Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):241-241
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(5):241-246
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500007
PURPOSE: to assess the knowledge, attitude and practice of breast self-examination (BSE) of women from the municipality of São Luís (MA), Brazil, and associated socio-demographic variables. METHODS: prospective and cross-sectional study, with conglomerate sampling, in which 552 women from 14 census sections of São Luís were included during the period from January to September 2003. The knowledge, attitude and practice (dependent variables) were evaluated by means of analysis of the responses of the women as "adequate" or "inadequate". The main independent variables were: age, schooling, family income and marital and menopausal status. The χ2 test was used to determine the association between categorical variables and the measurement of the crude/adjusted Odds Ratio (OR) after multivariate analysis by means of logistic regression. RESULTS: although 1/3 of the studied population did not know about BSE, the group of women who were informed about it showed adequate knowledge (60.9%), practice (59.5%) and attitude (90%). The family history of breast cancer (8.9%) was not associated with better knowledge and practice. The media (63.6%) was found to be important in disseminating information about BSE. After multivariate analysis, women with a partner (OR=1.9) presented more adequate knowledge; women older than 50 years (OR=11.7) had a better attitude towards BSE; women with more than five years of schooling (OR=2) and with a partner (OR=1.7) were associated with a more correct practice of BSE. CONCLUSION: most of the patients know and practice the BSE in São Luís and their attitude towards the procedure is extremely positive. There was a great participation of the media in the dissemination of information concerning BSE.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):241-248
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500007
OBJECTIVE: to determine the frequency of macrosomia in babies born alive at a reference obstetric service, and its association with maternal risk factors. METHODS: a transversal descriptive study, including 551 women at puerperium, hospitalized at Instituto de Saúde Elpídio de Almeida, in Campina Grande (PB), Brazil, from August to October, 2007. Women, whose deliveries had been assisted at the institution, with babies born alive from one single gestation and approached in the first postpartum day, were included in the study. The nutritional and sociodemographic maternal characteristics were analyzed, and the ratio of macrosomia (birth weight >4.000 g) and its association with maternal variables were determined. Macrosomia was classified as symmetric or asymmetric according to Rohrer's index. Statistical analysis has been done through Epi-Info 3.5 software; the prevalence ratio (PR) and the confidence interval at 95% (CI 95%) were calculated. The research protocol was approved by the local Ethics Committee and all the participants signed the informed consent. RESULTS: the mean maternal age was 24.7 years old, and the mean gestational age was 38.6 weeks. Excessive gestational weight gain was observed in 21.3% of the pregnant women, and 2.1% of the participants had a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (gestational or clinic). A ratio of 5.4% of macrosomic newborns was found, 60 were asymmetric. There was no significant association between macrosomia, mother's age and parity. There was an association between macrosomia and overweight/obesity in the pre-gestational period (PR=2.9; CI 95%=1.0-7.8) and at the last medical appointment (PR=4.9; CI 95%=1.9-12.5), excessive weight gain (PR = 6.9; CI 95%:2.8-16.9), clinical or gestational diabetes (PR = 8.9; CI 95%:4.1-19.4) and hypertension (PR=2.9; CI 95%=1.1-7.9). The factors that persisted significantly associated with macrosomia in the multivariate analysis were the excessive weight gain during the gestation (RR=6.9; CI 95%=2.9-16.9) and the presence of diabetes mellitus (RR=8.9, CI 95%=4.1-19.4). CONCLUSIONS: considering that excessive gestational weight gain and diabetes mellitus were the factors more strongly associated with macrosomia, it is important that precocious detection measurements and adequate follow-up of such conditions be taken, aiming at preventing unfavorable perinatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):241-247
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles of infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and with male factor and/or tubal infertility (Control Group) and compare in vitro maturation (IVM) rates between the groups analyzed. METHODS: five infertile patients with PCOS and eight controls, submitted to stimulated cycles for intracytoplasmic sperm injection, were selected prospectively and consecutively, and respectively assigned to the study group and the Control Group. Immature oocytes (21 and 29, respectively, from PCOS and Control Group) were submitted to IVM. After IVM, oocytes with first polar body extruded were fixed and submitted to immunostaining and fluorescence microscopy for morphological evaluation of the spindle and of chromosome distribution. Statistical analysis was performed by the Fisher test with significance, when p<0.05. RESULTS: IVM rates were similar between groups (47.6 e 44.8%, respectively, for PCOS and Control Group). Six of the ten oocytes (60%) from the study group and four of the 12 oocytes (33.3%) from the Control Group presented meiotic anomalies of the spindle and/or anomalous chromosome distribution, without statistical difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS: data from the present study did not demonstrate significant difference neither in IVM rates nor in the proportions of meiotic anomalies between in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles from PCOS patients and control ones.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):241-246
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005304
It was to analyse the most critical areas in Obstetrics and to suggest measures to reduce or avoid the situations most often involved in these disputes.
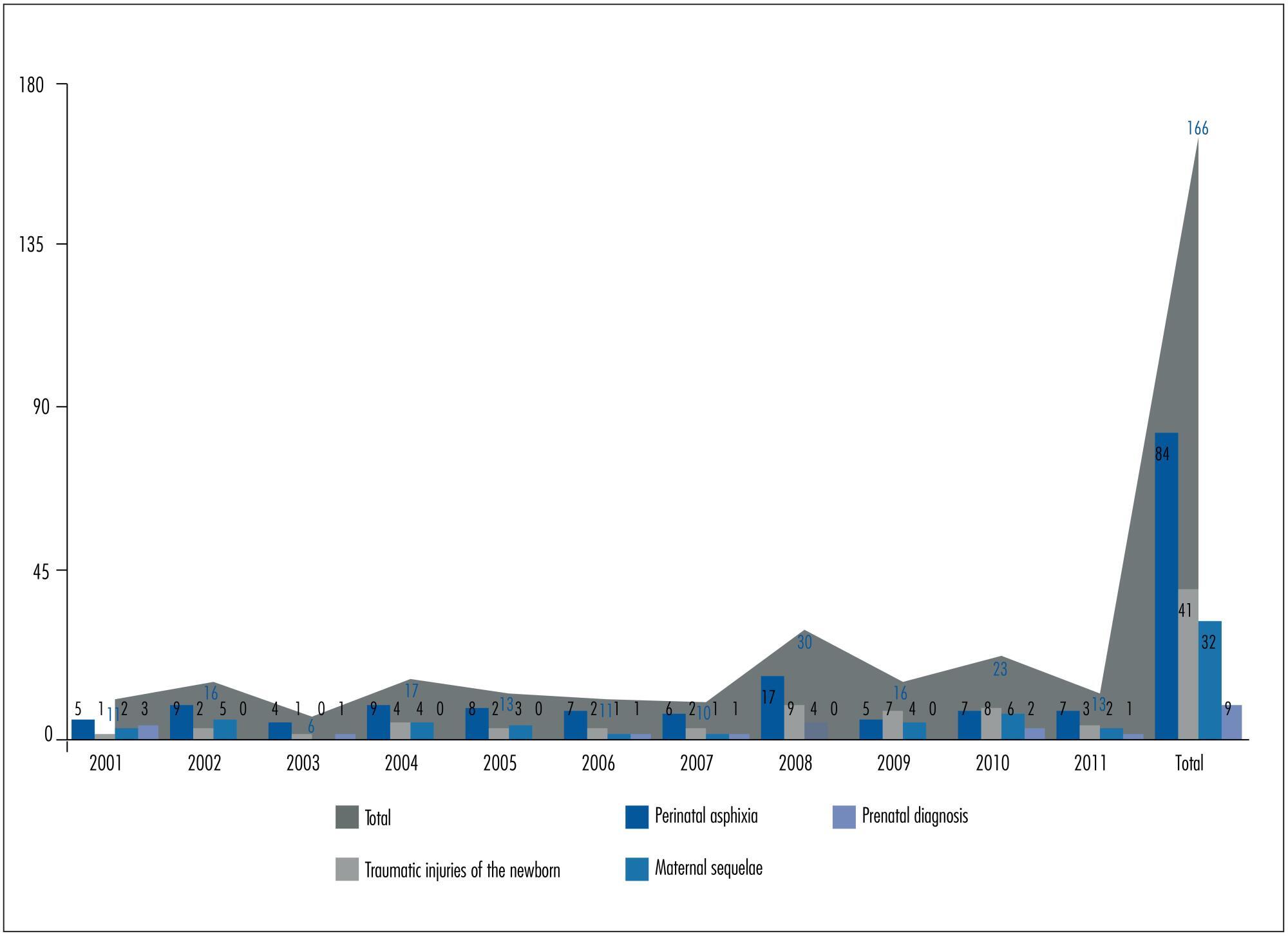
Obstetrics cases submitted to the Medico-legal Council since the creation of the National Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences in 2001 until 2011 were evaluated. A comprehensive characterization, determination of absolute/relative frequencies, hypothesis of a linear trend over the years and the association between each parameter was done.
The analysis has shown no significantly linear trend. The most common reasons for disputes were perinatal asphyxia (50%), traumatic injuries of the newborn (24%), maternal sequelae (19%) and issues related to prenatal diagnosis and/or obstetric ultrasound (5.4%). Perinatal asphyxia showed no significantly linear trend (p=0.58) and was usually related to perinatal deaths or permanent neurologic sequelae in newborn children. Traumatic injuries of the newborn, mostly related to instrumented deliveries, shoulder dystocia or vaginal delivery in breech presentation, has shown a significantly increased linear trend (p<0.001), especially related to instrumented deliveries. The delay/absence of cesarean section was the clinical procedure questioned in a significantly higher number of cases of perinatal asphyxia (68.7%) and of traumatic lesions of the newborn due to instrumented deliveries (20.5%).
It is important to improve and correct theoretical/practical daily clinical performance in these highlighted areas, in order to reduce or even avoid situations that could end up in medico-legal litigations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):241-245
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300011
The reduction of mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of the HIV-1 using zidovudine (ZDV) represents a cornerstone in the prenatal and obstetrical care to these patients. The invasive fetal and obstetric procedures are proscribed in HIV-1 infected pregnant patients, to avoid the increased risk of MTCT of this virus. The authors present a case of an HIV-1 infected woman with recurrent polyhydramnios. Four ultrasound-guided amniotic punctures were performed in the 23rd, 26th, 27th and 29th weeks of gestation, each one draining the respective volumes of 1,800, 1,450, 1,700 and 1,960 ml of clear amniotic fluid. The patient started preterm labor with 30 weeks and 5 days resulting in vaginal delivery of a male neonate weighing 1,690g and measuring 43cm. The baby presented a post natal diagnosis of a sodium-losing nephropathy and was submitted to three negative polymerase chain reaction tests for HIV-1. The authors point out that the option to manage cases of HIV-1 infected pregnancies that could need invasive obstetric procedures should be to give the patient 2 mg//kg of ZDV endovenously before the procedure, in order to avoid MTCT of HIV-1, as it has demonstrated good results in this case.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(4):241-246
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000400005
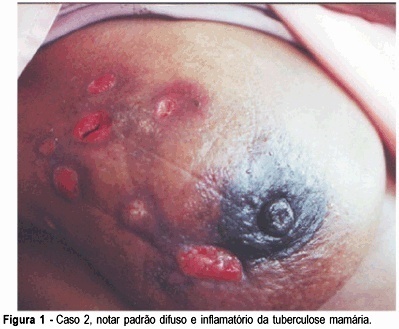
Purpose: to make a differential diagnosis in regard to breast carcinoma and to evaluate diagnostic and clinical methods in the treatment of breast tuberculosis and the follow-up after adequate treatment. Patients and Methods: three patients with breast tuberculosis were observed from March 2001 to March 2002; the first two were hospitalized at our Mastology Department and the third patient was treated at a private clinic. The clinical signs and symptoms, laboratory findings, response to therapy and follow-up were evaluated. Results: the average age of the patients was 40.6 years. The most frequent signs and symptoms were pain and breast tumor. In two patients the presumptive diagnosis was based on the clinical findings, on the histological findings (granulomatous inflammatory process), and on the therapeutic response to tuberculostatic drugs. Only one patient had a microbiological diagnosis, as Koch's bacillus was identified in a sample of her breast tissue. Treatment with a triple tuberculostatic regimen, including rifampin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide, led to the regression of the lesions. Conclusion: primary breast tuberculosis, a rare occurrence which may present clinically as a breast nodule and radiologically as carcinoma, should be taken into account when making the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with mammary mass.