You searched for:"Eliana Amaral"
We found (19) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):577-585
The aim of the current review is to present a systematic evaluation of reported human placental findings in cases of zika virus (ZIKV) infection.
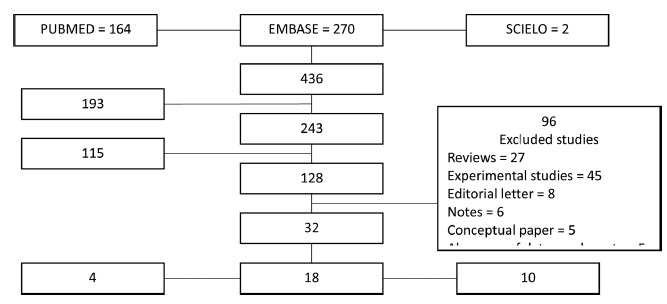
sources We reviewed the EMBASE, PUBMED, and SCIELO databases until June 2019, without language restrictions. Selection of studies The search terms placenta AND zika virus were used. The inclusion criteria of the studies were studies that reported placental findings in humans. Experimental studies, reviews, notes or editorials were excluded. A total of 436 studies were retrieved; after duplicate exclusion, 243 articles had their titles screened, and 128 had their abstract read; of those, 32 were included in the final analysis (18 case reports, 10 case series, and 4 cohorts)
We collected data concerning the author, year of publication, study design, number of participants, number of placental samples, onset of symptoms, perinatal outcomes, and main findings on histological analysis.
The placental pathologic findings were described as mild and nonspecific, similar to those of other placental infections, including chronic placentitis, chronic villitis, increased Hofbauer cells, irregular fibrin deposits, increased mononuclear cells in the villus stroma, villous immaturity, edema, hypervascularization, stromal fibrosis, calcification, and focal necrosis of syncytiotrophoblasts.
Zika infection presents unspecific placental findings, similar to other infections in the toxoplasmosis, other agents, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes (TORCH)group. Characterizing and standardizing placental findings after zika virus infection is key to understanding the mechanisms of congenital diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):544-549
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200003
PURPOSE: To describe the epidemiological cases and microbiological profile of Streptococcus agalactiae serotypes isolated from infected newborns of a Women's Health Reference Centre of Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. METHODS: Cross-sectional laboratory survey conducted from January 2007 to December 2011. The newborns' strains, isolated from blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples, were screened by hemolysis on blood ágar plates, Gram stain, catalase test, CAMP test, hippurate hydrolysis or by microbiological automation: Vitek 2 BioMerieux®. They were typed by PCR, successively using specific primers for species and nine serotypes of S. agalactiae. RESULTS: Seven blood samples, one cerebrospinal fluid sample and an ocular sample, were isolated from nine newborns with infections caused by S. agalactiae, including seven cases of early onset and two of late onset. Only one of these cases was positive for paired mother-child samples. Considering that 13,749 deliveries were performed during the study period, the incidence was 0.5 cases of GBS infections of early onset per 1 thousand live births (or 0.6 per 1 thousand, including two cases of late onset) with 1, 3, 2, zero and 3 cases (one early and two late onset cases), respectively, for the years from 2007 to 2011. It was possible to apply PCR to seven of nine samples, two each of serotypes Ia and V and three of serotype III, one from a newborn and the other two from a paired mother-child sample. CONCLUSIONS: Although the sample was limited, the serotypes found are the most prevalent in the literature, but different from the other few Brazilian studies available, except for type Ia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(2):52-55
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(4):188-195
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000400007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of urinary symptoms and association between pelvic floor muscle function and urinary symptoms in primiparous women 60 days after vaginal delivery with episiotomy and cesarean section after labor. METHODS: a cross-sectional analysis was conducted on women from an out patient clinic in São Paulo state, Brazil, 60 days after delivery. Pelvic floor muscle function was assessed by surface electromyography (basal tone, maximal voluntary contraction and mean sustained contraction) and by a manual muscle test (grades 0-5). In an interview, the urinary symptoms were identified and women with difficulty to understand, with motor/neurological impairment, pelvic surgery, diabetes, restriction for vaginal palpation and practicing exercises forpelvic floor muscles were excluded. The χ2 and Fisher Exact test were used to compare proportions and the Mann-Whitney test was used to analyze mean differences. RESULTS: 46 primiparous were assessed on average 63.7 days postpartum. The most prevalent symptoms were nocturia (19.6%), urgency (13%) and increased daytime urinary frequency (8.7%). Obese and overweight women had 4.6 times more of these symptoms (PR=4.6 [95%CI; 1.2-18.6; p value=0.0194]). Stress urinary incontinence was the most prevalent incontinence (6.5%). The mean values found for the basic tone, maximal voluntary contraction and sustained contraction were: 3 µV, 14.6 µV and 10.3 µV. Most of the women (56.5%) had grade 3 muscular strength. There was no association between urinary symptoms and pelvic floor muscle function. CONCLUSION: the prevalence of urinary symptoms was low 60 days postpartum and there was no association between pelvic floor muscle function and urinary symptoms.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):393-399
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800004
PURPOSE: to study cervical colonization in women with preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. METHODS: two hundred and twelve pregnant women with preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes were studied. Two cervical samples from each woman were collected and bacterioscopy and culture were performed. Association of cervical microorganisms and urinary tract infection, chorioamnionitis, fetal stress, antibiotic use, prematurity, neonatal infection, and neonatal death were evaluated. RESULTS: the prevalence of endocervical colonization was 14.2% (CI95%=9.5-18.9%), with similar results in preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. Group B streptococcus was the most prevalent organism (9.4%). Other organisms isolated were Candida sp, Streptococcus sp, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus sp. The most common findings of bacterioscopy were a reduced number of lactobacilli and a great number of leukocytes. Endocervical colonization was associated with a higher occurrence of urinary tract infection (23.8 versus 5.4%; p<0.01), early-onset neonatal infection (25.0 versus 7.3%; p<0.01) and neonatal mortality (two cases in colonized women; p<0.02) when compared with a negative culture of endocervical mucus. CONCLUSIONS: this study showed high prevalence of endocervical colonization despite the use of a nonselective culture media. The main microorganism isolated was group B streptococcus, but other organisms were present in one third of the studied population. More studies are needed to evaluate the influence of endocervical colonization on obstetrical outcome and on neonatal infection and mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):325-327
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):281-286
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000600003
PURPOSE: to assess the prevalence and risk factors associated with near miss and other severe maternal morbidity at a reference tertiary maternity. METHODS: this is a cross-sectional study on severe maternal morbidity at the Hospital e Maternidade Celso Pierro, Campinas, São Paulo, between October 2005 and July 2006, identified from infirmary, admission and delivery unit logbooks. Pregnant and post-partum women with severe maternal morbidity were identified according to clinical criteria proposed by Waterstone. Later, cases with more severe morbidity, called extremely severe maternal morbidity, were reclassified using Mantel criteria, based on organic dysfunction and clinical management. RESULTS: there were 114 severe maternal morbidity cases among 2,207 birth deliveries, with a ratio of other severe morbidity and extremely severe morbidity near miss of 44.9 and 6.8 cases/1,000 live births, respectively. Mean gestational age at delivery was 35 weeks, and 87% came from the reference area for the maternity service. Hypertension (severe pre-eclampsia) represented 96% of other severe morbidity, while hemorrhage represented 60% of all extremely severe cases, followed by hypertension. The prevalence of extremely severe morbidity among the severe morbidity cases was not associated with marital status, schooling, maternal age, type of delivery, parity, gestational age at birth and home place. CONCLUSIONS: the other morbidities were 6.6 times more frequent than near miss, and it was not possible to differentiate both groups by epidemiological risk factors.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):551-554