Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):215-220
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500005
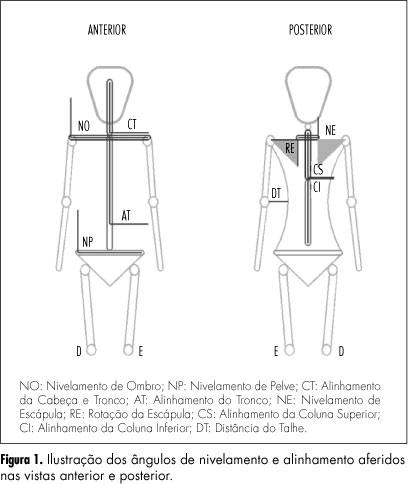
PURPOSE: To evaluate the body posture of women submitted to treatment for breast cancer, to identify the postural changes in the first three months after surgery and to investigate the correlation of these findings with the woman's age and type and side of surgery. METHODS: A longitudinal study that monitored the postural changes of 39 women who underwent mastectomy and quadrantectomy. Postural evaluation was performed using the technique of biophotogrammetry before surgery, after drain removal and three months after surgery. Statistical analysis was performed using parametric and nonparametric tests, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. RESULTS: The average age of the women studied was 50±10.5 years, 48.8% underwent mastectomy and the left breast was operated in 61.5% of them . There was no statistically significant difference in the women's posture during the study period. However, the pelvis and trunk of women submitted to quadrantectomy showed better alignment (90°) compared to the women submitted to mastectomy (91.3°). The women submitted to surgery in the left breast had shoulder elevation and ipsilateral inclination of the trunk within a short period of time. CONCLUSION: Postural changes were correlated with the type and side of surgery. The follow-up of this group after completion of treatment is needed to clarify long-term postural changes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(5):215-220
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000500005
PURPOSE: To evaluate factors associated with morbidities among Brazilian women aged 40-65 years and with 11 or more years of schooling. METHODS: A secondary analysis of a cross-sectional population-based study was conducted, using an anonymous self-report questionnaire completed by 377 women. Were evaluated, with this instrument, some morbidities (hypertension, diabetes, insomnia and depression) and sociodemographic, behavioral, clinical and reproductive factors. The association between morbidities and independent variables was evaluated by the Χ2 test. Multiple logistic regression analysis with stepwise selection criteria was used to select the major factors associated with morbid conditions. RESULTS: In the multiple regression analysis, insomnia was associated with bad/fair self-perception of health (OR=2.3) and nervousness (OR=5.1). Depression was associated with bad/fair self-perception of health (OR=3.7) and bad/poor leisure (OR=2.8). Hypertension was associated with obesity (OR=3.1) and being in postmenopausal (OR=2.6). Diabetes was associated with age above 50 years (OR=3.9) and obesity (OR=12.5). CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of morbidities was high and a worse self-perception of health and obesity were the main factors associated with morbidity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):216-221
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050006
To assess the effects of aerobic physical exercise on the Doppler velocimetry of fetal vessels in pregnant women with no clinical or obstetrical complications.
A cross-sectional study was conducted on 10 healthy low-risk pregnant women at 2 different gestational times: between the 26th and 29th week and 6 days, and at the end of pregnancy, between the 30th and 35th week. The patients were submitted to aerobic physical exercise on a treadmill until reaching fatigue. Ultrasonographic data were obtained at rest and after physical exercise (Doppler velocimetry indices for the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, ductus venosus, and uterine arteries). Data were analyzed statistically by the paired and independent Student's t-test using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) package, version 21.0.
A change in the pulsatility index was observed, with an indication of vasodilatation, with a median value of 1.1±0.1 before exercise and of 1.0±0.1 after exercise; the median value of the resistance index was 0.7±0.04 before exercise and 0.6±0.07 after exercise. The median systole/diastole ratio of the umbilical artery was 3.1±0.4 before exercise and 2.9±0.2 (p=0.03) after exercise at the beginning of pregnancy. No changes in the Doppler velocimetry parameters were observed for the uterine arteries, the middle cerebral artery or the ductus venosus after physical activity at either testing time. Paired analysis of pre- and post-activity data showed a reduction of resistance from the first to the second period (p<0.04).
Physical exercise does not lead to changes in systemic blood flow or fetal-placental flow in healthy pregnant women, confirming that exercises of mild to moderate intensity can be prescribed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):216-219
To evaluate the seroprevalence of positive markers for syphilis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) I and II, human T cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) I and II, and hepatitis B and C among women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF).
We conducted a retrospective analysis among patients who underwent IVF, between January 2013 and February 2016, and who had complete screening records.
We analyzed 1,008 patients who underwent IVF, amounting to 2,445 cycles. Two patients (0.2%) tested positive for HIV I and II and none for HTLV I and II. Three patients (0.3%) had positive screening for syphilis, and two (0.2%) had positive hepatitis C antibody test (anti-HCV). A positive hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HbsAg) test was observed in 4 patients (0.4%), while 47 (4.7%) patients were positive for IgG antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbC IgG), and only 1 (0.1%) was positive for IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbC IgM). The anti-HbS test was negative in 659 patients (65.3%). Only 34.7% of the patients had immunity against the Hepatitis B virus. Patients with an anti-HbS negative result were older than those with a hepatitis B test (anti-HbS) positive result (36.3 versus 34.9; p<0.001).
The present study showed lower infection rates than the Brazilian ones for the diseases studied in patients undergoing IVF. Only a few patients were immunized against hepatitis B.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):216-221
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005272
To compare obstetric outcomes of induced preterm twin births (under 32 weeks gestation) with those spontaneously conceived.
Prospective study of twin pregnancies (25 induced and 157 spontaneously conceived) developed over a period of 16 years in a tertiary obstetric center. Demographic factors, obstetric complications, gestational age at delivery, mode of delivery, birth weight and immediate newborn outcome were compared.
The analysis of obstetrical complications concerning urinary or other infections, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, fetal malformations, intrauterine fetal death, intrauterine growth restriction and intrauterine discordant growth reveal no significant statistical differences between the two groups. First trimester bleeding was higher in the induced group (24 versus 8.3%, p=0.029). The cesarean delivery rate was 52.2% in spontaneous gestations and 64% in induced gestations. Gestational age at delivery, birth weight, Apgar scores at first and fifth minutes, admissions to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and puerperal complications show no statistically significant differences between the two groups. These results were independent of chorionicity and induction method.
The mode of conception did not influence obstetric and neonatal outcomes. Although induced pregnancies have higher risk of first trimester bleeding, significant differences were not observed regarding other obstetric and puerperal complications and neonatal results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):216-218
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):216-218
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):216-221
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400009
PURPOSE: to identify the relationship between serum levels of leptin and the levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in women with pituitary suppression and to evaluate its possible interference on the reproductive axis. METHODS: a total of 64 patients submitted to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with recombinant FSH for assisted reproduction, due to a male or tubal factor, and 20 patients using estradiol valerate, for endometrial preparation in order to be submitted to oocyte donation treatment were studied. All patients used GnRH analogues before starting treatment in order to avoid premature LH surge. Data were analyzed statistically by the chi2 test, Student's t-test and the Pearson correlation test, when appropriate, with the level of significance set at p<0,05. RESULTS: it was observed that leptin levels correlated with body mass index (BMI) even though they had not influenced growth rate of these hormones. A positive correlation was observed between estradiol and leptin levels in both groups, as leptin levels increased from 10.42 to 15.68 ng/mL in the FSH group and from 11.09 to 14.5 ng/mL in the estradiol group, following estradiol increase. The growth rate of leptin was higher in women with higher estradiol levels, i.e., who had induced cycles with recombinant FSH, than in those who received estradiol valerate (159.60±58.01 and 136.73±34.17, respectively). CONCLOSION: we may state that leptin correlated with BMI and that both FSH and estradiol do interfere in the regulation of leptin production in women.