You searched for:"Marcelo Zubaran Goldani"
We found (1) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):220-229
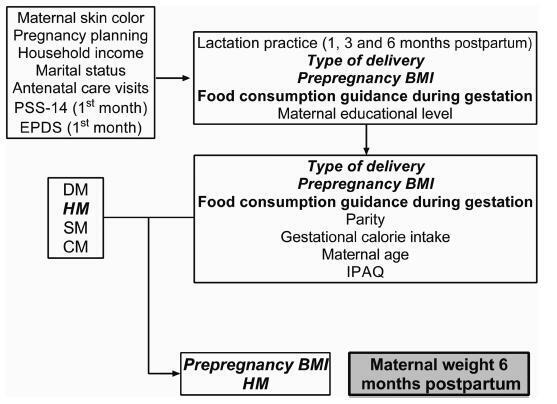
Different intrauterine environments may influence the maternal prepregnancy body weight (BW) variation up to 6 months postpartum. The objective of the present study was to verify the association of sociodemographic, obstetric, nutritional, and behavioral factors with weight variation in women divided into four groups: hypertensive (HM), diabetic (DM), smokers (SM), and control mothers (CM).
It was a convenience sample of 124 postpartum women recruited from 3 public hospitals in the city of Porto Alegre, state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, between 2011 and 2016.Multiple linear regressions and generalized estimating equations (GEE) were conducted to identify the factors associated with maternal weight variation. For all GEE, the maternal weight measurements were adjusted for maternal height, parity, educational level, and the type of delivery, and 3 weight measurements (prepregnancy, preceding delivery, and 15 days postpartum) were fixed.
A hierarchical model closely associated the maternal diagnosis of hypertension and a prepregnancy body mass index (BMI) classified as overweight with maternal weight gain measured up to the 6th month postpartum (the difference between the maternal weight at 6months postpartum and the prepregnancy weight). These results showed that the BW of the HM group and of overweight women increased ~ 5.2 kg 6 months postpartum, compared with the other groups. Additionally, women classified as overweight had a greater BW variation of 3.150 kg.
This evidence supports the need for specific nutritional guidelines for gestational hypertensive disorders, as well as great public attention for overweight women in the fertile age.