You searched for:"José Focchi"
We found (11) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):50-52
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100009
Compound nevus of the uterine cervix is very rare. Benign and malignant melanotic lesions of endo and exocervix have been rarely documented. The present case of compound nevus in the uterine exocervix was found in a 47-year-old woman without gynecologic complaints. Diagnosis was suspected by colposcopic evaluation and confirmed trough histopathological examination. The treatment was concluded with total abdominal hysterectomy based on the possible malignant transformation of these lesions and the difficult patient follow-up.
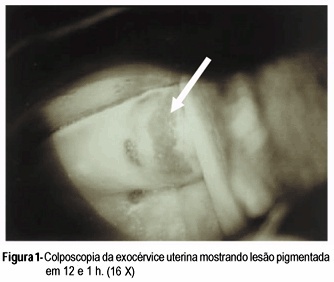
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):726-730
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200004
PURPOSE: to study the influence of the use of oral contraceptives (OC) on the number of Langerhans' cells in women without cervical infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). METHODS: thirty women who presented abnormal cervical cytology and colposcopy-guided biopsy with samples of uterine cervix negative for HPV were selected. The absence of HPV DNA was confirmed by hybrid capture. Langerhans' cells were identified by immunohistochemistry using anti-S100 antigens. The cells visualized in light microscopy were counted using the Cytoviewer software. The nonparametric Wilcoxon rank sum test was employed for statistical analysis. RESULTS: the average number of Langerhans' cells in OC users was 320.7/mm² and in non-users 190.7/mm², this difference being statistically nonsignificant. In the intermediary layer of the cervical epithelium a tendency towards the increase of these cells was observed, with the averages 192.1/mm² for OC users and 93.4/mm² for non-users (p=0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the present study reports a tendency towards the increase in the number of the Langerhans' cells among OC users. This result suggests the OC may induce alterations in the number of Langerhans' cells, but considering the limited number of cases, more studies should be developed for a definitive conclusion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):289-294
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400004
OBJECTIVE: to study the relationship of biobehavioral factors, such as age, menarche, number of gestations, and age of first sexual intercourse, with changes in Langerhans'cells in women with negative hybrid capture for HPV. METHODS: thirty women referred due to abnormal cervical cytology or premalignant cervical lesions were studied and underwent colposcopy, guided biopsy and histopathological exams. The Langerhans' cells were identified by immunohistochemical (S100+) exams. Langerhans' cells visualized in brown color were counted using the software Cytoviewer. The nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test was employed for statistical analysis. RESULTS: the number of Langerhans' cells in women who had menarche after 13 years old presented statistically significant difference (173.34 cell/mm²) compared to the group whose menarche occurred before 13 (271.41 cell/mm²). The age at the first sexual intercourse was associated with the low number of Langerhans' cells, 127.15 cell/mm² and 250.14 cell/mm², respectively, for the beginning of the sexual activity up to 17 years old and after 17 (p=0.03). Previous cauterizations of the uterine cervix have been related to a lower number of Langerhans' cells in the epithelium, with the average 120.30 cell/mm² as compared to 236.06 cell/mm² for those women who never underwent that procedure (p=0.05). Other factors such as the patient's age and the number of gestations showed no statistically significant differences in the density of Langerhans' cells. CONCLUSIONS: the present study reports the association of biobehavioral factors with decrease in the number of Langerhans' cell.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):213-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300007
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the effectiveness of the hygroscopic dilator in the colposcopic examination of the endocervical canal in patients with high-grade lesion in the cytopathology and unsatisfactory colposcopy. METHODS: prospective study, including 62 patients with unsatisfactory colposcopic examination and cytology compatible with high-grade intraepithelial lesion. The patients were submitted to dilation of the endocervical canal by means of a hygroscopic dilator. After dilation, the new colposcopic findings were recorded, and then conization was made through loop electrosurgical excision procedure. The incidence of neoplasic involvement of surgical margins was compared between patients with examinations modified toward satisfactory results and those that remained with unsatisfactory colposcopy. In order to compare the incidence of involved margins and the incidence of residual disease, two retrospective control-groups were used: the GinSat group (n = 35): patients with unsatisfactory colposcopy; GSat group (n = 38): patients with satisfactory colposcopy and endocervical atypy. RESULTS: 80.6% of the cases presented satisfactory colposcopic vision after dilation. 80.4% of those presented disease-free resection margins. The incidence of disease-free resection margins in patients with persistent unsatisfactory colposcopy after dilation was 36.3%. Affected surgical margins occurred in 28% of the group that had undergone dilation, 28.5% of the cases in GinSat group, and 31.5% in the Gsat group. Follow-up showed the incidence of residual disease in 7.5% of the patients under dilation, 28.5% in the GinSat group and 28.9% in the GSat group. CONCLUSION: the use of hygroscopic dilation improved visualization of lesions of difficult access to the colposcopic examination, thus permitting reduction in the percentage of residual neoplasic disease in patients with unsatisfactory colposcopy treated with loop electrosurgical excision procedure.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(6):339-345
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000600004
Purpose: to quantify the vessels and epithelial proliferation, applying immunohistochemical staining with anti-CD34 as well as anti-PCNA markers, in intra-epithelial neoplasia of the uterine cervix. Methods: in the present study, 16 patients with CIN III, 16 with CIN II, 21 with CIN I and 11 with normal cervix (control group) were investigated. Slide analysis was performed at the same time by two observers, in 10 consecutive sites using 100X and 400X magnification, both in the highest vascularization (CD34) and proliferative activity sites (PCNA). Results: the means obtained with the use of anti-PCNA in intraepithelial neoplasias were: 78.2% (CIN III), 52.1% (CIN II), 33.3% (CIN I) and 4.6% (control group), while 199.1 vessels (CIN III), 162.0 vessels (CIN II), 111.7 vessels (CIN I) and 124.4 vessels (control group) were quantified using anti-CD34 as a vascular marker. Conclusion: the results showed that both markers, anti-PCNA and anti-CD34, are useful for investigating proliferative and angiogenic activity, respectively. However, anti-PCNA showed better and more accurate results than anti-CD34 in differentiating intraepithelial neoplasias.
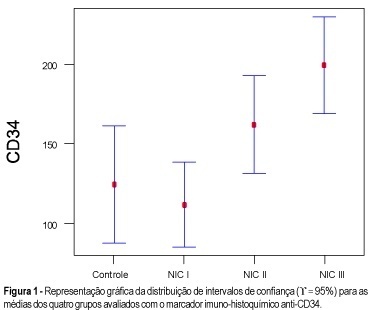
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):396-401
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the significance of neoangiogenesis for the prognosis of endometrial carcinoma, by quantifying and comparing the vessels with the grade of histologic differentiation and tumor staging. METHODS: the 56 studied cases consisted of 11 atrophic endometria, 10 proliferative endometria, 10 GI, 13 GII and 12 GIII adenocarcinomas. Two histologic sections were obtained for each case: one was stained with hematoxylin-eosin and the other was sent for a immunohistochemical study with anti-CD34. The utilized histometric method was vessel counting at the tumoral growth interface with the adjacent stroma, and in the control group, at the endometrial gland interface with the stroma. Couting was done by a KS300, evaluating 10 fields at 100X magnification. RESULTS: the counted vessel means were 11.6 for atrophic endometria, 13.2 for proliferative endometria, 15.3 for GI adenocarcinoma, 19 for GII adenocarcinoma, and 22.7 for GIII adenocarcinoma. In the group of stage I patients, it was observed that the mean number of vessels (18.6) was similar to that observed in stages II, III and IV (20.9) computed together. CONCLUSION: less differentiated adenocarcinomas were more angiogenic than well-differentiated carcinomas and normal endometrium. Vessel counting was not influenced by the disease stage as an isolated factor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(4):209-215
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000400003
Purpose: to evaluate a populational sample of the screening proposed by the National Program of Uterine Cervical Cancer Control (PNCC), regarding the following issues: frequency of unsatisfactory cytologic results, cytologic frequency of atypical squamous or glandular cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS, AGCUS), low- or high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL), comparing the cytologic results with anatomicopathological results of colposcopically directed biopsies. Methods: through the written, broadcasting television and oral midia, women between 35 and 49 years were requested to have a preventive cytopathological test, to be collected by the authorized public health or other institutions accredited by SUS. The slides were analyzed by the program-authorized laboratories and all those patients from the populational sample from the municipality of Naviraí in the State of Mato Grosso do Sul with cellular alterations were submitted to colposcopy and directed biopsy. Results: the frequency of cytologic alterations of the ASCUS, AGCUS and SIL types was 3.3%, an index that is close to that predicted by the PNCC (4%); the percentage of samples that were unsatisfactory for evaluation was high (12.5%); among the ASCUS, AGCUS or low grade-SIL patients, 27.3% presented intraepithelial lesions of a high grade in the anatomicopathological study; while patients with cytology compatible with high grade-SIL, the directed biopsy revealed that 12.5% presented low-grade intraepithelial lesions. Conclusions: the choice of oncological cytology as the only method for the screening in the program allowed high indexes of false-negatives (27.3%) and of false-positives (12.5%). In the screening of cervical neoplasms, colposcopy has shown to be an important and indispensable method to guide the therapeutical management to be adopted.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(6):349-354
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000600002
Purpose: to evaluate the histopathologic results of cone specimens of patients undergoing loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) and their relationship with the localization of the lesion. Methods: in a retrospective study, 134 clinical reports of patients with abnormal findings of cervical cytology and/or biopsy undergoing LEEP were reviewed. The colposcopic findings were divided into three groups according to the localization of the lesion. Group I (n = 36): patients with ectocervical lesions and fully visible squamocolumnar junction; Group II (n = 50): patients with lesions at the ectocervix and endocervix, and Group III (n = 48): patients with unsatisfactory colposcopy. Results: the mean age in Group I was 33 years and there were 8.3% positive margins. In Group II the mean age was 39 years, with 36% positive margins. Group III had a mean age of 48 years and presented 29.2% positive margins. The percentage of residual disease was 4.2% in Group I, 31.6% in Group II and 35.5% in Group III. Conclusion: patients with lesions at the endocervical canal showed a higher rate of positive margins. Patients with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia at the endocervical canal and older than 40 years have a greater chance of showing positive margins and residual disease, therefore requiring stricter cytologic and colposcopic follow-up.