You searched for:"Maria Cristina Picinato Medeiros de Araújo"
We found (5) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):524-529
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100008
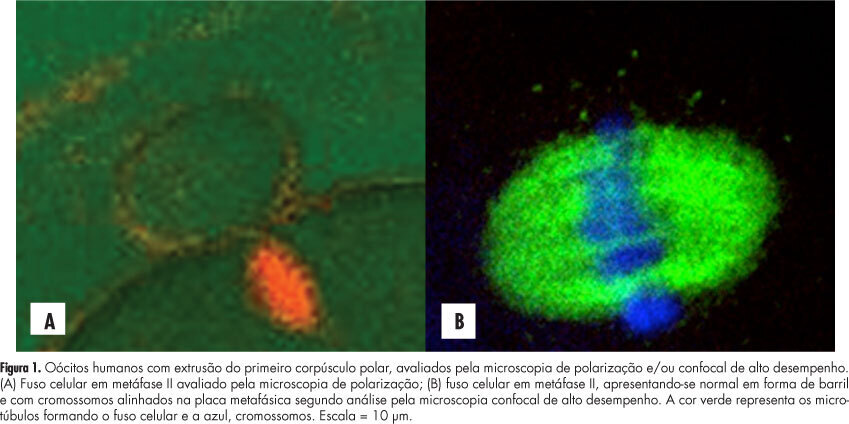
PURPOSE: To evaluate the concordance between polarization microscopy and confocal microscopy techniques in the evaluation of the meiotic spindle of human oocytes matured in vivo. METHODS: Prospective study that evaluated oocytes with the first polar extruded body obtained from infertile women who had undergone ovarian stimulation for intracytoplasmic sperm injection. The oocytes with the first polar extruded body were evaluated by polarization microscopy and were then immediately fixed and stained for microtubule and chromatin evaluation by high-performance confocal microscopy. We determined the correlation of polarization microscopy with confocal microscopy in the detection of meiotic oocyte anomalies, and we also evaluated the percentage of oocytes with a visible and non-visible cell spindle by polarization microscopy and with meiotic normality and abnormalities by confocal microscopy. Confidence intervals, Kappa's index and concordance between the methodologies were calculated, considering immunofluorescence microscopy analysis as the golden-standard for evaluating normal spindle and oocyte chromosome distribution. RESULTS: We observed that 72.7% of metaphase II oocytes with a nonvisible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy showed no meiotic abnormalities by confocal analysis and 55.6% of metaphase II oocytes with a visible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy were found to be abnormal oocytes by the confocal analysis. Only 44.4% of oocytes with a visible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy were found to be normal by confocal analysis. Concordance between the methods was 51.1% (Kappa: 0.11; 95%CI -0.0958 - 0.319). CONCLUSIONS: The low correlation between polarization microscopy and confocal microscopy in the assessment of oocyte meiotic spindle suggests that visualization of the meiotic spindle of human oocytes at metaphase II by polarization microscopy is not a good indicator of oocyte meiotic normality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):360-365
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700007
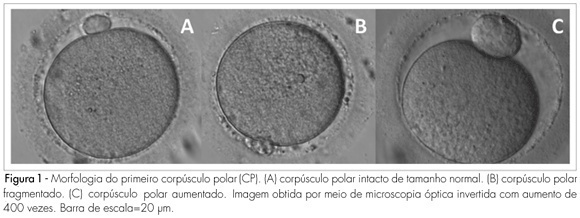
PURPOSE: to determine the relationship between the morphology of the first spindle pole of human oocytes and rates of fertilization, fragmentation and embryo quality in procedures of Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). METHODS: retrospective study of 582 consecutive ICSI cycles, from July 2003 to July 2005. The morphology of the first spindle pole (SP) was assessed through the analysis of 3,177 oocytes in metaphase II, immediately before the ICSI procedure, always by the same observer. SP has been classified in the following categories: normal size intact, fragmented or augmented SP. Fertilization rate and fragmentation, and the number and rate of good quality embryos in each one of the three groups studied have been evaluated, 48 hours after ICSI (D2). Embryos with four cells, without fragmentation and with symmetric blastomeres in D2 were considered as of good quality. RESULTS: rates of fertilization, fragmentation and of good quality embryo formation, resulting from oocyte insemination, with augmented SP (20.7, 16.7 and 5% respectively) were significantly lower than the ones from intact and normal size SP (70.8, 62.5 and 19%, respectively) or from fragmented SP oocytes (69.7, 60.5 and 17.1%, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: it has been observed that the presence of augmented first spindle pole is related to worse rates of fertilization, fragmentation and bad quality embryo formation. Nevertheless, fragmentation in the first spindle pole of the oocyte does not seem to affect ICSI results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):413-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800007
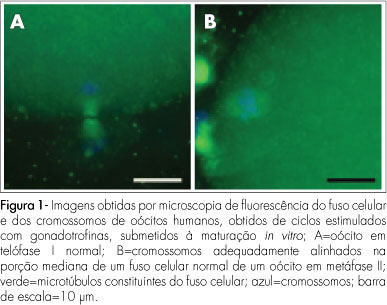
PURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro mature oocytes from stimulated cycles of infertile women with endometriosis, and with male and/or tubal infertility factors (Control Group), comparing the rates of in vitro maturation (IVM) between the two groups evaluated. METHODS: fourteen patients with endometriosis and eight with male and/or tubal infertility factors, submitted to ovarian stimulation for intracytoplasmatic sperm injection have been prospectively and consecutively selected, and formed a Study and Control Group, respectively. Immature oocytes (46 and 22, respectively, from the Endometriosis and Control Groups) were submitted to IVM. Oocytes presenting extrusion of the first polar corpuscle were fixed and stained for microtubules and chromatin evaluation through immunofluorescence technique. Statistical analysis has been done by the Fisher's exact test, with statistical significance at p<0.05. RESULTS: there was no significant difference in the IVM rates between the two groups evaluated (45.6 and 54.5% for the Endometriosis and Control Groups, respectively). The chromosome and meiotic spindle organization was observed in 18 and 11 oocytes from the Endometriosis and Control Groups, respectively. In the Endometriosis Group, eight oocytes (44.4%) presented themselves as normal metaphase II (MII), three (16.7%) as abnormal MII, five (27.8%) were in telophase stage I and two (11.1%) underwent parthenogenetic activation. In the Control Group, five oocytes (45.4%) presented themselves as normal MII, three (27.3%) as abnormal MII, one (9.1%) was in telophase stage I and two (18.2%) underwent parthenogenetic activation. There was no significant difference in meiotic anomaly rate between the oocytes in MII from both groups. CONCLUSIONS: the present study data did not show significant differences in the IVM or in the meiotic anomalies rate between the IVM oocytes from stimulated cycles of patients with endometriosis, as compared with controls. Nevertheless, they have suggested a delay in the outcome of oocyte meiosis I from patients with endometriosis, shown by the higher proportion of oocytes in telophase I observed in this group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):241-247
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles of infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and with male factor and/or tubal infertility (Control Group) and compare in vitro maturation (IVM) rates between the groups analyzed. METHODS: five infertile patients with PCOS and eight controls, submitted to stimulated cycles for intracytoplasmic sperm injection, were selected prospectively and consecutively, and respectively assigned to the study group and the Control Group. Immature oocytes (21 and 29, respectively, from PCOS and Control Group) were submitted to IVM. After IVM, oocytes with first polar body extruded were fixed and submitted to immunostaining and fluorescence microscopy for morphological evaluation of the spindle and of chromosome distribution. Statistical analysis was performed by the Fisher test with significance, when p<0.05. RESULTS: IVM rates were similar between groups (47.6 e 44.8%, respectively, for PCOS and Control Group). Six of the ten oocytes (60%) from the study group and four of the 12 oocytes (33.3%) from the Control Group presented meiotic anomalies of the spindle and/or anomalous chromosome distribution, without statistical difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS: data from the present study did not demonstrate significant difference neither in IVM rates nor in the proportions of meiotic anomalies between in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles from PCOS patients and control ones.