245
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400014
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(5):246-251
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000500007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of cytogenetic alterations and chromosomic polymorphism in couples with a subfertility phenotype in a Brazilian population. METHODS: karyotype analysis through G and C banding of 1,236 individuals who presented the subfertility phenotype, from two different centers (public and private) were included in the study. These patients were classified in two sub-groups: one with two or more gestational consecutive losses or not and the o with, at least, one gestacional loss or absence of conception. Karyotype results were evaluated in different groups and frequencies were calculated. Statistical analyses were carried out through Fisher's exact test and Odds Ratio analysis. RESULTS: approximately 25% of the cases presented abnormal karyotype results, including numerical and structural alterations and also polymorphic variants. In both centers, the prevalence of polymorphic variants was 8.9 and 3.8%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: there was no significant difference between the prevalence of polymorphic variants and other abnormalities in individuals with or without previous history of reproductive loss. The results of the present study reinforce the need of adequate disclosure of complete cytogenetic information in the karyotype results, with specific attention in relation to the polymorphic variants.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(9):246-251
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000900005
PURPOSE: To estimate the prevalence of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy and to identify maternal factors associated with its consumption. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study with 280 women from the city of Diamantina (MG), Brazil. The dependent variable was use of a folic acid supplement during pregnancy, and the independent variables were age and maternal schooling, number of prenatal care visits, parity, marital status and presence or absence of anemia. Poisson regression analysis was used to assess the association of independent variables with the dependent variable. RESULTS: Women with less education, adolescents, and number of prenatal visits less than seven were 1.61 (95%CI=1.34-1.93), 1.18 (95%CI=1.03-1.35) e 1.18 (95%CI=1.02-1.37) more likely not to consume the supplement during pregnancy, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of consumption of folic acid among pregnant women was low, associated with maternal age and education and number of prenatal visits.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):246-252
to evaluate the quality of life of HIV positive (HIVþ) pregnant women using the HIV/AIDS Target Quality of Life (HAT-QoL) instrument.
cross-sectional study, conducted between May 2014 and November 2015 , with HIVþ pregnant women selected by convenience sampling. Sociodemographic and behavioral data were collected through interviews, and the HAT-QoL questionnaire was applied. Clinical and laboratorial data were collected from medical records.
twenty-seven pregnant women participated in the study. Their mean age was 27 years (standard deviation - SD: 7.3). The majority (59%) had up to 8 years of education, 52% identified themselves as white, 56% were unemployed, and 59% had a household income higher than the minimum wage. The mean infection time by the virus was 68.4 months (5.7 years). The majority (74%) were contaminated with HIV through sexual intercourse, and 67% declared not having a HIVþrelative. Regarding the use of condoms, 41% reported using them sporadically, and the same number did not have proper knowledge about them. Only 23 patients (85%) reported having been prescribed antiretrovirals. Fourteen (64%) had a CD4 count higher than 500 cells/mm3, and 13 pregnant women (59%) had an undetectable viral load. The scores from the quality of life questionnaire dimensions that were more affected are: infection "disclosure concerns" (mean: 39.8; SD: 27.1), followed by "financial concerns" (mean: 49.1; SD: 36), and "HIV acceptance" (mean: 49.1; SD: 35.8). The dimension with the best score was "medication concerns" (mean: 80.8; SD: 26.5).
quality of life has been increasingly used as a clinical outcome evaluation parameter. The results of this study contribute to the establishment of interventions based on the needs of HIVþ pregnant women.