Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(5):238-245
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000500006
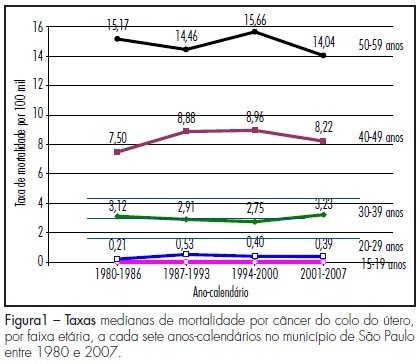
PURPOSE: to compare the coverage of conventional Papanicolaou cytology in women aged 15 to 59 years between two home surveys, related to some personal attributes and to the tendency to die from cervical cancer. METHODS: we analyzed data collected in two home surveys, with complex sampling, in the city of São Paulo, Brazil, over the years from 1987 to 2001 and 2002. The self-reported answers of 968 women in the first inquiry and of 1,125 women in the second inquiry were compared regarding the reply to the question about the execution of the Papanicolaou test "sometimes in a lifetime" in relation to age distribution, black skin, marital status, years of education and tendency to die because cervical cancer during the period from 1980 to 2007. The Fisher exact test was used to compare the sample regarding each item, with the level of significance set at p value >5%. RESULTS: from the first to the second inquiry there was a 24% increase in the execution of conventional Papanicolaou cytology (from 68.8% to 85%). The greatest variations in the increased coverage related to the personal attributes of the women were detected in black skin color, among single women and among women of lower schooling. Regarding the tendency to mortality rates due to cervical cancer, no clear ascending or declining tendency was observed along the 28 years studied (1980 to 2007). CONCLUSION: there was an increase in access to the cytological Papanicolaou test among the most vulnerable women. Since 2001 and 2002, the 85% coverage already reached WHO recommendation, although without a clear trend of decline in mortality due to cervical cancer in the following years, indicating that screening is only part of an effective and organized program for the control of cervical cancer, whose model must guarantee full women's health care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):238-239
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):238-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400006
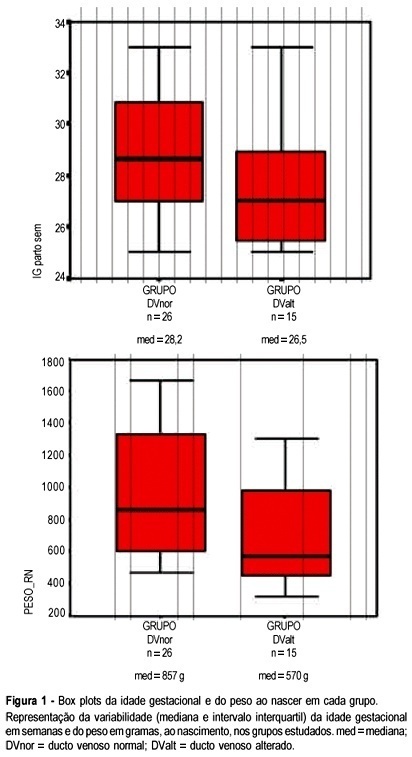
PURPOSE: to evaluate the relationship between S/A ratio in ductus venosus (DV) and perinatal outcomes in fetuses with brain sparing reflex. METHODS: the study was designed as an observational, sectional study with prospectively collected data. Forty-one fetuses with brain sparing reflex and gestational age between 25 and 33 weeks were studied between November 2002 and July 2005. The newborns were observed during the neonatal period in the intensive care unit of "Clínica Perinatal Laranjeiras" in order to find adverse outcomes. The study population was divided into two groups according to DV assessment. In the normal group all the fetuses with S/A ratio values of 3.6 or less were included, and in the abnormal group the fetuses with values of S/A ratio greater than 3.6. The statistical analysis was performed by the Mann-Whitney U-test, chi2 test and Fisher exact test. The results were considered significant when p<0.05. Gestational age, birth weight and Apgar score less than 7 at 5 min were evaluated. Perinatal outcome parameters were: intrauterine death, neonatal mortality, seizures, intraventricular hemorrhage, leukomalacia, need of surfactant, mechanical ventilation, myocardical failure, necrotizing enterocolitis, and length of stay in the intensive care unit. RESULTS: among the assessed 41 fetuses, 26 (63.4%) showed normal DV S/A ratio and the other 15 (36.6%) developed an abnormal DV S/A ratio (>3.6). There was no statistically signicant difference between the groups according to gestational age at delivery and Apgar <7. The only significant association was between abnormal DV S/A ratio and neonatal death (p=0.049; Fisher's exact test). No statistically significant association was observed for the other studied variables. CONCLUSIONS: our results suggest that abnormal DV blood flow detected by Doppler examination is not associated with adverse perinatal outcomes, except for neonatal mortality. This association may be considered statistically borderline (p=0.049). Excluding fetuses with birth weight less than 400 g, there was no other association between DV and neonatal mortality. The abnormal DV S/A ratio was not associated, in our study, with perinatal mortality in viable preterm fetuses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):238-244
To analyze the historical clinical outcomes of children with myelomeningocele (MMC) meeting the criteria for fetal surgery, but who underwent postnatal primary repair.
Data from children undergoing postnatal MMC repair between January 1995 and January 2015 were collected from the Neurosurgery Outpatient Clinic’s medical records. Children were included if they had ≥1 year of postoperative follow-up andmet the criteria for fetal surgery. The children’s data were then stratified according to whether they received a shunt or not. The primary outcome was mortality, and secondary outcomes were educational delays, hospitalization, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), and renal failure.
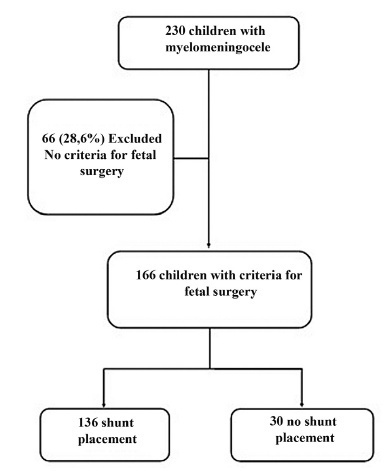
Over the 20-year period, 231 children with MMC were followed up. Based on clinical data recorded at the time of birth, 165 (71.4%) qualify of fetal surgery. Of the 165 patients, 136 (82.4%) underwent shunt placement. The mortality rate was 5.1% in the group with shunt and 0% in the group without, relative risk (RR) 3.28 (95% confidence interval, 95% CI, 0.19-55.9). The statistically significant RRs for adverse outcomes in the shunted group were 1.86 (95% CI, 1.01-3.44) for UTI, 30 (95% CI, 1.01-537) for renal failure, and 1.77 (95% CI, 1.09-2.87) for hospitalizations.
Children with MMC qualifying for fetal surgery who underwent shunt placement were more likely to have recurrent UTIs, develop renal failure, and be hospitalized. Since approximately half of the shunt procedures could be avoided by fetal surgery, there is a clinical benefit and a possible financial benefit to the implementation of this technology in our setting.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):239-241
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):239-241
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400009
Osteoporosis is an important disease which can affect millions of patients all over the world, leading to complications, often even to death. Prevention and the early diagnosis may help in the success of treatment but there are diseases which can occur at the same time. Primary hyperparathyroidism is a diagnosis which must be remembered in women after the menopause.
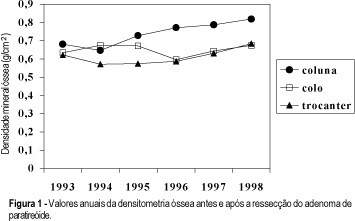
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):239-245
to evaluate the agreement between the clinical and pathological stagings of breast cancer based on clinical and molecular features.
this was a cross-sectional study, in which clinical, epidemiological and pathological data were collected from 226 patients who underwent surgery at the Prof. Dr. José Aristodemo Pinotti Women's Hospital (CAISM/Unicamp) from January 2008 to September 2010. Patients were staged clinically and pathologically, and were classified as: understaged, when the clinical staging was lower than the pathological staging; correctly staged, when the clinical staging was the same as the pathological one; and overstaged, when the clinical staging was greater than the pathological staging.
understaged patients were younger (52.2 years; p < 0.01) and more symptomatic at diagnosis (p = 0.04) when compared with correctly or overstaged patients. Clinicopathological surrogate subtype, menopausal status, parity, hormone replace therapy and histology were not associated with differences in staging. Women under 57 years of age were clinically understaged mainly due to underestimation of T ( tumor staging) (p < 0.001), as were the premenopausal women (p < 0.01). Patients whose diagnosis was made due to clinical complaints, and not by screening, were clinically understaged due to underestimation of N (lymph nodes staging) (p < 0.001).
the study shows that the clinicopathological surrogate subtype is not associated with differences in staging, while younger women diagnosed because of clinical complaints tend to have their breast tumors understaged during clinical evaluation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):239-242