You searched for:"Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon"
We found (21) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1134-1140
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)is an entity with evolving conceptual nuances that deserve full consideration. Gestational diabetes leads to complications and adverse effects on the mother's and infants' health during and after pregnancy. Women also have a higher prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) related to the hyperglycemic status during pregnancy. However, the exact pathophysiological mechanism is still uncertain. We conducted a narrative review discussing the impact of GDM on the women's pelvic floor and performed image assessment using three-dimensional ultrasonography to evaluate and predict future UI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):322-331
To establish the Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) scores for each domain before and during pregnancy, and to publish the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI.
Pregnant women were recruited during antenatal care; the PSRI was administered to 244 women prenatally at Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, at Universidade do Estado de São Paulo (UNESP, in the Portuguese acronym). The PSRI scores were estimated based on the Kings Health Questionnaire (KHQ) and the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form survey (SF-36). The raw scale type was used to standardize the minimal value and amplitude of each domain. For each domain, the score varied from 0 to 100, and the composite score was obtained as the domain average. The composite score before and during pregnancy was determined by the sum of the scores of all specific domains for each divided by the full domain number. The categorization of the scale into quartiles was established when all PSRI-specific and composite scores were combined.
The composite and specific scores for each domain were categorized into quartiles: 0 < 25 as “very bad;” 25 < 50 as “bad;” 50 < 75 as “good” and 75 to 100 as “excellent.” The mean scores were lower during pregnancy than before pregnancy in 8 of the 10 domains. The Brazilian Portuguese PSRI version is presented.
This study allowed the establishment of the PSRI composite and specific scores for each domain, and the categorization of scores into quartiles: very bad, bad, good and excellent. In addition, the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI is presented in full for application in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(5):222-228
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500004
PURPOSE: to compare two screening tests for diabetes and their results to pregnancy outcomes. METHODS: in total, 279 pregnant women were submitted to two screening tests for gestational diabetes - fasting glycemia plus risk factors (FG + RF) and to the simplified glucose tolerance test (GTT50g). Screening by FG + RF consisted of the determination of fasting glycemia and anamnesis for the identification of risk factors on the occasion of the first prenatal visit. The GTT50g was performed between the 24th and the 28th week of pregnancy and consisted of the determination of plasma glycemia under fasting conditions and one hour after an oral overload with 50 g glucose. Positive and negative results were compared to pregnancy outcome. The dependent variables were: type of delivery, gestational age, weight and ponderal index at birth, Apgar indexes <7 in the 1st and 5th minutes, need for admission to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), duration of hospitalization, and neonatal death. Data were analyzed statistically through the Students t-test, and the level of significance was set at 5%. RESULTS: only two of the perinatal variables studied were distinguished by the tests. An abnormal GTT50g was associated with a greater proportion of cesarean deliveries (58.7 versus 34.3%) and a positive FG + RF association was related to a higher rate of premature births (15.4 versus 5.4%). The other dependent variables did not differ among patients with positive and negative results of the two screening tests. CONCLUSIONS: despite the relation between prematurity and a positive FG + RF association, the increase of caesarean sections and the abnormal GTT50g, it would be a critical failure to accept these associations as definitive. Among others explanations, multiple intercurrent factors and the characteristics of the screening tests themselves should be considered.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):375-378
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):253-259
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the insulin therapy protocol and its maternal and perinatal outcome in patients with clinical or gestational diabetes in a high risk reference service. METHODS: descriptive and prospective study including 103 pregnant women with gestational or clinical diabetes treated with insulin and attended by the reference service from October 2003 to December 2005. Gemellarity, miscarriages, unfinished prenatal care and deliveries not attended by the service were excluded. The gestational age at the beginning of the treatment, dosage, doses/day, increment of insulin (UI/kg), glycemic index (GI) and perinatal outcomes were compared. ANOVA, Fisher’s exact test and Goodman’s test considering p<0.05 were used. RESULTS: multiparity (92 versus 67.9%), pre-gestational body mass index (BMI) >25 kg/m² (88 versus 58.5%), weight gain (WG) <8 kg (36 versus 17%) and a high increment of insulin characterized the gestational diabetes. For the patients with clinical diabetes, despite the highest GI (120 mg/dL (39.2 versus 24%)) at the end of the gestational period, insulin therapy started earlier (47.2 versus 4%), lasted longer (56.6 versus 6%) and higher doses of insulin (92 versus 43 UI/day) were administered up to three times a day (54.7 versus 16%). Macrosomia was higher among newborns from the cohort of patients with gestational diabetes (16 versus 3.8%), being the only significant neonatal outcome. There were no neonatal deaths, except for one fetal death in the cohort of patients with clinical diabetes. There were no differences in the other neonatal complications in both cohorts, and most of the newborns were discharged from hospital up to seven days after delivery (46% versus 55.8%). CONCLUSIONS: the analysis of these two cohorts has shown differences in the insulin therapy protocol in quantity (UI/day), dosage (UI/kg weight) and number of doses/day, higher for the clinical diabetes cohort, and in the increment of insulin, higher for the gestational diabetes cohort. Indirectly, the quality of maternal glycemic control and the satisfactory perinatal outcome have proven that the treatment protocol was adequate and did not depend on the type of diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):91-98
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200006
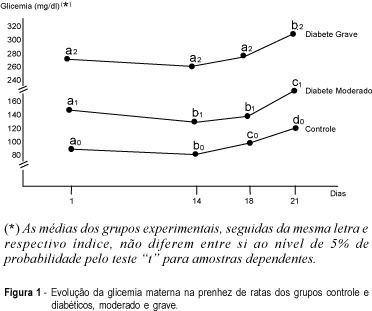
Purpose: placental alterations were evaluated in macrosomatia and fetal growth retardation in pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Three groups of rats, used as experimental models, were studied: control, moderate and severe diabetes. Material and Method: cesarian sections were carried out on the 18th or 21st day of pregnancy. Maternal and fetal glycemia, newborn weight, placental weight, relationship between placental and fetal weight, DNA, RNA and protein contents and the glycogen deposited on placental membranes were analyzed. Results: there was a higher number of macrosomic newborns in the moderate diabetes group, whose placentas were rich in DNA with progressive decrease of glycogen in their membranes towards the end of pregnancy. There was a predominance of small for date newborns in the severe diabetes group. Their placentas showed a small DNA proportion, an increase in RNA synthesis and a tendency to higher protein production, with no change in the glycogen deposit. Conclusions: we conclude that fetal growth deviation in moderate and severe maternal diabetes between the 18th and 21st days of pregnancy is related to several placental alterations. In the moderate form there were only cellular hyperplasia and disappearance of placental glycogen at the end of pregnancy. In the severe diabetes group there was thickening of maternal-fetal membranes during this period. There was cellular hyperplasia and hypertrophy associated with the maintenance of glycogen reserves in the placental membranes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):571-574
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):310-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500008
Maternal mortality rate (MM) is a health quality indicator that is directly influenced by the economic, cultural and technological level of a country. Official data of MM in Brazil, although underestimated, point to the lack of quality in pregnancy, childbirth and puerperium care services. This characteristic is common in developing countries, where poorer pregnant women as well as those facing greater difficulty to quality care access are found. Prenatal care cannot prevent major childbirth complications, which are important causes of MM; however, some interventions during the prenatal period can favor maternal prognosis and prevent MM. In this setting, this study brings a scientifically based update concerning effective interventions for maternal mortality prevention during the prenatal period. The most important strategies consist of a tripod with specific interventions related to maternal health promotion, risk prevention and assurance of nutritional support during gestation, in addition to criteria to investigate gestational risk and inclusion of the pregnant woman in the basic component of the prenatal care model. It ends with the definition of priorities in the prevention of MM related to eclampsia/preeclampsia and reinforces the importance of normalization of reference systems for obstetric emergency cases.