You searched for:"Gilberto Uemura"
We found (8) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):30-35
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005134
To evaluate the prevalence of low bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors.
In this cross-sectional study, 115 breast cancer survivors, seeking healthcare at a University Hospital in Brazil, were evaluated. Eligibility criteria included women with amenorrhea ≥12 months and age ≥45 years, treated for breast cancer and metastasis-free for at least five years. BMD was measured by DEXA at the lumbar spine (L1-L4) and femoral neck. Low BMD was considered when total-spine and/or femoral-neck T-score values were <-1.0 Delphi Score (DP) (osteopenia and osteoporosis). The risk factors for low BMD were assessed by interview. Data were analyzed statistically by the χ2 test and Fisher's exact test.
The mean age of breast cancer survivors was 61.6±10.1 years and time since menopause was 14.2±5.6 years, with a mean follow-up of 10.1±3.9 years. Considering spine and femoral neck, 60% of breast cancer survivors had low BMD. By evaluating the risk factors for low BMD, a significant difference was found in the percent distribution for age (higher % of women >50 years with low BMD), personal history of previous fracture (11.6% with low BMD versus 0% with normal BMD) and BMI. A higher frequency of obesity was observed among women with normal BMD (63%) compared to those with low BMD (26.1%) (p<0.05).
Postmenopausal breast cancer survivors had a high prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):118-123
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300005
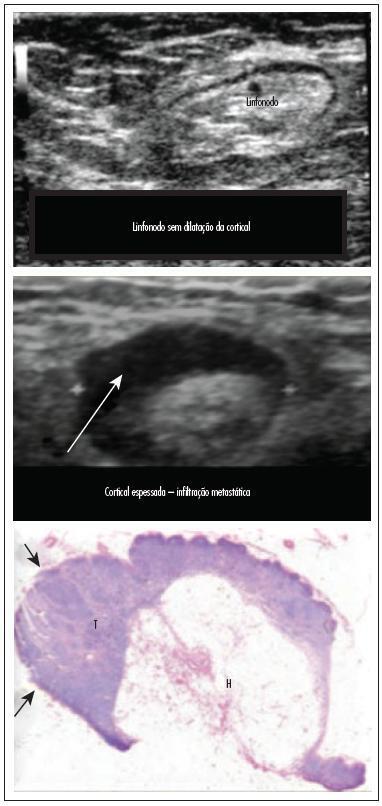
To assess the feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasound combined with ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (US-FNA) cytology and clinical examination of axillary lymph node in patients with breast cancer.
In this prospective study, 171 axillae of patients with breast cancer were evaluated by clinical examination and ultrasonography (US) with and without fine needle aspiration (FNA). Lymph nodes with maximum ultrasonographic cortical thickness > 2.3 mm were considered suspicious and submitted to US-FNA.
Logistic regression analysis showed no statistically significant correlation between clinical examination and pathologically positive axillae. However, in axillae considered suspicious by ultrasonography, the risk of positive anatomopathological findings increased 12.6-fold. Cohen's Kappa value was 0.12 for clinical examination, 0.48 for US, and 0.80 for US-FNA. Accuracy was 61.4% for clinical examination, 73.1% for US and 90.1% for US-FA. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis demonstrated that a cortical thickness of 2.75 mm corresponded to the highest sensitivity and specificity in predicting axillary metastasis (82.7 and 82.2%, respectively).
Ultrasonography combined with fine-needle aspiration is more accurate than clinical examination in assessing preoperative axillary status in women with breast cancer. Those who are US-FNA positive can be directed towards axillary lymph node dissection straight away, and only those who are US-FNA negative should be considered for sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(10):458-463
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001000006
PURPOSE: To analyze the time between the first symptom and treatment in patients treated for breast cancer in public hospitals in the Federal District. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional analysis. We interviewed 250 women diagnosed with breast cancer treated in six hospitals of the State Department of Health of the Federal District from November 2009 to January 2011. The time intervals studied were the time between the detection of the symptoms and treatment subdivided into intervals until and after the first medical appointment. The variables were: age, menopausal status, color, educational level, average monthly household income, origin, reason for the initial consultation, staging, tumor size, laterality, metastasis to axillary lymph nodes, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and type of surgery. The Mann-Whtney test was used to assess the association of these variables with the time intervals until treatment. RESULTS: The mean age was 52 years, with a predominance of white women (57.6%), from the Federal District (62.4%), with a family income of up to 2 minimum wages (78%), and up to four years of schooling (52.4%). The staging of the disease ranged from II to IV in 78.8% of the women. The time between the first symptom and treatment was 229 days (median). After detection of the first symptom, 52.9% of the women attended a consultation within 30 days and 88.8% took more than 90 days to start treatment. Women with elementary school education had a greater delay to the start of treatment (p=0.049). CONCLUSIONS: There was a significant delay to start treatment of women with breast cancer in public hospitals of the Federal District, suggesting that efforts should be made to reduce the time needed to schedule medical appointments and to diagnose and treat these patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(4):196-202
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400007
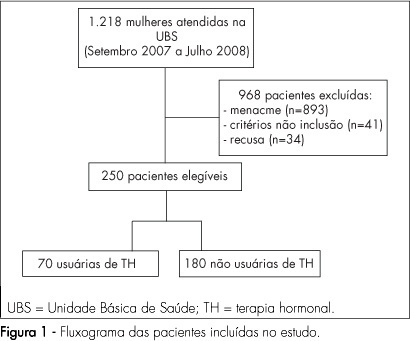
PURPOSE: to evaluate the quality of life of post-menopause women, users and non-users of hormonal therapy (HT), in a Healthcare Unit in Franca, São Paulo, Brazil. METHODS: a clinical transversal study, carried out with 250 post-menopausal women, with ages from 45 to 70 years old, attended to in Healthcare Units, from September 2007 to August 2008. Participants were divided into two groups: HT users (n=70) and non-users (n=180). Women making continuous HT use for at least six months were considered as users. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics have been evaluated. Blatt-Kupperman's menopausal index has been applied to assess climacteric symptoms, and the Women's Health Questionnaire (WHQ), to assess their quality of life. Fisher's exact test or χ2 and Mann-Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis's tests have been used for the statistical analysis. RESULTS: no significant difference has been found in the comparison of groups, concerning age, menarche, menopause, parity and body mass index. It has been seen that 67.2% of the women were married, 83.2% had attended primary school and 53.2% were housewives, with no difference between the groups. HT users reported lower frequency of climacteric symptoms (BKMI) with moderate and marked intensity, as compared to non-users (p<0.001). Even though HT users presented lower average score in cognitive deficit (p<0.001), vasomotor symptoms (p=0.04), sleeping problems (p<0.001), attractiveness (p=0.02) from the WHQ, there has been no difference in the total score, as compared to non-users. CONCLUSIONS: post-menopausal women, HT users and non-users, admitted at Healthcare Units, have not presented differences in global quality of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):625-632
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200005
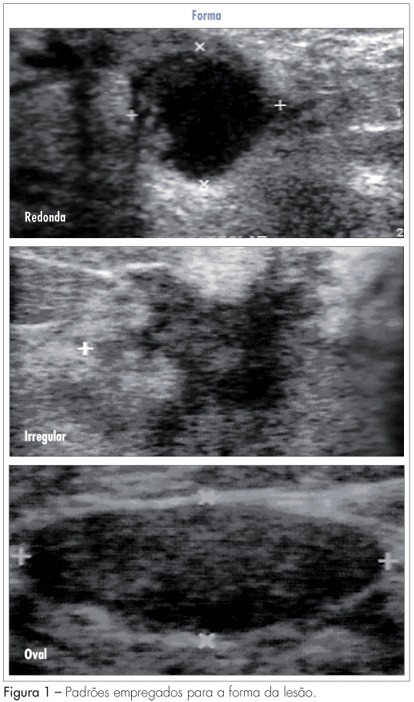
PURPOSE: to analyze which characteristics proposed by the BIRADS lexicon for ultrasound have the greatest impact on distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions. METHODS: ultrasonography features from the third edition of the BIRADS were studied in 384 nodes submitted to percutaneous biopsy from February 2003 to December 2006, at the Medical School of Botucatu. For the ultrasonography, the equipment Logic 5 with a 7.5-12 MHz multifrequential linear transducer was used. The ultrasonography analysis of the node considered the features proposed by the BIRADS lexicon for ultrasound. The data were submitted to statistical analysis by the logistic regression model. RESULTS: the benign lesions represented 42.4% and the malignant, 57.6%. The logistic regression analysis found an odds ratio (OR) for cancer of 7.69 times when the surrounding tissue was altered, of 6.25 times when there were microcalcifications in the lesions interior, of 1.95 when the acoustic effect is shadowing, of 25.0 times when there was the echogenic halo, and of 7.14 times when the orientation was non-parallel. CONCLUSIONS: among the features studied, the lesion limit, represented by the presence or not of the halogenic halo, is the most important differentiator of the benign from the malignant masses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(1):18-26
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000100004
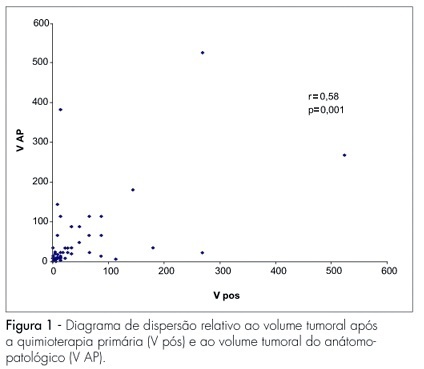
PURPOSE: to evaluate the loco-regional response to primary chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer at stages II and III. METHODS: a retrospective and analytical clinical study carried out in 97 patients with an average age of 52.2 years old, with breast cancer at stages II and III, attended from January 1993 to December 2004, and submitted to 3 to 4 cycles of primary chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil - 500 mg/m2, epirubicin - 50 mg/m2 and cyclophosphamide - 500 mg/m2 or doxorubicin - 50 mg/m2 e cyclophosphamide - 500 mg/m2, and then to loco-regional surgical conservative or radical surgical treatment. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used to study the association among the variables (age, menopausal state, pre-chemotherapy tumoral volume, axillary condition, stage, therapeutic scheme and number of cycles), while Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for the quantitative variables (tumoral volume according to the anatomo-pathological study and the post-chemotherapy clinical tumoral volume. The significance level was 5%. RESULTS: there were 56.8% of cases at stage II and 43.2% at stage III. Approximately 50% of the patients received FEC50 and 50% AC. Objective clinical response with primary chemotherapy was obtained in 64.9% of the cases. Full clinical response occurred in 12.3% of patients, while full pathological response occurred in 10.3% of the cases. CONCLUSIONS: there was a statistically significant correlation between the number of cycles and the response to primary chemotherapy. Patients who received 4 cycles had better response than those who received 3 cycles. There was also a statistically significant concordance between the evaluation through clinical examination of the response to primary chemotherapy and the pathological findings. No statistically significant correlation was observed concerning age, menopausal status, tumoral volume, and pretreatment of axillary damage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):301-301
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500010