You searched for:"Carlos Gilberto Almodin"
We found (5) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):409-414
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700007
Purpose: to determine whether the transfer day or the stage that the embryo is transferred interferes in pregnancy and implantation rates. Methods: oocytes we recovered from 107 patients and submitted to in vitro fertilization. The embryos were cocultured on Vero cells and transferred on day 3 or day 5 post-fertilization, after morphological assessment. Results: the implantation rate of the transferred embryos on day 5 was significantly higher than when the embryos were transferred on day 3, but the pregnacy rates did not change. However, a significant difference was observed in the pregnancy rates for embryos transferred at the expanded blastocyst stage (70.6% of pregnancy) when compared to 20.0% and 10.5% at the earlier blastocyst and morula stages, respectively. Conclusions: the implantation and pregnancy rates were significantly increased when the embryos were transferred at the expanded blastocyst stage, but the culture media and culture conditions now available are not able to provide a satisfactory rate at this stage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):533-538
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900006
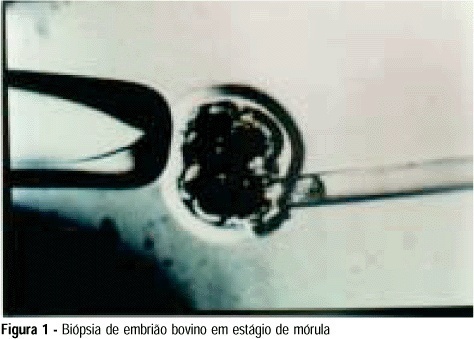
Purpose: to develop an animal model for the study of, and training in, bovine biopsies. Methods: cow ovaries were obtained from a slaughterhouse and transported to the laboratory where the oocytes were aspirated, maturated and submitted to in vitro fertilization. On the 5th day after fertilization, the embryos were biopsied, with the zona pellucida being opened with a cutting blade fitted to the light microscope. One or two blastomeres were removed from the embryos and left in coculture for three additional days. After this time, embryo development was evaluated in comparison to a control group by morphological study and cell counts using specific staining for nuclei. Results: forty of the 57 biopsied embryos reached the blastocyst stage (70.2%) and hatching was observed in 11 (27.5%). Forty-two blastocysts were obtained in the control group (73.7%) and 11 of them hatched (26.2%). Cell counts showed no significant differences between groups. Conclusions: we conclude that the proposed protocol is technically feasible and supplies a good number of embryos because of the easy technique for obtaining bovine oocytes, thus representing a method that could be adopted for training.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):612-612
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800012
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(9):589-595
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000900007
Purpose: to compare the embryonic development obtained with two different culture methods (sequential medium or coculture in Vero cells). Methods: oocytes were recovered from 110 patients and submitted toin vitro fertilization. The embryos of half of the patients were co-cultured with Vero cells and the embryos of the other half were cultured in sequential G1:2/G2:2 medium for five days. The embryos were transferred on the 5th day after fertilization after morphological evaluation for the determination of blastula formation rate. Pregnancy was defined by ultrasonography and a fetal heartbeat was determined 13 weeks after transfer. Results: the expanded blastocyst rate found in our study was 15.9 and 14% with Vero cells and G1:2/G2:2, respectively. With Vero cells 36.0% of patients became pregnant and the implantation rate was 18.9%. When G1:2/G2:2 was used, the pregnancy and implantation rates were 28.9 and 14.9%, respectively. Only 17 patients had blastocysts after coculture in Vero cells, with a 76.5% pregnancy rate and a 63.5% implantation rate. When embryos were cultured in G1/G2, 21 patients presented blastocysts and the pregnancy and implantation rates were 57.1 and 76.0%, respectively. Conclusion: there was no significant difference in pregnancy or implantation rates between the 2 types of culture. When expanded blastocysts were transferred, the implantation and pregnancy rats increased with both culture types. In these patients, regardless of the type of culture used, a larger number of oocytes was obtained, suggesting that the implantation and pregnancy rates are affected not only by the culture conditions but also by the quality of the eggs, since "good responders" had better results.