Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):67-73
To evaluate the underestimation rate in breast surgical biopsy after the diagnosis of radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion through percutaneous biopsy.
A systematic review was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations. The PubMed, SciELO, Cochrane, and Embase databases were consulted, with searches conducted through November 2020, using specific keywords (radial scar OR complex sclerosing lesion, breast cancer, anatomopathological percutaneous biopsy AND/OR surgical biopsy).
Study selection was conducted by two researchers experienced in preparing systematic reviews. The eight selected articles were fully read, and a comparative analysis was performed.
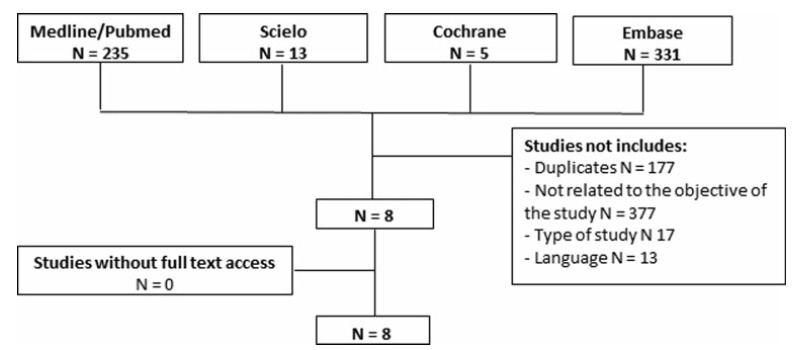
A total of 584 studies was extracted, 8 of which were selected. One of them included women who had undergone a percutaneous biopsy with a histological diagnosis of radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion and subsequently underwent surgical excision; the results were used to assess the underestimation rate of atypical and malignant lesions.
The overall underestimation rate in the 8 studies ranged from 1.3 to 40% and the invasive lesion underestimation rate varied from 0 to 10.5%.
The histopathological diagnosis of a radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion on the breast is not definitive, and it may underestimate atypical andmalignant lesions, which require a different treatment, making surgical excision an important step in diagnostic evaluation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):74-82
To compare the perinatal outcomes of fetuses with isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia after fetal endoscopic tracheal occlusion (FETO) and antenatal expectant management.
In this rapid review, searches were conducted in the MEDLINE, PMC, EMBASE and CENTRAL databases between August 10th and September 4th, 2020. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-RCTs or cluster-RCTs published in English in the past ten years were included.
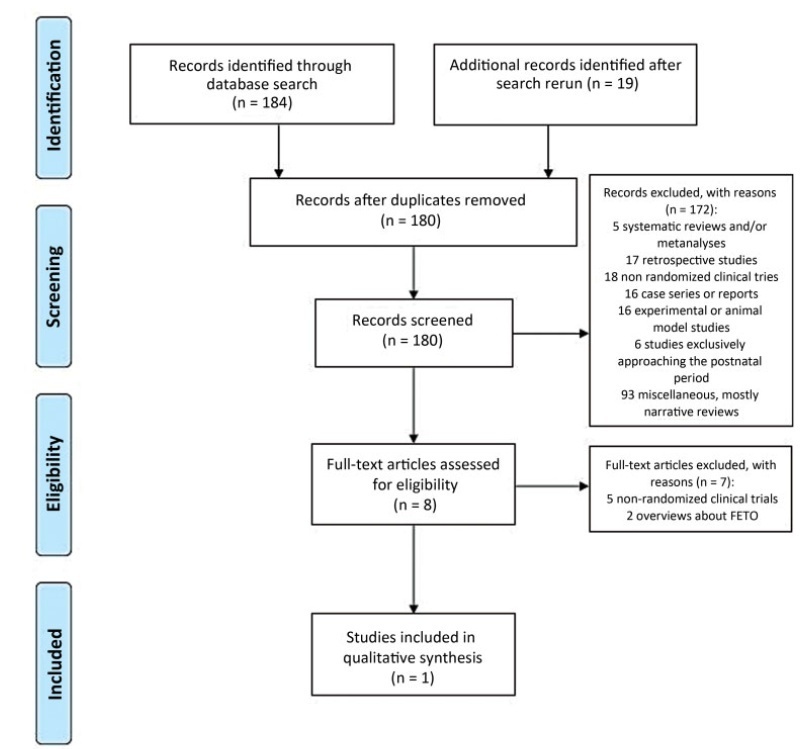
We retrieved 203 publications; 180 studies were screened by abstract. Full-text selection was performed for eight studies, and 1 single center RCTmet the inclusion criteria (41 randomized women; 20 in the FETO group, and 21 in the control group).
Data collection was performed independently, by both authors, in two steps (title and abstract and full-text reading).
There were no cases of maternal mortality. The mean gestational age at delivery was of 35.6±2.4 weeks in the intervention group, and of 37.4±1.9 weeks among the controls (p<0.01). Survival until 6 months of age was reported in 50% of the intervention group, and in 5.8% of the controls (p<0.01; relative risk: 10.5; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.5-74.7). Severe postnatal pulmonary hypertension was found in 50% of the infants in the intervention group, and in 85.7% of controls (p=0.02; relative risk: 0.6; 95%CI: 0.4-0.9). An analysis of the study indicated some concerns of risk of bias. The quality of evidence was considered moderate to low.
Current evidence is limited but suggests that FETO may be an effective intervention to improve perinatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):83-88