You searched for:"José Maria Soares Júnior"
We found (33) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):101-106
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) and raloxifene (Ral), alone or combined, on the rat endometrium. METHODS: fifty-six adult rats were ovariectomized and randomly divided into seven groups: GCont (control); GCEE (CEE 50 µg/kg); GCEE/25 (CEE 25 µg/kg); GRal/0.75 (Ral 0.75 mg/kg); GRal/0.4 (Ral 0.4 mg/kg); GCEERal (50/0.75) - (CEE 50 µg/kg + Ral 0.75 mg/kg), and GCEE-Ral (25/0.4) - (CEE 25 µg/kg + Ral 0.4 mg/kg). The drugs were orally administered (gavage) for 21 consecutive days. At the end of the experiment, all animals were anesthetized and sacrificed. Fragments of uterus were removed, fixed in 10% formaldehyde and processed for paraffin inclusion. The histological sections were stained by HE and submitted to histomorphometric evaluation. The following parameters were analyzed: thickness of superficial epithelium and number of endometrial glands/mm² and of blood vessels/mm². The data were evaluated using ANOVA followed by the Turkey-Kramer test. RESULTS: in the GCont and only Ral treatment (GRal/0.75 and GRal/0.4) the endometrium showed signals of atrophy. In the groups treated with only CEE signs of endometrial proliferation were observed, mainly in group GCEE/50. Also, there was endometrial proliferation in the groups that received combined CEE and Ral (Ral GCEE (50/0.75) and GCEE-Ral (25/0.4)), but it was more intensive in the animals treated with isolated estrogen than in those that received combined estrogen and raloxifene. CONCLUSION: raloxifene may partially block the action of estrogen on the castrated adult rat endometrium.
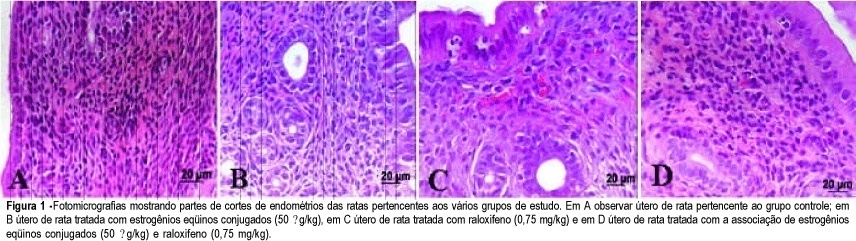
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):118-124
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of the association of estrogen and androgen on the quality of life and sexuality of women during climacterium. METHODS: ninety-six postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms and sexual dysfunction were included. The participants were randomly divided into three treatment groups with 32 pacients each: placebo, conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) (0.625 mg per day) and CEE (0.625 mg per day) associated with methyltestosterone (2.5 mg per day). The length of the treatment period was three months. The Women Health Questionnaire (WHQ) and the Modified Sexuality Questionnaire were applied to evaluate the quality of life and sexuality before and after the treatment. Some parameters of cardiovascular risk, endometrial echo and hepatic toxicity were evaluated. ANOVA was used for data analysis followed by the Fisher test and the Shapiro-Wilk post hoc test. RESULTS: the improvement in WHQ parameters was significant in the hormonal treatment groups (CEE and CEE + methyltestosterone) compared to the placebo group. However, there were no differences in somatic symptoms among the three groups. The association of estrogen with androgen significantly improved sexual function (score (mean): 64 vs 67, p<0.05) and depressive humor (score (mean): 75 vs 80, p<0.05) compared to estrogen alone. This therapy also presented a large number of WHQ questions with a high score (p<0.05). The use of CEE associated with methyltestosterone decreased the total cholesterol (212±42 and 194±43, before and after the treatment, respectively) and HDL colesterol (56±16 and 48±14, before and after the treatment, respectively), and slightly increased the endometrial echo (4.7±2.3 and 5.5±2.3, before and after the treatment, respectively). No signifcant changes in liver enzymes during the treatment period was detected. CONCLUSIONS: estrogen associated with methyltestosterone resulted in significant improvement in the quality of life and sexuality of postmenopausal women. This effect was superior to estrogen alone and placebo. The effect of treatment with the estrogen-androgen association was evident regarding depressive humor and sexual function questions of the WHQ.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):161-163
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300007
A tocolytic treatment is described with the use of terbutaline in a case of cardiotocographic prolonged deceleration of fetal heart rate with successful outcome.
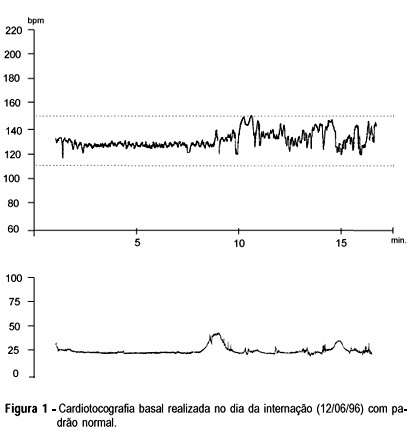
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):183-190
Considering that myths and misconceptions regarding natural procreation spread rapidly in the era of easy access to information and to social networks, adequate counseling about natural fertility and spontaneous conception should be encouraged in any kind of health assistance. Despite the fact that there is no strong-powered evidence about any of the aspects related to natural fertility, literature on how to increase the chances of a spontaneous pregnancy is available. In the present article, the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO, in the Portuguese acronym) Committee on Endocrine Gynecology provides suggestions to optimize counseling for non-infertile people attempting spontaneous conception.
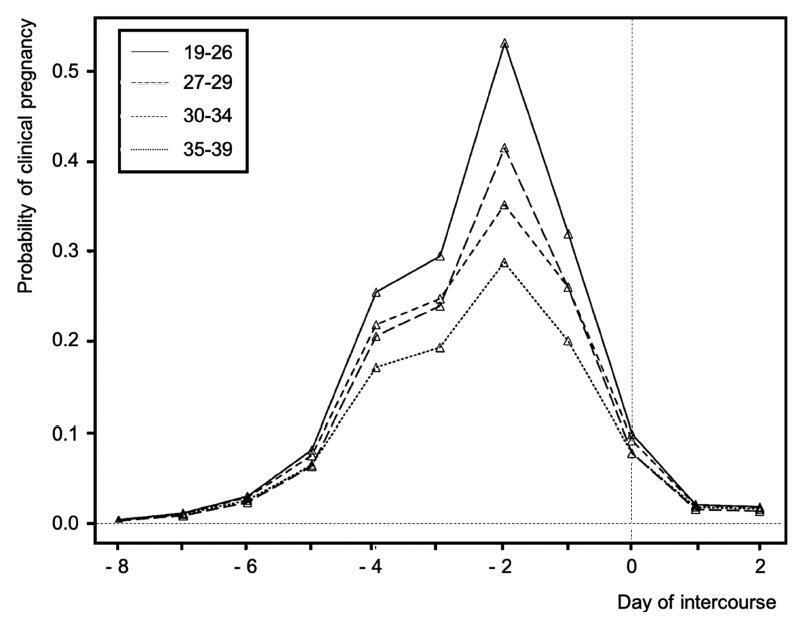
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):204-209
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400007
PURPOSE: to analyze the effects of isoflavones and estrogens on the morphology, morphometry and VEGF expression of the adult female rat mammary gland. METHODS: Forty-five adult female rats were oophorectomized; 28 days after surgery they were divided into 3 groups of 15 animals each: CON - control (treated with propylenoglycol); ISO - isoflavones (100 mg/kg) and CEE - conjugated equine estrogens (50 µg/Kg). Drugs or vehicle were given orally once a day for 60 days. After this, the animals were killed and the first pair of inguinal mammary glands was immediately removed; part of the material was processed for routine histological study and the remaining tissue was frozen for further analyses of the expression of VEGF mRNA by means of the RT-PCR technique. RESULTS: We observed that mammary ducts were atrophic in the control (CON) and isoflavone-treated (ISO) groups. In these groups the mammary glands were composed of a large concentration of adipose tissue with some ducts and rare alveolar structures. In the CEE group the ducts were well developed with many buds and alveolar structures. The number of mammary gland alveoli was higher in CEE than in the other groups (CON = 1.4 ± 2.1; ISO = 1.6 ± 3.8; CEE = 12.3 ± 7.1 alveoli/mm²; p<0.05%); also, the cell volume was higher (CON = 14.9 ± 4.9; ISO = 11.4 ± 6.9; CEE = 27.4 ± 9.7 µm³, p< 0.05%). The same was observed with regard to the number of blood vessels (CON = 16.4 ± 1.5; ISO = 18.4 ± 2.1; CEE = 37.1 ± 4.1 vessels/mm², p< 0.05). The expression of VEGF in the CEE group was higher than in the other groups, which did not significantly differ from each other in this respect. CONCLUSION: Our data did not show any proliferation effect in the mammary tissue of adult oophorectomized rats treated with isoflavones (100 mg/kg) during 60 days.
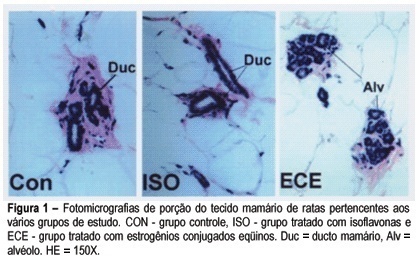
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(9):223-226
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):227-231
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400004
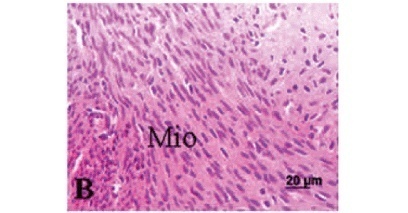
PURPOSE: to evaluate histomorphometric changes in the rat myometrium upon treatment with isoflavones, as compared with estrogens, using histological and morphometric techniques. METHODS: twenty-eight oophorectomized adult rats were randomly divided into four treatment groups: GPropi = propylene glycol (control); GExtr10 - 10 mg/kg soybean extract; GExtr300 - 300 mg/kg soy bean extract; GCee - 200 µg/kg conjugated equine estrogens (Cee). Drugs or drug vehicle were administered by gavage once a day for 21 days. Upon sacrifice, the uteri were removed and weighed. Fragments of uterine horns were collected and fixed in 10% formaldehyde and processed for paraffin inclusion. The histological sections were stained by hematoxylin and eosin and evaluated microscopically by means of an image analyzer to quantify the myometrial thickness and the number of blood vessels and eosinophils. The data were studied by analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test. RESULTS: isoflavones in the concentration of 300 mg/kg induced a significant increase in the myometrium thickness (GExtr300=25.6±5.0 mm) compared to control (GPropi=5.5±0.5 mm). The effect of this high dose is similar to the estrogen effect (GCee=27.5±7.9 mm). In low doses (10 mg/kg), the effect was similar to control. Isoflavones (GExtr300) induced also an increase in the number of blood vessels (GPropi=3.5±1.6; GExtr300=10.2±3.6 vessels/mm²) and of eosinophils (CPropi=0.15±0.01; GExtr300=4.3±0.9 eosinophils/mm²). These effects were comparable to those produced by Cee treatment in GCee (9.2±1.1 eosinophils/mm²). CONCLUSION: a high-dose treatment with isoflavones (300 mg/kg per day, 21 days) elicited an estrogen-like, highly significant proliferative action on the rat myometrium.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):248-252
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500005
PURPOSE: to analyze the isoflavone and estrogen effects on the postmenopausal quality of life. METHODS: this is a randomized and double-blind study with 79 postmenopausal patients, 12 months of amenorrhea, 40 years old or more and body mass index (BMI) above 30 kg/m². The participants were randomly divided into two treatment groups: GECP received orally two capsules, every 12 hours, one contained 0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogen and another placebo (n=33); GECS received two capsules of 150 mg extract of soy, with 60 mg isoflavone (n=32). Both treatments were administered for six months. The Quality Menopause Specific Questionnaire of Life was applied before and after one, three and six months of treatment. The parameters of gynecological cancer risk were evaluated. ANOVA and the Tukey test were used for data analysis. RESULTS: there was a reduction in the values of the vasomotor parameters after six months of treatment, 1.6±0.8 and 2.4±1.6, compared to before therapy, 4.0±2.2 and 4.2±2.3 in GECP and GECS, respectively. The psychological aspects showed reduction in values after six months of therapy, 2.5±1.2 and 2.9±1.4, compared to before treatment, 3.6±1.6 and 4.1±1.9 in GECP and GECS, respectively. Similar results were obtained on the physical aspects and in the sexual symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: isoflavones may positively act on life quality of postmenopausal women. This effect was similar to conjugated equine estrogen.