Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):23-28
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100006
To evaluate changes in body and internal organ weight of autopsied children in the perinatal period and their relationship with the cause of death.
One hundred and fifty three cases of perinatal autopsies performed at a university hospital in Southeastern Brazil ere included. Information about cause of perinatal death, date of autopsy, gestational age, perinatal weight and organ weight was obtained from the autopsy protocols and medical records of the mother and/or the newborn. Four groups of causes of death were defined: congenital malformations, perinatal hypoxia/anoxia, ascending infection and hyaline membrane. Brain, liver, lungs, heart, spleen, thymus and adrenals were analyzed.
The weight of children with perinatal hypoxia/anoxi (1,834.6±1,090.1 g versus 1,488 g), hyaline membranes (1,607.2±820.1 g versus 1,125 g) and ascending infection (1,567.4±1,018.9 g versus 1,230 g) was higher than expected for the population. Lung weight was higher in cases with ascending infection (36.6±22.6 g versus 11 g) and lower in cases with congenital malformations (22.0±9.5 g versus 40 g). Spleen weight was higher in children with ascending infection (8.6±8.9 g versus 3.75 g ) and adrenal weight was lower in cases with congenital malformations (3.9±2.1 g versus 5.5 g). Thymus weight was lower in cases with miscellaneous causes (3.7±1.2 g versus 7.5 g) and spleen weight was lower in patients with lung immaturity (0.4±0.1 g versus 1.7 g). All results showed significant differences.
This study demonstrates that variations in the weight of children and the weight of their organs are related to the types of cause of perinatal death. These data may contribute to a better interpretation of autopsy findings and their anatomical and clinical relationship.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(1):23-28
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000100004
PURPOSE: to determine the expression of HER-2 protein in fine-needle aspirates obtained from infiltrating breast duct carcinoma and in the corresponding surgical specimens and to correlate HER-2 expression with histological grade. Methods: forty-eight smears fixed in alcohol and previously stained by the Papanicolaou technique and histological sections of corresponding paraffin-embedded tissue blocks were submitted to immunohistochemistry by the avidin-biotin-peroxidase method using a polyclonal antibody (A0485-Dako). The reactions were carried out simultaneously with antigen recovery. The results were analyzed by a semiquantitative method according to the HercepTest score. Scores of 3+ were considered to be positive. RESULTS: positivity was observed in 39.6% of the smears and in 35.4% of the respective histological sections, with almost perfect cytohistologic concordance (kappa 0.82). The method of evaluation of histological sections was found to be reproducible regarding the smears and standardized the interpretation of the results. The correlation between HER-2 positivity and histological grade was not statistically significant but there was a tendency towards HER-2 expression in less differentiated tumors. CONCLUSION: the positivity of the immunocytochemical reactions observed in smears was comparable to that obtained in the histological sections, indicating that the material obtained by fine-needle aspiration biopsies previously stained by the Papanicolaou technique can be used for the evaluation of HER-2 expression.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):230-230
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):230-234
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the patient's age as an outcome predictor in an in vitro fertilization (IVF) program. METHODS: transversal study, which has included 302 women with ages varying from 24 to 46 years old, submitted to IVF, from May 2005 to July 2007. The patients were divided in three groups, according to their age: G<35 (n=161), G 36-39 (n=89) e G>40 (n=52). The number of collected oocytes, the fertilization rates, the number of transferred embryos, the embryonary quality and the pregnancy rate were evaluated. Statistical analysis was realized through Kruskal-Wallis variance analysis and χ2 test. RESULTS: in the G<35 group, an average of 8.8 oocytes by patient was obtained; in the G 36-49 group, 7.4; and in the G>40 group, 1.6. The number of oocytes obtained in G>40 group was significantly lower than in the other two groups (p<0.001).The fertilization rate was similar in the three groups, 61.4, 65.8 e 64.6% (p=0.2288), respectively. The percentage of good quality embryos was not statistically different among the three groups either, with rates of 57.4, 63.2 and 56.0% (p=0.2254), respectively. The average number of transferred embryos in each group was 3.1 (G<35), 2.8 (G 36-39) and 1.5 (G>40), respectively, with statistically significant decrease in the G>40 group (p<0.001). Concerning pregnancy rates, the G>40 group has presented a rate of 9.6%, a result which is significantly lower (p=0.0330) than the one presented by the G<35 and G 36-39 groups (26.1 e 27.0%, respectively), with no significant difference between themselves. CONCLUSIONS: though the embryonary quality is not different among women from different age groups, the number of collected oocytes, the number of transferred embryos and the pregnancy rate indicate that the women's age is an important predictive factor of success for the techniques of assisted reproduction and should be taken into consideration when this kind of treatment is proposed to women over 40.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):230-234
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500002
PURPOSE: to analyze the factors associated with the reproductive future of patients wishing to become pregnant after having being submitted to tubal ligation (TL), attended at a public service. METHODS: a prospective study including 98 patients previously submitted to TL, who came to the Human Reproduction Center of the University Hospital of Brasilia (HUB), from January 1996 to January 2004, wishing to become pregnant again These patients were followed up from their first appointment till the end of the study, when they answered a structured questionnaire about the social demographic aspects at both the moment they asked for the TL and the reversion of the procedure. RESULTS: the patients’ average age at the TL procedure was 25 years old. Among them, 55.1% were younger than 25, 46.9% had three or more children, and ten of them had only one child. The most common reasons for the TL procedure were: contraception (48%), financial difficulties (25.5%) and marital problems (15.3%). The major causes for wishing a new pregnancy were: a new relationship/marriage (80.6%), the desire of having another child with the same partner (8.2%), and the death of a child (6.1%). The regret time informed by most of the patients was between two and four years, and the search for reversion was between six and ten years. About 83.6% of the sample referred lack of information about the procedure and the difficulties of reversion. Twenty patients were submitted to TL reversal procedure; from the ten who became pregnant, only six delivered babies, after a full-term pregnancy. Eight patients were referred to in vitro fertilization treatment, four of them became pregnant and two delivered healthy babies. CONCLUSIONS: TL in young vulnerable women, not informed about the definitive condition of the method, may increase the search for attended reproduction services and impair their reproductive future, as far as only 8.1% of the sample delivered babies and reached their goal.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):230-235
To assess the perinatal and maternal outcomes of pregnant women with cystic fibrosis (CF) and severe lung impairment.
This was a series of cases aiming to review the maternal and fetal outcomes in cases of singleton pregnant women with a diagnosis of CF. We have included all of the cases of singleton pregnancy in patients with CF who were followed-up at the obstetrics department of the Medical School of the Universidade de São Paulo, between 2003 and 2016. The exclusion criteria were the unattainability of the medical records of the patient, and delivery at other institutions. A forced expiratory volume in 1 second < 50% was considered as severe lung impairment. We have also analyzed data regarding maternal hospitalization and respiratory exacerbations (REs).
Pregnant women with CF and severe lung impairment did not present an association with spontaneous prematurity, fetal growth restriction or fetal demise. All of the cases involved multiple RE episodes requiring antibiotic therapy. The median (range) of events per patient was of 4 (2-4) events.
Cystic fibrosis patients with severe lung impairment may achieve successful term pregnancies. However, pregnancies of women with CF are frequently complicated by REs, and this population may require hospital admission during the course of the pregnancy. Cystic fibrosis patients should be followed by a specialized team with experience in treating respiratory diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):231-237
To analyze whether acetylsalicylic (ASA) intake modifies the mean uterine arteries pulsatility index (UtA-PI) at the 2nd or 3rd trimester in a cohort of pregnant women with abnormal mean UtA-PI at between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation.
This is a retrospective cohort study. Singleton pregnancies with abnormal mean UtA-PI at between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation were studied. The participants were divided into 3 groups: 1) If the participant did not take ASA during pregnancy; 2) If the participant took ASA before 14 weeks of gestation; and 3) If the participant took ASA after 14 weeks of gestation. The mean UtA-PI was evaluated at the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, and it was considered to improve when it decreased below the 95th percentile. The prevalence ratio (PR) and the number needed to treat (NNT) werecalculated.
A total of 72 participants with a mean UtA-PI>95th percentile at the 1st trimester of gestation were evaluated. Out of the 18 participants who took ASA, 8 participants started it before 14 weeks of gestation and 10 after. A total of 33.3% of these participants had improved the mean UtA-PI at the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of gestation, although it was not statistically significant (p=0.154). The prevalence ratio was 0.95 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.31-1.89), but between the 1st and 2nd trimesters of gestation, the PR was 0.92 (95%CI: 0.21-0.99) and it was statistically significant.
The present work demonstrates a modification of the mean UtA-PI in participants who took ASA compared with those who did not. It is important to check if ASA can modify the normal limits of uterine arteries because this could have an impact on surveillance.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):231-238
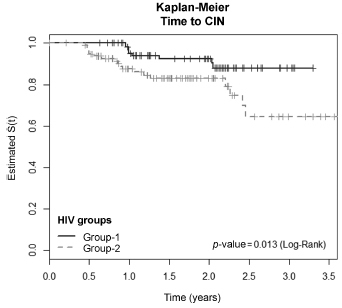
To evaluate the incidence and factors associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical infection by human papillomavirus (HPV) among HIV-positive and HIV-negative women.
A cohort of 103 HIV positive and 113 HIV negative women were monitored between October 2008 and February 2012, for at least one year. Procedures included cervical cytology, DNA/HPV detection by polymerase chain reaction, colposcopy with biopsy if necessary, followed by an interview for exposure characteristics data. CIN was based on the histopathological results.
The incidence of CIN was of 8.8 and 4.6 cases/100 women-years in HIVpositive and HIV-negative women, respectively. HIV-positive women presented a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.8 for CIN and developed lesions earlier (0.86 year) than HIVnegative women (2 years) (p = 0.01). The risk of developing CIN decreased with age (HR = 0.9) and marital status (HR = 0.4). HPV patients presented a higher incidence of CIN when compared HIV-positive and HIV-negative women (p = 0.01). The incidence of HPV cervical infection was 18.1 and 11.4 cases/100 women-years in HIV-positive and HIV-negative women, respectively. Those HIV-positive presented earlier HPV infection (p = 0.002). The risk of developing HPV infection decreased with age and was higher among HIV-positive women. HPV 16 was the most common type in HIV-positive women, and also the type most closely associated with CIN in HIV-negative women.
HIV-positive women had a greater incidence of HPV and CIN, and in a shorter time interval. More rigorous and timely clinical control is required for this group.