You searched for:"Antonio Alberto Nogueira"
We found (31) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1102-1109
To evaluate the use of misoprostol prior to hysteroscopy procedures regarding technical ease, the presence of side effects, and the occurrence of complications.
This is a retrospective, observational, analytical, case-control study, with the review of medical records of 266 patients followed-up at the Gynecological Videoendoscopy Sector of the Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto of the Universidade de São Paulo (HCFMRP – USP, in the Portuguese acronym) from 2014 to 2019, comparing 133 patients who used the drug before the procedure with 133 patients who did not.
The occurrence of postmenopausal uterine bleeding was the main indication for hysteroscopy and revealed a statistical difference between groups (p < 0.001), being present in 93.23% of the patients in the study group and in 69.7% of the patients in the control group. Only 2 patients (1.5%) in the study group reported adverse effects. Although no statistical differences were observed regarding the occurrence of complications during the procedure (p = 0.0662), a higher total number of complications was noted in the group that used misoprostol (n = 7; 5.26%) compared with the group that did not use the drug (n = 1; 0.75%), a fact that is clinically relevant. When evaluating the ease of the technique (measured by the complete performance of all steps of the hysteroscopy procedure), it was verified that although there was no difference between groups (p = 0.0586), the control group had more than twice as many incompletely performed procedures (n = 17) when compared with the group that used misoprostol previously (n = 8), which is also clinically relevant.
The use of misoprostol prior to hysteroscopy in our service indicated that the drug can facilitate the performance of the procedure, but not without side effects and presenting higher complication rates.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):181-185
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400003
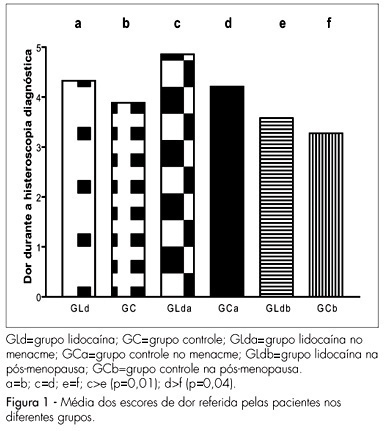
PURPOSE: to determine the efficacy of 10% lidocaine spray applied to the cervix before the procedure of diagnostic hysteroscopy, in order to reduce the painful process and the discomfort caused by the exam. METHODS: a total of 261 consecutive patients participated in the study, which was conducted from March 2004 to March 2005. The patients were randomly assigned to one of two groups: one group receiving topical lidocaine spray (lidocaine group - LdG) and the other, receiving no medication before the procedure (control group - CG). In the LdG patients, thirty milligrams of 10% lidocaine spray were applied to the surface of the cervix five minutes before hysteroscopy started. Immediately, after the end of the procedure, the patients from both groups were asked to respond to a questionnaire about pain and to quantify the pain, in centimeters, using a 10-cm non-graduated visual analog scale. The unpaired t test, the Mann-Whitney test and the chi2 test were used for statistical analyses, considering p significant if lower than 0.05. RESULTS: there was no statistically significant difference between groups regarding age, parity or percentage of patients in menacme or menopause, or regarding the indications for the procedure and the hysteroscopic findings. A biopsy was necessary in 57 of the 132 LdG patients and in 48 of the 129 CG patients (p=0.96). The mean pain score was 4.3±2.9 in LdG and 3.9±2.5 in CG (p=0.2). A difference in the mean pain score was observed only among patients in menacme and menopause receiving or not the lidocaine spray, with p=0.01 and p=0.04 respectively. CONCLUSIONS: the use of lidocaine spray during diagnostic hysteroscopy does not minimize the discomfort and pain of the patients and therefore should not be applied.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):223-226
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400007
Purpose: to evaluate retrospectively the obstetrical and perinatal aspects of multiple pregnancies with the death of one fetus. Methods: a retrospective study on 26 pregnant women with multiple pregnancies and death of one twin. A conservative approach was followed and the patients were followed-up clinically with blood clotting tests. Results: in 50% of the cases fetal death occurred between 20 and 32 weeks of pregnancy. The time between death and resolution of pregnancy ranged from 6 to 148 h. Death of the other twin occurred in two cases. In 15 cases, the surviving twin had a good course, with two of them presenting slight neurological sequelae. In the other nine cases the other twin died after birth. No pregnant woman developed coagulation disorders.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):251-258
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500002
Purpose: to evaluate whether prophylactic use of ampicillin could avoid or reduce maternal and perinatal infectious morbidity caused by premature rupture of membranes (PROM), and to extend the gestation period in those women. Methods: this was a prospective, randomized and double-blind study, carried out evaluating 121 pregnant women with PROM, randomized into two study groups. The treatment group (61 patients) received ampicillin and the control group (60 patients) received placebo. The placebo had the same characteristics as ampicillin (kind of packaging and color of the capsules) and was used in the same time regimen. The considered parameters for maternal infection were febrile morbidity (fever index), and the presence of chorioamnionitis and/or endometritis. The studied neonatal parameters were Apgar score (1st and 5th minutes), bacterial colonization of auditory canal, and blood culture. The statistical tests performed were Fisher's exact test, Wilcoxon, and chi². Results: it was observed that ampicillin did not prolong the gestation, nor did it reduce the postpartum febrile morbidity or the rates of chorioamnionitis and/or endometritis. Ampicillin did not reduce the perinatal infectious morbidity nor improve the birth outcomes. All these results were consistent in cases of less than 72 h PROM. The limited number of cases with time of PROM greater than 72 h did not permit statistical analysis free of type II error. Conclusions: based on these results it was possible to conclude that the prophylactic use of ampicillin by pregnant women with less than 72 h PROM did not reduce either infectious maternal or perinatal morbidity. However, the presence of group B Streptococcus agalactiae in the blood culture from a neonate in the control group showed the necessity to start antibiotic treatment of pregnant women colonized by this microorganism.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):253-253
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):289-292
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000500010
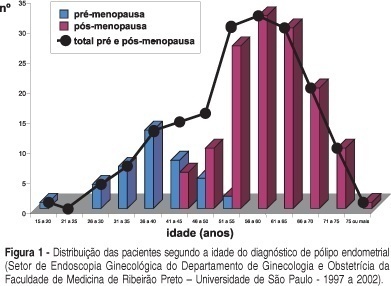
Endometrial polyps are benign lesions, with a low potential of malignancy. In the reproductive period their diagnosis is established in symptomatic patients with abnormal uterine bleeding or infertility. Postmenopausal women are mostly asymptomatic but in approximately one third of the cases there is an association with abnormal bleeding. They are more frequent after the menopause and risk factors of cancer of the endometrium have not been associated in the same way as risk for endometrial polyps, although they are hormone-dependent as in patients in use of tamoxifen, for instance. Their definitive diagnosis is established by hysteroscopy-guided biopsy and their most effective treatment is hysteroscopic resection. Polyps may recur after treatment. Polypectomy is highly satisfactory after the menopause, is less successful in symptomatic women in the reproductive period and improves fertility rates in infertile women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(7):299-301